As a result of using the tax corrector increases. What is the effect of financial leverage
Let's assume that there are two enterprises with the same level of economic profitability and the same value of assets. However, only own funds are used as sources of financing for the first enterprise, and own and borrowed funds for the second.
There is a situation in which, with the same economic profitability, due to differences in the structure of financing, different meanings profitability own funds(RSS). This difference in these performance indicators of the two organizations is called the "financial leverage effect".
How sources of funding for activities affect profitability
The effect of financial leverage (EFF) is an increase in the value of the return on equity, which occurs as a result of the use of loans, despite their payment. From this follows two conclusions:
1) An enterprise that uses only its own funds in its activities, without resorting to services credit institutions, keeps their profitability within the limits of RCC=(1-T)*ER, where T is the value of the interest rate of income tax.
2) An enterprise that uses funds received on credit to carry out its activities changes the RCC - increases or decreases it depending on the size of the interest rate and the ratio of the shares of borrowed and own funds. In such situations, there is such a phenomenon as the effect of financial leverage.
RSS=(1-T)*ER+EFR
To determine the value of the EFR, it is necessary to find the value of the indicator called the average interest rate (SIR). This indicator is found as the ratio of the existing financial costs of credit funds to total amount funds borrowed by the company.

Components of the effect of financial leverage
The effect of financial leverage is formed by two components:
1. Differential: (1-T)*(ER-SRSP).
2. The leverage of financial leverage, which is found as the ratio of borrowed funds to own.
The formula for calculating the EGF is determined by the product of these two components.
Basic Rules
1. The effect of financial leverage shows whether the loan will be beneficial for the enterprise. A positive value of the EGF indicator means that attraction borrowed money beneficial to the organization and expedient.
2. Attracting an additional loan increases the value of the leverage indicator, and accordingly, the risk of non-repayment of borrowed funds also increases. This is offset by an increase in the interest rate on loans. Consequently, the average calculated interest rate also increases.
3. The effect of financial leverage also determines whether the enterprise has the opportunity to emergency attract additional loan funds. To do this, you need to monitor the value of one of its components - the differential. The differential must be positive, and some margin of safety must be maintained for this indicator.
financial leverage characterizes the ratio of all assets to equity capital, and the effect of financial leverage is calculated accordingly by multiplying it by the economic profitability indicator, that is, it characterizes profitability equity(the ratio of profit to equity).
The effect of financial leverage is an increment to the return on equity obtained through the use of a loan, despite the payment of the latter.
An enterprise using only its own funds limits their profitability to about two-thirds of economic profitability.
РСС - net profitability of own funds;
ER - economic profitability.
An enterprise using a loan increases or decreases the return on equity, depending on the ratio of own and borrowed funds in liabilities and on the interest rate. Then there is the effect of financial leverage (EFF):
![]() (3)
(3)
Consider the mechanism of financial leverage. In the mechanism, a differential and a shoulder of financial leverage are distinguished.
Differential - the difference between the economic return on assets and the average calculated interest rate (AMIR) on borrowed funds.
Due to taxation, unfortunately, only two-thirds of the differential remain (1/3 is the profit tax rate).
Shoulder of financial leverage - characterizes the strength of the impact of financial leverage.
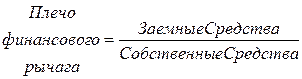 (4)
(4)
Let's combine both components of the effect of financial leverage and get:
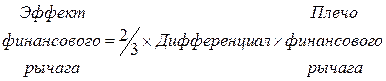 (5)
(5)
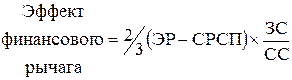 (6)
(6)
Thus, the first way to calculate the level of financial leverage effect is:
 (7)
(7)
The loan should lead to an increase in financial leverage. In the absence of such an increase, it is better not to take a loan at all, or at least calculate the maximum maximum amount of credit that leads to growth.
If the loan rate is higher than the level of economic profitability of the tourist enterprise, then increasing the volume of production due to this loan will not lead to the return of the loan, but to the transformation of the enterprise from profitable to unprofitable.
Here we should highlight two important rules:
1. If a new borrowing brings the company an increase in the level of financial leverage, then such borrowing is profitable. But at the same time, it is necessary to monitor the state of the differential: when increasing the leverage of financial leverage, a banker is inclined to compensate for the increase in his risk by increasing the price of his “commodity” - a loan.
2. The creditor's risk is expressed by the value of the differential: the larger the differential, the lower the risk; the smaller the differential, the greater the risk.
You should not increase the financial leverage at any cost, you need to adjust it depending on the differential. The differential must not be negative. And the effect of financial leverage in world practice should be equal to 0.3 - 0.5 of the level of economic return on assets.
Financial leverage allows you to assess the impact of the capital structure of the enterprise on profit. Calculation this indicator expedient in terms of evaluating the effectiveness of the past and planning the future financial activities enterprises.
Advantage rational use financial leverage is the ability to generate income from the use of capital borrowed at a fixed interest in investment activities that bring a higher interest than paid. In practice, the value of financial leverage is affected by the scope of the enterprise, legal and credit restrictions and so on. Too much high value financial leverage is dangerous for shareholders, as it involves a significant degree of risk.
Commercial risk means uncertainty about possible outcome, the uncertainty of this result of activity. Recall that risks are divided into two types: pure and speculative.
Financial risks are speculative risks. An investor, making a venture capital investment, knows in advance that only two types of results are possible for him: income or loss. A feature of financial risk is the likelihood of damage as a result of any operations in the financial, credit and exchange areas, transactions with stock securities, that is, the risk that follows from the nature of these operations. Financial risks include credit risk, interest rate risk, currency risk, risk of lost financial benefit.
The concept of financial risk is closely related to the category of financial leverage. Financial risk is the risk associated with a possible lack of funds to pay interest on long-term loans and borrowings. The increase in financial leverage is accompanied by an increase in the degree of riskiness this enterprise. This is manifested in the fact that for two tourist enterprises with the same volume of production, but different level financial leverage, the variation in net profit due to changes in the volume of production will not be the same - it will be greater for an enterprise with a higher level of financial leverage.
The effect of financial leverage can also be interpreted as the change in net income per ordinary share (as a percentage) generated by a given change in the net result of the operation of investments (also as a percentage). This perception of the effect of financial leverage is typical mainly for the American school of financial management.
