Calculate the company's return on equity for the reporting year. Calculation of return on capital indicators based on accounting data
Profitability indicator equity ROE (Return On Equity) is one of the most important financial indicators for investors. Unlike the return on assets (ROA) indicator, ROE characterizes the efficiency of using not all of the company's capital, but only that part of it that belongs to its shareholders. Expressed as a percentage and calculated as:
- ROE = Net Profit / Cost share capital x 100
- ROE = Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity x 100
Magnitude net profit takes up fiscal year, excluding dividends paid on ordinary shares (taken into account when calculating the ROCE ratio), but taking into account dividends paid on preferred shares (if any). Share capital is taken without taking into account preference shares.
ROE is the rate at which a company's shareholders' funds work. So, if ROE = 20%, this means that for every dollar invested by shareholders, the company generated $0.20 in net income.
Comparing return on equity with return on assets (ROA) gives an idea of financial leverage - financing through borrowed money
For ordinary shares, the return on common equity (ROCE) indicator is used. Expressed as a percentage and calculated as:
- ROCE = Net Income - Preferred Dividends / Cost of Shareholders' Capital - Preferred Shares x 100
- ROCE = Net Income - Preferred Dividends / Shareholder's Equity - Preferred Stocks x 100
ROE should be compared with the ROE of similar companies, as well as with those available in the market alternative options investments. If the company's ROE is consistently below market rates of return, then it is more advisable to liquidate the business and invest money in market assets.
As ROE increases, the P/B multiplier should also increase. Low ROE and high P/B may indicate that the stock is overvalued. High ROE and low P/B mean that the market underestimates the company's potential.
It is also important to consider that the company can improve its ROE ratio, buying back its own shares from the market, thereby reducing their number in circulation and increasing the return on equity. As a result, this may give the investor an erroneous impression of the issuer's business performance.
Concerning normative value ROE, then in the long term the return on capital should not be lower than low-risk investments in financial instruments. Because if the return on capital of a business is lower than the rates on deposits in large banks or on bonds, then the business ceases to be profitable for its owners.
- For example, if it is expected that in the next 3 years deposit rates will be in the range of 8-10%, then any business that will bring 10-12% on capital is unpromising, since it must be taken into account that the risks of doing business are much higher, than investments in government bonds or deposits.
Thus, the prospects of a business are assessed taking into account rates on low-risk investments (bonds or deposits in large banks) and risk premiums (corporate, market, economic, political, etc.).
Traditionally most high profitability American and European corporations show the lowest, and the lowest, regardless of the economic cycle, is shown by Japanese companies.
Return on equity (ROE, return on equity) is a financial indicator expressing profit on share capital. Close to the indicator return on investment ROI.
The indicator shows the ratio of net profit for the period to the equity capital of the enterprise.
Formula for calculating ROE ratio
Net income does not include dividends on common stock, and equity does not include preferred stock.ROE = PE / SK
, Where:
PE - net profit;
SK - equity capital.
Benefits of ROE
ROE ratio is one of the most important indicators for investors, top managers, and owners of an enterprise, as it shows the effectiveness of their own investments (with the exception of borrowed funds).Disadvantages of ROE
Analysts question the reliability of the ROE indicator, believing that return on equity ratio overestimates the company's value. There are 5 factors that make ROE not completely reliable:- Long project duration - the longer the analysis period, the higher the ROE.
- A small share of total investments on the balance sheet. The smaller the share the higher the ROE.
- Uneven depreciation. The more unevenly in reporting period depreciation, the higher the ROE.
- Slow return on investment. The slower the project pays off, the higher the ROE.
- Growth rates and investment rates. How younger company, the faster the balance grows, the lower the ROE.
Standard ROE value
ROE norm For developed countries is 10-12%. For developing countries with high inflation rates - many times more. On average, 20%. Roughly speaking, return on equity is the rate at which a company attracts investment.Analysis of return on equity ratio by division of the company (by business area) can clearly show the effectiveness of investing funds in one or another area of business, for the production of one or another product or service. Also for the investor ROE comparison for two companies in which he has an interest, can show the most effective in terms of return.