Using this formula, they answer the question of how many percent the net profit per ordinary share will change if the net result of the operation of investments (profitability) changes by one percent.
After a series of transformations, you can go to the formula of the following form:
Hence the conclusion: the higher the interest and the lower the profit, the more power financial leverage and the higher the financial risk.
When forming a rational structure of sources of funds, one must proceed from the following fact: to find such a ratio between borrowed and own funds, in which the value of the enterprise's share will be the highest. This, in turn, becomes possible with a sufficiently high, but not excessive effect of financial leverage. The level of debt is for the investor a market indicator of the well-being of the enterprise. Extremely high specific gravity borrowed funds in liabilities indicates increased risk bankruptcy. If the tourist enterprise prefers to manage with its own funds, then the risk of bankruptcy is limited, but investors, receiving relatively modest dividends, believe that the enterprise does not pursue the goal of maximizing profits, and begin to dump shares, reducing market value enterprises.
There are two important rules:
1. If the net result of the operation of investments per share is small (and at the same time the financial leverage differential is usually negative, the net return on equity and the dividend level are lower), then it is more profitable to increase equity by issuing shares than to take out a loan: attracting borrowed funds funds costs the company more than raising its own funds. However, there may be difficulties in the process of initial public offering.
2. If the net result of exploitation of investments per share is large (and at the same time the financial leverage differential is most often positive, the net return on equity and the dividend level are increased), then it is more profitable to take a loan than to increase own funds: raising borrowed funds costs the enterprise cheaper than raising own funds. Very important: it is necessary to control the strength of the impact of financial and operational leverage in the event of their possible simultaneous increase.
Therefore, you should start by calculating the net return on equity and net earnings per share.
 (10)
(10)
1. The pace of increasing the turnover of the enterprise. Increased turnover growth rates also require increased funding. This is due to the increase in variables, and often fixed costs, almost inevitable swelling accounts receivable, as well as with many other most different reasons including cost-push inflation. Therefore, on a steep rise in turnover, firms tend to rely not on internal, but on external funding with an emphasis on increasing leverage in it, since issuance costs, initial public offering costs and subsequent payments dividends often exceed the value of debt instruments;
2. Stability of turnover dynamics. An enterprise with a stable turnover can afford a relatively larger share of borrowed funds in liabilities and more fixed costs;
3. Level and dynamics of profitability. It is noted that the most profitable enterprises have a relatively low share of debt financing on average over a long period. The enterprise generates sufficient profits to finance development and pay dividends, and is increasingly self-sufficient;
4. Structure of assets. If the company has significant assets general purpose, which by their very nature are capable of serving as collateral for loans, then an increase in the share of borrowed funds in the liability structure is quite logical;
5. The severity of taxation. The higher the income tax, the less tax incentives and opportunities to use accelerated depreciation, the more attractive it is for the enterprise debt financing due to the attribution of at least part of the interest for the loan to the cost;
6. Attitude of creditors to the enterprise. The game of supply and demand in the money and financial markets determines the average conditions loan financing. But specific conditions the provision of this loan may deviate from the average depending on the financial and economic situation of the enterprise. Whether bankers compete for the right to provide a loan to an enterprise, or money has to be begged from creditors - that is the question. Much depends on the answer real opportunities enterprises for the formation of the desired structure of funds;
8. Acceptable Degree risk for business leaders. The people at the helm may be more or less conservative in terms of the definition acceptable risk when making financial solutions;
9. Strategic target financial settings of the enterprise in the context of its actually achieved financial and economic position;
10. Market status briefly and long-term capital. With an unfavorable situation in the money and capital market, it is often necessary to simply obey the circumstances, postponing until better times the formation of a rational structure of sources of funds;
11. Financial flexibility of the enterprise.
Example.
Determining the amount of financial leverage economic activity enterprises on the example of the hotel "Rus". Let us determine the expediency of the size of the attracted credit. The structure of enterprise funds is presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Structure financial resources enterprises of the hotel "Rus"
| Index | Value |
| Initial values | |
| Hotel asset minus credit debt, million rubles | 100,00 |
| Borrowed funds, million rubles | 40,00 |
| Own funds, million rubles | 60,00 |
| Net result of investment exploitation, mln. rub. | 9,80 |
| Debt servicing costs, million rubles | 3,50 |
| Estimated values | |
| Economic profitability of own funds, % | 9,80 |
| Average calculated interest rate, % | 8,75 |
| Financial leverage differential excluding income tax, % | 1,05 |
| Financial leverage differential including income tax, % | 0,7 |
| Financial Leverage | 0,67 |
| Effect of financial leverage, % | 0,47 |
Based on these data, the following conclusion can be drawn: the Rus Hotel can take out loans, but the differential is close to zero. Minor changes in manufacturing process or higher interest rates can "reverse" the effect of leverage. There may come a time when the differential becomes less than zero. Then the effect of financial leverage will act to the detriment of the hotel.
Financial leverage
The effect of financial leverage shows by what percentage the return on equity is increased by attracting borrowed funds.
The effect of financial leverage arises due to the difference (differential) between the return on assets and the cost of borrowed funds. The differential must not be negative.
The differential reflects the lender's risk: the larger the differential, the lower the risk.
Financial leverage
Effect of financial leverage: using leverage, ceteris paribus, causes an increase in earnings before interest and taxes to lead to a stronger increase in earnings per share.
Knowledge of the mechanism of the impact of financial leverage on the level of return on equity and the level of financial risk allows you to purposefully manage both the cost and the capital structure of the enterprise.
FL makes it possible to use the "tax shield":
unlike share dividends, the amount of interest on the loan is deducted from the total taxable income.
Financial leverage
The effect of financial leverage is also calculated taking into account the effect of inflation (debts and interest on them are not indexed).
As inflation rises, the cost of borrowing becomes lower ( interest rates fixed) and the result from their use is higher.
If interest rates are high or the return on assets is low, financial leverage begins to work against the owners.
Financial leverage reflects the degree of dependence of the enterprise on creditors, that is, the amount of risk of loss of solvency.
Financial leverage:
Financial leverage ratio(shoulder of financial leverage) is defined as the ratio of borrowed capital to equity capital (according to the market valuation of assets).
The effect of financial leverage is also calculated:
EGF \u003d (1 - Kn) * (ROA - Zk) * ZK / SK.
where ROA - return on total capital before taxes (the ratio of gross profit to the average value of assets),%;
SC - the average annual amount of own capital;
Kn - taxation coefficient, in the form of a decimal fraction;
Tsk - weighted average price of borrowed capital, %;
ZK - the average annual amount of borrowed capital.
Financial leverage:
The formula for calculating the effect of financial leverage contains three factors:
(1 - Kn) - does not depend on the enterprise.
(ROA - Tsk) - the difference between the return on assets and the interest rate for a loan. It is called differential (D).
(LC/SK) - financial leverage (FR).
Optimal, especially Russian practice, the financial leverage ratio is considered equal to 1.
A value up to 2 can be acceptable (for large public companies, this ratio can be even higher).
With large values of the coefficient, the organization loses its financial independence, and its financial position becomes extremely unstable.
The most common ratio in developed economies is 1.5 (ie 60% debt and 40% equity).
Example:
|
№ p/n |
Indicators |
Enterprises |
||
|
The average amount of capital (assets), of which: | ||||
|
Average amount of equity | ||||
|
Average amount of borrowed capital | ||||
|
The amount of gross profit (excluding interest accounting) | ||||
|
Coeff. return on assets (excluding interest), % | ||||
|
Average interest rate for a loan, % | ||||
|
The amount of interest (column 3 × gr.6 / 100) | ||||
|
Gross profit including interest (column 4 - colum 7) | ||||
|
income tax rate, | ||||
|
The amount of income tax (column 8 × colum 9) | ||||
|
Net profit (column 8 - gr. 10) | ||||
|
Coeff. profitability of the UK, % (gr. 11 × 100 / gr. 2) | ||||
|
Increasing the profitability of the insurance company due to the use of borrowed capital, in % (in relation to the previous A) | ||||
Example: Formation of the effect of financial leverage
There is no effect of financial leverage for enterprise A, since it does not use borrowed capital in its activities.
For company B, this effect is:
EFL \u003d (1 - 0.2) × (20-10) × (200 / 800) \u003d 2
For enterprise B, this effect is:
EFL \u003d (1 - 0.2) × (20-10) × (500 / 500) \u003d 8
Financial leverage
The higher the share of borrowed funds in the total amount of capital used by the enterprise, the greater the level of profit it receives on equity.
The financial leverage differential is the main condition that forms its positive effect, which manifests itself only if gross profit level generated by the assets of the enterprise, exceeds the average size percent for the used loan (including not only its direct rate, but also other unit costs for its attraction, insurance and servicing).
The higher positive value differential of financial leverage, the higher, other things being equal, its effect will be.
Financial leverage:
Financial leverage and operating leverage are closely related methods.
FL also increases semi-fixed costs in the form of loan interest payments, but since lenders do not participate in the distribution of the company's income, variable costs are reduced.
Increasing financial leverage has a twofold effect:
more operating income is required to cover fixed financial costs
when cost recovery is achieved, profits begin to grow faster with the growth of each unit of additional operating income
Financial leverage:
Operating leverage shows the dynamics of operating profit in response to changes in the company's revenue
Financial leverage characterizes the change in profit before tax after paying interest on loans and borrowings in response to changes in operating profit.
The total (cumulative) leverage gives an idea of how much percentage change in profit before taxes after interest payment for a change in revenue by 1%.
Total lever = OL x FL
This indicator will allow you to determine by what percentage the net profit will change with a change in sales by 1%.
Financial leverage:
Production and financial risks are multiplied and form the total risk of the enterprise.
Financial and operational leverage (potentially effective) can be dangerous because of the risks they contain.
The task of financial management is to balance these two elements.
Small operating leverage can be increased by raising debt capital.
High operating leverage can be offset by low financial leverage.
Financial leverage:
The funding rule is based on the leverage effect:
if attracting additional borrowed funds gives a positive effect of financial leverage, then such borrowing is profitable,
but at the same time, it is necessary to monitor the differential, since with an increase in the leverage of financial leverage, lenders tend to compensate for their risk by increasing the rate for the loan.
1.2 Components of financial leverage

ZK - borrowed capital;
SC - equity.
As you can see, this formula has three components (Appendix B):
Tax corrector (or tax shield) of financial leverage (1 - TSA) - shows the extent to which the effect of financial leverage is manifested in connection with different levels profit taxation. Tax shield - a decrease in the amount of a company's tax liabilities caused by an increase in costs deductible from taxable income (depreciation and interest payments) 5 . The size of the tax shield can be calculated as the tax rate multiplied by the increase in such costs.
The tax corrector of financial leverage practically does not depend on the activities of the organization, because income tax rate is set by law. At the same time, in the process of managing financial leverage, a differential tax corrector can be used in the following cases:
if differentiated profit tax rates are established for various types of activities;
if for various types of activities the legislation (TC RF) provides for tax incentives by profit;
if individual subsidiaries of the organization operate in free economic zones of their country, where there is a preferential income tax regime;
if subsidiaries operate in other states with a lower level of income taxation.
Under these conditions, by influencing the structure of production and, in turn, the composition of profits by the level of taxation, it is possible to reduce the average rate of taxation of profits and increase the impact of the tax corrector on the effect of financial leverage (ceteris paribus).
Differential - characterizes the difference between the level of economic profitability of assets and the average calculated interest rate on borrowed funds; The SIRT, as a rule, does not coincide with the interest rate mechanically taken from the loan agreement, and is calculated as the ratio of all actual financial costs for all loans for the analyzed period to the total amount of borrowed funds used in the analyzed period, multiplied by 100. At the same time, the return on assets is equal to (ROA ) is equal to the ratio net profit received by the company for the period, to average company assets for the period.
Leverage leverage (or proportionality factor) - characterizes the strength of the impact of financial leverage - this is the ratio between the amount of borrowed capital (LC) and own capital (SC). Own capital characterizes total cost funds of the enterprise, owned by him by right of ownership and used by him to form a certain part of his assets. This part of the assets, formed from the equity capital invested in them, is net assets enterprises. Borrowed capital characterizes enterprises attracted to finance the development on a returnable (compensated) basis cash or other property values. All forms of borrowed capital used by an enterprise represent its financial obligations to be repaid within the stipulated time 6 .
The selection of these components allows you to purposefully manage the change in the effect of financial leverage in the formation of the capital structure.