When assessing standard value of ROE It's worth considering replacement costs. If on this moment available securities with a low risk indicator, yielding 16% per annum, and the main line of business gives an ROE of 9%, then the ROE goal should be set higher, or the business as a whole should be reviewed.
How to calculate profitability? Based on what accounting reports? This article is devoted to the answers to these, as well as many other questions regarding the calculation of the main financial indicators of an enterprise and their correct interpretation.
What is profitability?
Profitability ( from him. Rentabel - useful, profitable, profitable) are called a set of relative indicators of enterprise performance. The profitability of an enterprise reflects the level of efficiency in the use of resources at the disposal of the enterprise.
Profitability ratio is one of the key tools financial analysis. This is a universal indicator that allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of use various resources enterprises.
What is profitability in simple words ? Calculation of profitability allows you to determine specific gravity arrived ( gross or net) per unit of resource being assessed.
How is profitability measured?
Profitability indicators can be presented in in monetary terms. In this case, the coefficient will contain information about how much profit a resource unit generates. However, most often profitability ratios are expressed as percentages.
ROI video:
Types of profitability and how to calculate profitability
Enterprise profitability analysis is based on the calculation of a set of coefficients.
Formulas for calculating all profitability indicators without exception include profit in monetary terms divided by the book value of the asset directly or indirectly involved in generating this profit.
The following are used in financial analysis:
- Return on sales ( Profit Margin),
- Profitability of fixed assets,
- Return on equity ( own and borrowed),
- return on investment,
- Personnel profitability.
This is far from full list profitability indicators used in financial analysis. However, other indicators are, to one degree or another, derived from those listed.
Sales return formula
Return on sales ( ROS) – profitability of sales (in many textbooks on financial analysis you can find the abbreviation PM ( Profit Margin)) is one of the most popular financial analysis ratios. It is calculated by the formula:
RM = Operating ( marginal) profit/sales volume or
RM = line 050 of the balance sheet/line 010 of the income statement.
The popularity of this coefficient is explained, first of all, by the fact that it allows quickly evaluate work efficiency enterprise management.
In fact, this indicator reflects the ability of an enterprise to generate profit through competent pricing policy And effective management operating costs. These “abilities” are the key to the reliability of any enterprise.
It should be noted that the return on sales ratio is not a “self-sufficient” evaluation criterion, however, like most other financial analysis ratios.
The share of profit in the trade turnover of an enterprise for a particular period is uninformative. His significant disadvantage is that its calculation does not take into account the volume of assets involved in generating profit and their turnover period.
Using this coefficient for comparison various enterprises (even one field of activity) doesn't make much sense either.

Such a comparison may only be of interest to statistics buffs, because cost formation algorithms for different enterprises may vary greatly. First of all, this applies to manufacturing enterprises.
By the way, the PM coefficient is most often used for analysis trading enterprises and extremely rare for enterprises in manufacturing and other areas that are characterized by high capital intensity.
It is advisable to use the return on sales ratio to evaluate the effectiveness of various projects within one multi-industry enterprise.
In this case, the evaluation criterion is the value of the indicator.
It can also be used to assess the effectiveness of medications taken management decisions– to do this, analyze the dynamics of changes in the indicator over certain period (as a rule, several operating cycles of the enterprise).
Profitability formula products sold (profitability of sales) For manufacturing enterprise can serve as a demonstration of a well-thought-out flexible pricing policy.
Quite often, the numerator of the formula for calculating profitability uses not operating profit, but net profit. This coefficient is called “net return on sales”.
In our opinion, the profitability of sales in this edition even less informative. It is of little use for assessing individual divisions of a multi-industry enterprise, primarily because when calculating net profit, depreciation of general production and non-production fixed assets is taken into account, and the criteria for distributing such costs between centers of financial responsibility are always “ weak point» any accounting system.