With a positive value of the differential, any increase in the proportionality coefficient will cause an even greater increase in the return on equity, and with a negative value of the differential, the increase in the coefficient will lead to an even greater decrease in the return on equity. However, the increase in the effect of financial leverage has certain limits and it is necessary to realize the deep contradiction and inseparable connection between the differential and the shoulder of the financial lever. In the process of increasing the share of borrowed capital, the level of financial stability enterprises, which increases the risk of bankruptcy. This forces lenders to increase the level of lending rates, taking into account the inclusion of an increasing premium for additional financial risk. This increases the average calculated interest rate, which (with given level return on assets) leads to a reduction in the differential.
With a high value of the leverage of financial leverage, its differential can be reduced to zero, at which the use of borrowed capital does not increase the return on equity. At negative value differential, the return on equity will decrease, since part of the profit generated by equity capital will be spent on servicing the borrowed capital used for high stakes interest on a loan. Thus, attracting additional borrowed capital is advisable only if the level of economic profitability of the enterprise exceeds the cost of borrowed funds.
Calculation of the average calculated interest rate is carried out according to the weighted arithmetic average formula.
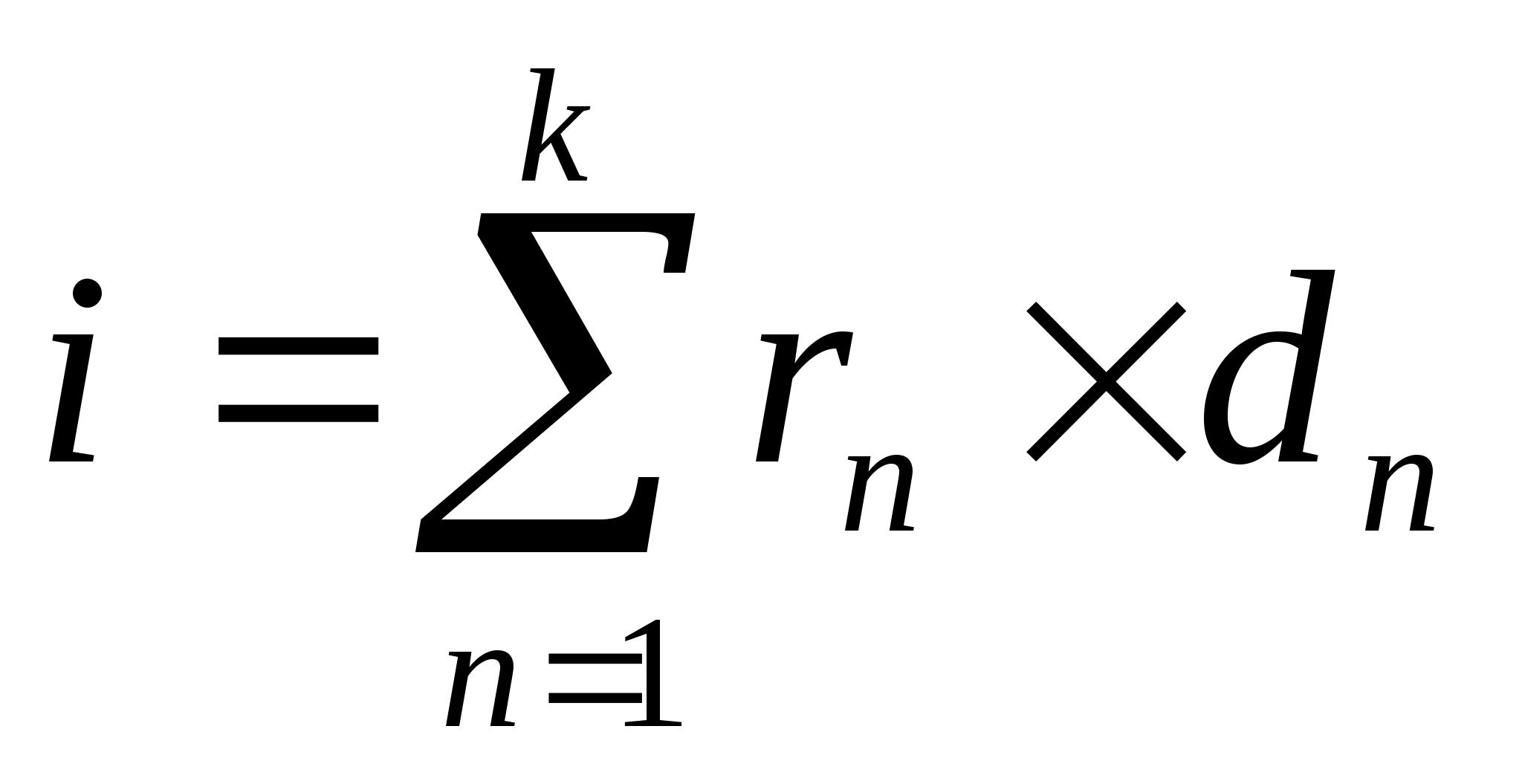 ,
(3)
,
(3)
i is the average calculated interest rate;
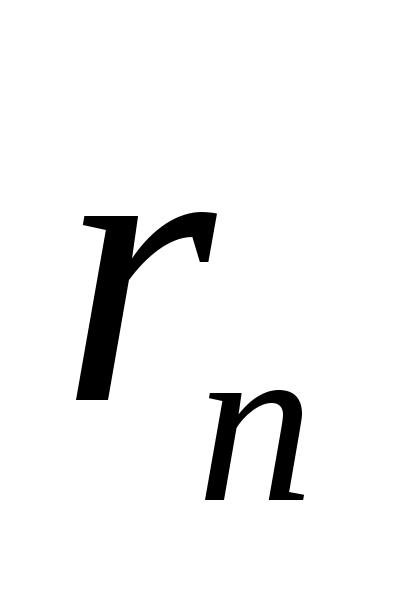 - the cost of the n-th source of borrowed funds;
- the cost of the n-th source of borrowed funds;
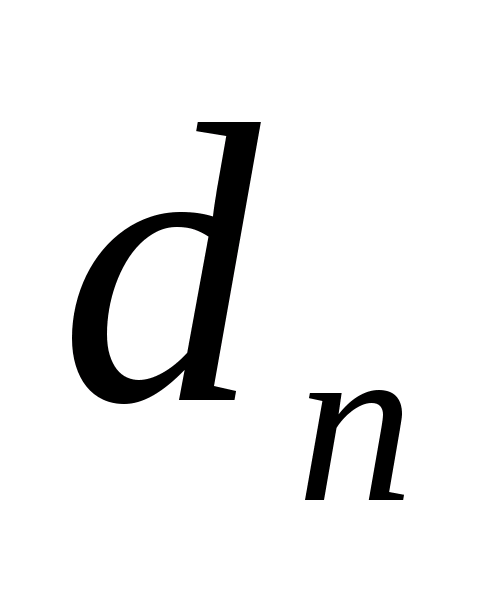 - share of the n-th source of borrowed capital in the cost of all borrowed capital.
- share of the n-th source of borrowed capital in the cost of all borrowed capital.
The calculation of the effect of financial leverage allows you to determine the marginal limit of the share of the use of borrowed capital for a particular enterprise, to calculate the acceptable lending conditions.
1.3 Approaches to assessing the effect of financial leverage
There are two approaches to assessing the effect of financial leverage: American and European 7 .
The effect of financial leverage in the American sense is the percentage change cash flow, received by the owner of equity, with a change in the return on assets by 1%. The effect is expressed in the fact that a slight change in the total return leads to a significant change in the cash flow received by the owner of equity. The effect of financial leverage in the American concept shows by how many percent net profit will increase if operating profit changes by 1%.
EGF =, 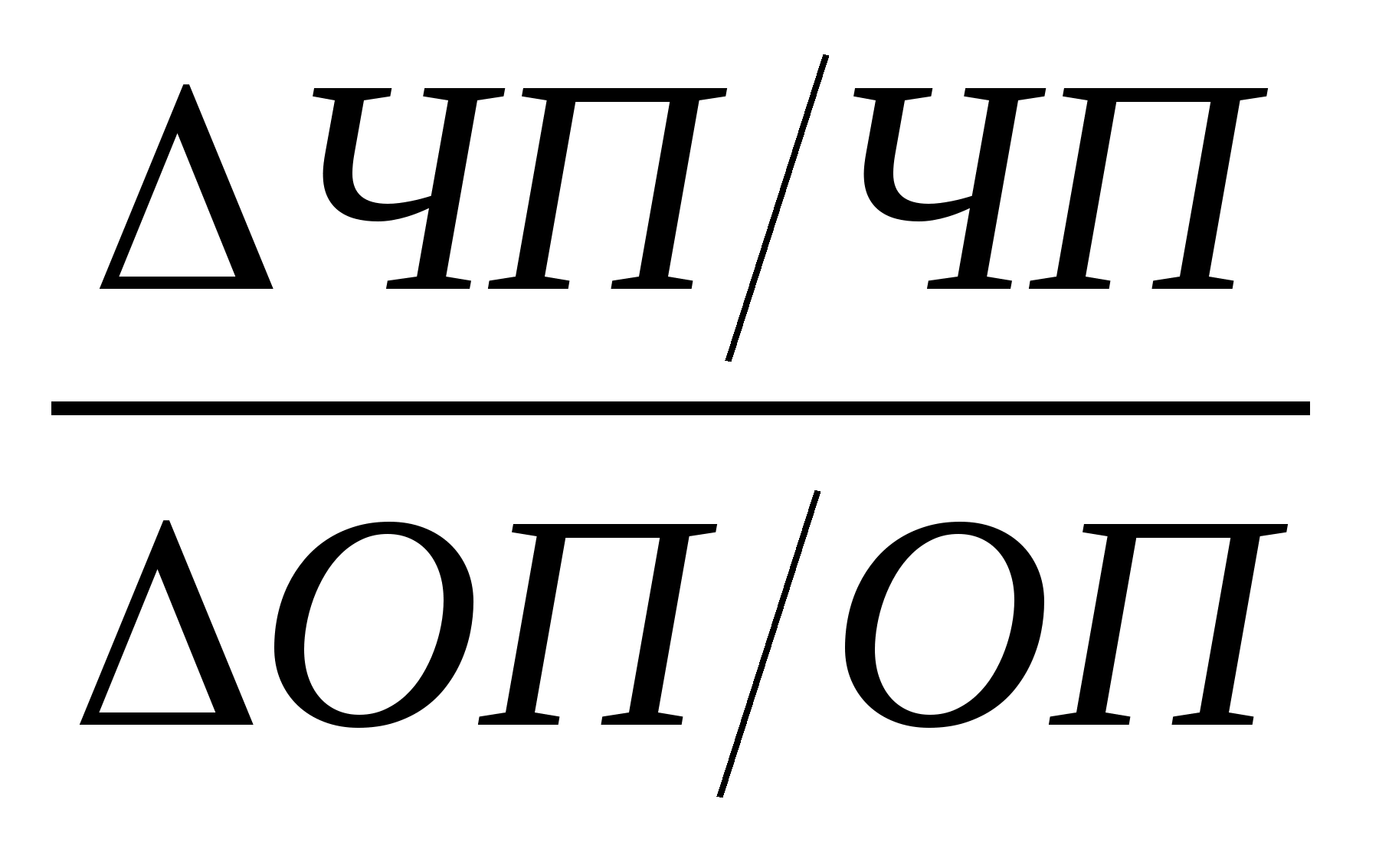 where (4)
where (4)
PE - net profit;
OP - operating profit.
Net income can be expressed in terms of operating profit and interest payable as follows:
The average calculated interest rate is excluded from the formula because when operating profit changes, the fee for the use of borrowed funds does not change.