Using this indicator, you can compare different enterprises.

Production profitability formula
The production profitability ratio is calculated as the ratio of gross profit from sales finished products to the costs of its production and sale.
Like Profit Margin, the production profitability indicator is an operational indicator; its use is advisable when conducting a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of the functioning of departments or projects of a multi-industry enterprise.
Also this indicator used to determine the profitability threshold - the minimum volume of finished products, the sale of which will generate a profit volume sufficient to cover production and pre-sale costs.
The profitability threshold is also called the break-even point.
The formula for calculating the break-even point is as follows:
PR = PZ/KN, Where
PR – profitability threshold, PP – fixed costs, and KN is the coefficient of trade margin (margin).
Return on fixed assets
The ability of an enterprise to generate profit is a very superficial characteristic of the effectiveness of its operation.
The previously discussed return on sales can serve as an evaluation criterion for the work of the trading department; it allows one to assess the ability of the enterprise to effectively manage highly liquid assets. current assets (goods and finished products) and control the level of transaction costs.
The next stage of assessment financial condition enterprise and the efficiency of its functioning is the calculation of the profitability of its non-current assets, in particular, fixed assets.
This coefficient is calculated using the formula:
Return on fixed assets (ROFA) = Net profit/total (book) value of fixed assets.
This indicator reflects the dynamics of the return of funds invested in non-current assets. In addition, the use of this coefficient allows us to fairly objectively assess the effectiveness of the enterprise’s business model.
The degree of correlation of this indicator with various business processes allows us to identify those that require optimization. Based on this coefficient, you can do the following:
- Conduct comparative analysis efficiency of various production areas;
- Assess the quality of work performed and the qualifications of workers at production sites;
- Assess the manufacturability of production.
The return on fixed assets indicator is of interest not only to internal users. Along with return on capital indicators, about which we'll talk Further, it is a convenient financial analysis tool that is used by potential investors and lenders.

Return on assets. Economic profitability
Economic profitability as a tool of financial analysis activity of an enterprise is one of the main objects of attention of company management, since this aggregate and cumulative indicator demonstrates not only the dynamics of the movement of all types of financial and production assets enterprises.
With its help, you can assess the structure of these assets, the level of production and other operating costs.
The coefficient is calculated using the formula:
Economic profitability ratio = Profit before tax / Average asset value * 100.

Return on equity: balance sheet formula
Return on equity ratio ( ROE) reflects the ratio of net profit to the enterprise's equity capital ( 1st section of the liabilities side of the balance sheet).
In other words, this coefficient shows how much profit the owners of the enterprise received for each invested ruble.
Formula for calculating the coefficient:
ROE = net profit/average equity.
In the process of assessing the effectiveness of investments, this indicator is compared with alternative investment objects, incl. with the deposit rate of commercial banks.
This is the simplest option for calculating ROE. Its main disadvantage is that it does not take into account the structure of equity capital, or more precisely, it does not allow one to determine what part of equity capital acts as a source of financing current assets.
The Dupont formula does not have this drawback.
ROE = (Net Profit/Revenue) * (Revenue/Assets) * (Assets/Equity)
The coefficient calculated using this formula is more informative. When calculating it, not only capital productivity is taken into account, but also the degree of financing of assets using equity capital.
Calculation of profit and return on sales, video:
Factor analysis of profitability
Factor analysis is one of the ways comprehensive assessment financial condition of the enterprise based on the above ratios. It is based on mathematical modeling.
Factor analysis involves creating mathematical connections (dependencies) between the studied indicators. Such multifactor models can be of the following types:
- Additive ( the resulting factors are summed or subtracted),
- Multiplicative ( factors multiply),
- Multiples. Dividing factors into each other.
A wide selection of modeling algorithms allows you to reproduce with high accuracy in mathematical formulas real business– processes.