Substituting the net profit, expressed through the operating, we get that:
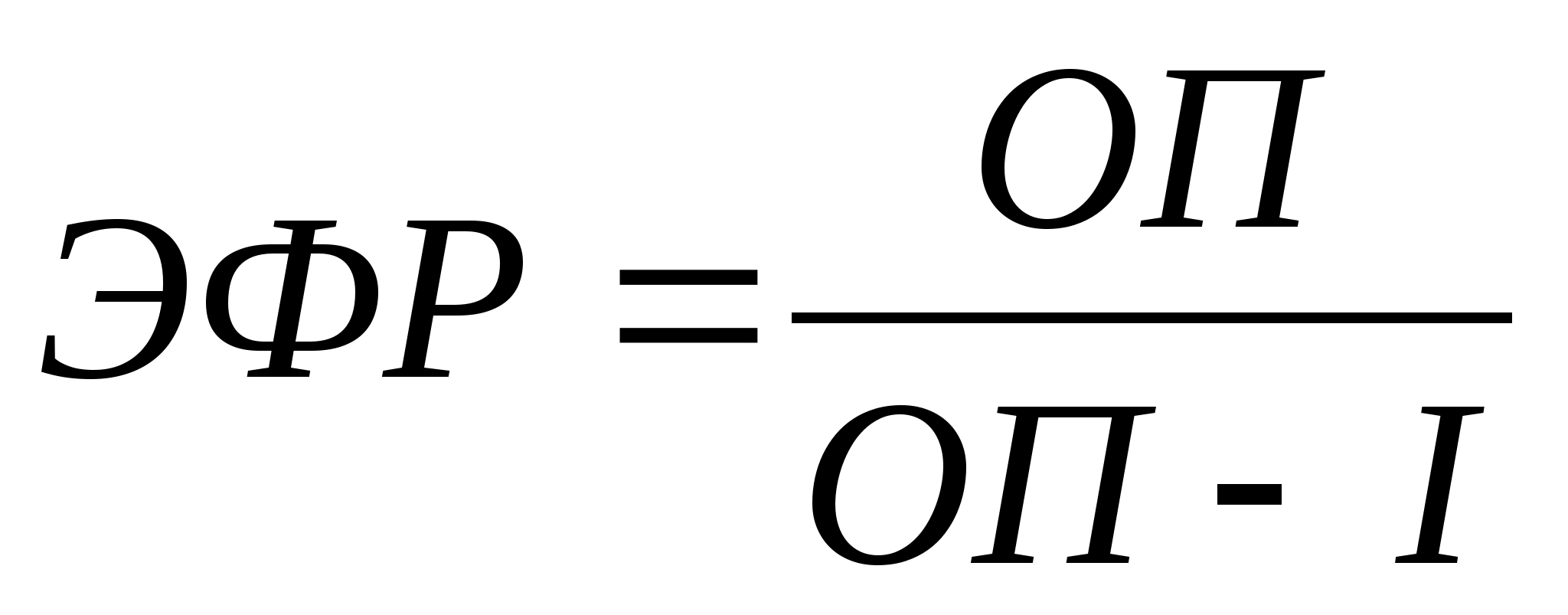 (7)
(7)
It can be seen from the obtained formula that if the effect of financial leverage is positive, then it makes sense to attract borrowed funds, if it is negative, then there is no point.
In the European approach, the effect of financial leverage is the difference between the return on equity and the return on assets. Those. additional profitability of the owner of equity arising from the attraction of borrowed capital with a fixed percentage. The essence of the European concept is expressed in the following formula:
To calculate the effect of financial leverage, the following formula is used:
EFR - the effect of financial leverage;
SNP - profit tax rate, expressed as a decimal fraction;
– return on assets ratio;
i is the average calculated interest rate;
ZK - borrowed capital;
SC - equity.
Those. from a European point of view, the effect of financial leverage arises from the discrepancy between the economic return on assets and the "price" of borrowed funds.
The effect of financial leverage is an increase in the net return on equity resulting from the use of borrowed sources(European approach).
The effect of financial leverage is an increase in net profit per share (American approach).
Fundamental difference between the stated approaches is shown in the figure (Appendix A).
The financial leverage ratio is a leverage that multiplies (in proportion to the multiplier or ratio changes) the positive or negative effect obtained through corresponding value differential. With the differential value unchanged, the financial leverage ratio is the main generator of both the increase in the amount and level of return on equity, and the financial risk of losing this profit.
In order for the effect of lowering the differential not to exceed the effect of attracting a loan, it is necessary to stabilize the effect of financial leverage. To do this, consider two situations. In the first case, borrowed capital consists of accounts payable, which is free, therefore, the interest rate for a loan and the amount of bank loans may not be taken into account, i.e. the interest rate and bank loan value are 0. In the second case, the loan is used and the interest rate and bank loan values are not 0.
 |
For the convenience of studying the material, we divide the article financial leverage into topics:
An indicator that reflects the level of additional profit when using borrowed capital is called the effect of financial leverage.
It is calculated using the following formula:
EGF \u003d (1 - Sn) x (KR - Sk) x ZK / SK,
Where:
EFR is the effect of financial leverage, %.
Sn - rate, in decimal terms.
KR - asset ratio (the ratio of gross profit to average cost assets), %.
Sk is the average interest rate for a loan, %. For a more accurate calculation, you can take the weighted average rate for the loan.
ZK - average amount used borrowed capital.
SC - the average amount of equity capital.
(1-Sn) - does not depend on the enterprise.
(KR-SK) - the difference between the return on assets and the interest rate for a loan. It is called differential (D).
(LC/SK) - financial leverage (FR).
Let's write the formula for the effect of financial leverage in short:
EGF \u003d (1 - Cn) x D x FR.
2 conclusions can be drawn:
The effectiveness of the use of borrowed capital depends on the ratio between the return on assets and the interest rate for the loan. If the rate for a loan is higher than the return on assets, the use of borrowed capital is unprofitable. - Ceteris paribus, greater financial leverage produces greater effect.
Effect of financial leverage
Profit formation management involves the use of appropriate organizational and methodological systems, knowledge of the main mechanisms of profit formation and modern methods its analysis and planning. When using a bank loan or debt securities, interest rates and the amount of debt remain constant throughout the term loan agreement or maturity of the securities. , associated with debt servicing, do not depend on the volume of production and sales of products, but directly affect the amount of profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise. Since interest on bank loans and debt securities refer to ( operating expenses), then the use of debt as a source of financing is cheaper for the enterprise than other sources for which payments are made from (for example, shares). However, an increase in the share of borrowed funds in the capital structure increases the risk of insolvency of the enterprise. This should be taken into account when choosing funding sources. It is necessary to determine the rational combination between own and borrowed funds and the degree of its influence on. One of the main mechanisms for achieving this goal is financial leverage.Financial leverage (leverage) characterizes the use of borrowed funds by the enterprise, which affects the value of return on equity. Financial leverage is an objective factor that arises with the advent of borrowed funds in the amount of capital used by the enterprise, allowing it to receive additional profit to own capital.
The idea of financial leverage according to the American concept is to assess the level of risk based on fluctuations in net profit caused by a constant value of the company's debt service costs. Its action is manifested in the fact that any change in operating profit (earnings before interest and taxes) generates more significant change net profit.
Interpretation of the financial leverage ratio: it shows how many times earnings before interest and taxes exceed net income. The lower limit of the coefficient is one. The greater the relative amount of borrowed funds attracted by the enterprise, the greater the amount of interest paid on them, the higher the impact of financial leverage, the more variable the net profit. Thus, increasing the share of borrowed financial resources in the total amount of long-term sources of funds, which, by definition, is equivalent to an increase in the strength of the impact of financial leverage, other things being equal, leads to greater financial instability, expressed in less predictable net profit. Since the payment of interest, unlike, for example, the payment of dividends, is mandatory, then with relatively high level financial leverage, even a slight decrease in profits may have adverse effects compared to a situation where the level of financial leverage is low.
The higher the force of financial leverage, the more non-linear the relationship between net income and earnings before interest and taxes becomes. A slight change (increase or decrease) in earnings before interest and taxes under conditions of high financial leverage can lead to a significant change in net income.
The increase in financial leverage is accompanied by an increase in the degree of enterprise associated with a possible lack of funds to pay interest on loans and borrowings. For two enterprises with the same volume of production, but different levels of financial leverage, the variation in net profit due to changes in the volume of production is not the same - it is greater for an enterprise with a higher value of the level of financial leverage.
The European concept of financial leverage is characterized by an indicator of the effect of financial leverage, which reflects the level of additionally generated return on equity with a different share of the use of borrowed funds. This method of calculation is widely used in the countries of continental Europe (France, Germany, etc.).
EGF \u003d (1-Np) * (Ra-Tszk) * ZK / SK
- financial leverage differential (ra-C,k), characterizing the difference between the profitability of the company's assets and the weighted average calculated interest rate on loans and borrowings;
The amount of borrowed capital per ruble of own. In terms of inflation, the formation of the effect of financial leverage is proposed to be considered depending on the rate of inflation. If the amount of the company's debt and interest on loans and borrowings are not indexed, the effect of financial leverage increases, since debt servicing and the debt itself are paid for with already depreciated money:
EGF \u003d ((1-Np) * (Ra - Tsk / 1 + i) * ZK / SK,
where i - characteristic of inflation (inflationary rate of price growth), in fractions of units.
In the process of managing financial leverage, a tax corrector can be used in the following cases:
If differentiated tax rates are established for various types of activities of the enterprise;
- if the enterprise uses income tax benefits for certain types of activities;
- if individual subsidiaries of the enterprise operate in free economic zones their country, where there is a preferential income tax regime, as well as in foreign countries.
In these cases, by influencing the sectoral or regional structure of production and, accordingly, the composition of profit in terms of its taxation level, it is possible, by reducing the average profit tax rate, to reduce the impact of the financial leverage tax corrector on its effect (ceteris paribus).
The financial leverage differential is a condition for the emergence of the effect of financial leverage. A positive EGF occurs when the return on total capital (Ra) exceeds the weighted average price borrowed resources(Tszk).
The difference between the return on total capital and the cost of borrowed funds will increase the return on equity. Under such conditions, it is beneficial to increase the financial leverage, i.e. the share of borrowed funds in the capital structure of the enterprise. If Pa is less than Tsk, a negative EGF is created, resulting in a decrease in the return on equity, which can eventually become the cause.
The higher the positive value of the differential of financial leverage, the higher, other things being equal, its effect.
Due to the high dynamism of this indicator, it requires constant monitoring in the process of profit management.
This dynamism is driven by a number of factors:
Just like other exporting countries, Russia uses a wide arsenal of means to regulate international credit relations - these are tax and customs benefits, state guarantees and subsidizing interest rates, subsidies and loans. However, to a greater extent Russian state supports large corporations and banks, usually with a solid state participation, that is, itself. But medium and small businesses get little from the flow of benefits that spills onto large businesses. On the contrary, loans for the purchase of imported equipment are provided to small and medium-sized companies that are not included in small business support programs at significantly more stringent rates than for big business, conditions.
On exchange rate and the direction of movement of world capital is also affected by the difference in interest rates in different countries. An increase in interest rates stimulates the inflow of foreign capital into the country and vice versa, and the movement of speculative, "hot" money increases the instability of the balance of payments. But it is unlikely that the regulation of interest rates is productive due to the need to control liquidity, which means that it can interfere. At the same time, the Central Bank reduced the rate of deductions to the Mandatory Reserve Fund for ruble deposits. This measure is justified by the fact that reserve requirements are lower in Europe, and Russian banks find themselves in unequal conditions.
financial leverage profitability
The effect of financial leverage (EFF) shows by what percentage the return on equity increases by attracting borrowed funds into the turnover of the enterprise and is calculated by the formula:EGF \u003d (1-Np) * (Ra-Tszk) * ZK / SK
Where Np - the income tax rate, in fractions of units;
Rp - return on assets (the ratio of the amount of profit before interest and taxes to the average annual amount of assets), in fractions of units;
Tsk - the weighted average price of borrowed capital, in fractions of units;
ZK - average annual cost loan capital; SC is the average annual cost of equity capital.
There are three components in the above formula for calculating the effect of financial leverage:
Tax corrector of financial leverage (l-Np), which shows the extent to which the effect of financial leverage is manifested in connection with different levels of income taxation;
- financial leverage differential (ra-C,k), characterizing the difference between the profitability of the company's assets and the weighted average calculated interest rate on loans and borrowings;
- leverage of the financial leverage CC/SC
Operational and financial leverage
The concept of "leverage" comes from the English "leverage - the action of a lever", and means the ratio of one value to another, with a small change in which the indicators associated with it change greatly.Most common the following types leverage:
Production (operational) leverage.
financial leverage.
All companies use financial leverage to some extent. The whole question is what is the reasonable ratio between one's own and borrowed capital.
The ratio of financial leverage (shoulder of financial leverage) is defined as the ratio of borrowed capital to equity capital. It is best to calculate it by market valuation assets.
The effect of financial leverage is also calculated:
EGF \u003d (1 - Kn) * (ROA - Zk) * ZK / SK.
where ROA - return on total capital before taxes (the ratio of gross profit to the average value of assets)%;
SC - the average annual amount of own capital;
Kn - taxation coefficient, in the form decimal fraction;
Tsk - weighted average price of borrowed capital, %;
ZK - the average annual amount of borrowed capital.
The formula for calculating the effect of financial leverage contains three factors:
(1 - Kn) - does not depend on the enterprise.
(ROA - Tsk) - the difference between the return on assets and the interest rate for a loan. It is called differential (D).
(ZK/SK) - Financial leverage (FR).
You can write the formula for the effect of financial leverage in a shorter way:
EGF \u003d (1 - Kn) x D x FR.
The effect of financial leverage shows by what percentage the return on equity is increased by attracting borrowed funds. The effect of financial leverage arises due to the difference between the return on assets and the cost of borrowed funds. The recommended EGF value is 0.33 - 0.5.
The effect of financial leverage is that, other things being equal, the use of leverage leads to the fact that the growth of the corporation's earnings before interest and taxes leads to a stronger increase in earnings per share.
The effect of financial leverage is also calculated taking into account the effect of inflation (debts and interest on them are not indexed). With an increase in the inflation rate, the fee for using borrowed funds becomes lower (interest rates are fixed) and the result from their use is higher. However, if interest rates are high or the return on assets is low, financial leverage begins to work against owners.
Leverage is a very risky business for those enterprises whose activities are cyclical. As a result, several consecutive years of low sales can lead heavily leveraged businesses to bankruptcy.
For more detailed analysis changes in the value of the financial leverage ratio and the factors that influenced it use the methodology of the 5th financial leverage ratio.
Thus, financial leverage reflects the degree of dependence of the enterprise on creditors, that is, the magnitude of the risk of loss of solvency. In addition, the company gets the opportunity to take advantage of the "tax shield", since, unlike dividends on shares, the amount of interest on the loan is deducted from the total amount of profit subject to taxation.
Operating leverage (operating leverage) shows how many times the rate of change in sales profit exceeds the rate of change in sales revenue. Knowing the operating leverage, it is possible to predict the change in profit with a change in revenue.
This is the ratio of constants and variable costs company and the impact of this relationship on earnings before interest and taxes (operating income). Operating leverage shows how much profit will change if revenue changes by 1%.
The price operating leverage is calculated by the formula:
Rts \u003d (P + Zper + Zpost) / P \u003d 1 + Zper / P + Zpost / P
where: B - sales revenue.
P - profit from sales.
Zper - variable costs.
Zpost - fixed costs.
Rts - price operating leverage.
pH is a natural operating lever.
Natural operating leverage is calculated by the formula:
Rn \u003d (V-Zper) / P
Considering that B \u003d P + Zper + Zpost, we can write:
Rn \u003d (P + Zpost) / P \u003d 1 + Zpost / P
Operating leverage is used by managers to balance different kinds costs and increase income accordingly. Operating leverage makes it possible to increase profits when the ratio of variable and fixed costs changes.
Participating in the formation and use of funds of monetary resources, financial leverage should affect economic activity economic agencies, stimulate economic growth, increase labor productivity, improve product quality, perform all other tasks related to the organization of production in conditions of commercial calculation. The impact of financial levers on the development of social production depends on the functions with which they are endowed, and on the implementation of these functions in practice. So, historical experience shows that taxes, when applied correctly, bring great benefits to the state, and when erroneous - irreparable harm. Even the technical tax practice plays very important role. A classic example This in the history of the Soviet economy is the fact that the surplus appropriation was replaced by a tax in kind. As a result, the tax began to be levied in a different form and this led to positive results, although the severity of taxation remained almost at the same level. Hence the conclusion - all financial levers require the most careful attitude both in their development and in their application.
Importance plays both in production and not production activities a system of financial incentives, which are levers of influence on social production. The transformation of finance into a tool that ensures the organic inclusion of commodity-money relations in the management mechanism market economy, strengthening the impact of finance on production in modern conditions management occurs through the improvement of all forms financial relations, including through the activation of financial incentives - encouragement for good performance and the application of sanctions for violations.
Various kinds of stimuli expressing the content financial mechanism, can be applied in the formation of income, savings and funds. Wide spectrum various benefits provided for taxes levied to the budget by partial or full release enterprises from their payment. The purpose of the incentive is to increase the funds allocated for activities related to the development of production, the social needs of employees, environmental actions, charitable purposes, and the expansion of production. certain types products (works, services). When concealing income or paying it late, apply different kind sanctions, both economic and administrative nature up to and including criminal liability.
Benefits and sanctions are also applied in the organization of financing and lending to the production activities of enterprises and organizations of all forms of ownership. For example, they can be applied for intended use funds, late payment bank loans.
It is also important to develop the quantitative parameters of each element of the financial mechanism, i.e., the determination of rates, norms and standards for the allocation and withdrawal of funds, the volume of individual funds, the level of spending financial resources, etc.
One of fundamental principles legislative and executive bodies associated with the use of financial levers and incentives, the development of norms and standards, is the operational accounting of changes in business processes and the timely impact on them, aimed at improving efficiency economic development states.
Action of financial leverage
Financial risk, entrepreneurial, production, risk associated with the activities of the company. The level of conjugate effect of financial and operational leverage. The total risk associated with the firm. Types of risk, methods for determining risk. Management (regulation) of the risk of economic and financial methods. Relationships between owners and managers. The risk arising from the activities of the owners. Economic, financial and other ways to minimize the risk associated with shareholders. The ability of a manager to report at a shareholder meeting as an important lever to reduce overall risk. Net profit per share.Back | |
- How to talk to collectors: important rules
- Fixed payment to the pension fund for individual entrepreneurs
- Mortgages for young teachers
- How to add okved code for ooo
- How to write an application to the tax office
- Legal support of business
- How to get a tax deduction for a wife's child
- In which bank is it better to open a current account for an individual entrepreneur?
- Tax on the sale of an apartment: how to reduce the amount to a minimum by legal means Tax on the cadastral value or sales
- Charter of LLC with one and several founders
- Requirements for LED lamps in educational institutions
- Completing income tax returns
- Check yourself: the procedure for conducting cash transactions Instructions for conducting cash transactions
- Documents of previous periods, VAT Did not reflect receipts in the last quarter of VAT
- Financial assistance from the employer at the birth of a child
- Notice of suspension of work due to non-payment of wages: form and sample
- Taxes and economic activity
- Application for financial assistance at the birth of a child
- Income minus expenses - a sample of the budget estimate of the HOA and a report on its implementation
- What to do if collectors threaten