Internal rate of return
Internal Rate of Return ( IRR) is used to determine economic efficiency investment projects.
It is expressed as a percentage and shows the rate at which the incoming ( positive) cash flow, during implementation investment project, will be equal to outgoing ( negative) cash flow.
When calculating the indicator internal norm High accuracy is very important for profitability, because The slightest mistakes made at this stage promise big troubles for the project developers in the future.
As a rule, IRR is calculated by iterative selection of interest rate values when calculating the NPV of a project. To make the work of designers easier today, powerful software systems who are capable of short time calculate all the necessary indicators.
Purpose of cost-benefit analysis- assess the ability of the enterprise to generate income on the capital invested in the enterprise.
The investment attractiveness of the organization and the amount of dividend payments depend on the level of profitability.
The characteristics of the profitability of an enterprise are based on the calculation of three main indicators - return on total capital, equity capital and share capital (Table 19, p. 205).
Return on total capital of all assets shows how much net profit without taking into account the cost of borrowed capital is per ruble of capital invested in the enterprise. IN international practice financial analysis, the return on total capital is determined by the formula:
Where Percent 2- the amount of interest accrued in the analyzed period on loans that reduce taxable profit, denominated. units;
Percent 1- interest on loans accrued in the analyzed period that does not reduce taxable profit, den. units
NP rate- profit tax rate, %.
Balance currency is defined as the average value of the total amount of liabilities in the period under review, that is, as
[Total liabilities (at the beginning of the period) + Total liabilities (at the end of the period)]/2
The calculations use data for the period (not on an accrual basis).
Currently, it is not uncommon for a situation where, when calculating the return on total capital, they deviate somewhat from the classical calculation algorithm - The numerator of the formula considers only net profit. This move makes the three main profitability indicators more comparable, since in this case it uses single base calculation - the amount of net profit.
Return on equity characterizes the effectiveness of using the company's own funds invested in it. Return on equity shows how much net profit is per ruble of equity.
Calculate similarly return on equity is interpreted, defined as the ratio of net profit to the amount of the organization’s share (authorized) capital .
To assess the performance of individual enterprises and compare enterprises with each other it is necessary that profitability indicators are presented in a form adequate for comparison.
Since the calculations of profitability indicators use data for the analyzed period, the result of the calculations will directly depend on the duration of this period. A comparison of profitability indicators Re1 = 5% (Enterprise 1) and Re2 = 8% (Enterprise 2) is correct only if both coefficients are determined for the same analysis periods - that is, both indicators are calculated for a month, quarter, half-year, year.
If Enterprise 1 carried out calculations by quarters, and Enterprise 2 - by years, then in comparable form the profitability indicators will have the values Re1 = 5%* = 20%, Re2 = 8%. Thus, the comparability of profitability indicators will be ensured if the indicators are brought to a single analysis interval, for example, to a year.
Presenting profitability indicators in annual terms is most convenient. The cost of capital in the market (interest and deposit rates) and the macroeconomic environment (inflation, refinancing rate) are characterized by indicators in annual terms. When calculating profitability in annual terms, an adequate basis is created for assessing the performance of a particular enterprise and comparing different enterprises with each other.
To analyze the effectiveness of managing the structure of an enterprise’s financing sources, the so-called leverage effect. The essence of the leverage effect is as follows:
An enterprise, using borrowed funds, increases or decreases return on equity. A decrease or increase in return on equity depends on the average cost of borrowed capital (average interest rate) and the size of financial leverage.
Financial leverage is called the ratio of debt and equity capital of an organization:
It is recommended to use in calculations the average values of debt and equity capital in the analyzed period - (data at the beginning of the period + data at the end of the period)/2. However, there is an approach that uses not average, but absolute values of equity and debt capital for a specific analyzed date. The choice of calculation method is based on average values or values for a specific reporting date- carried out on an individual basis.
It is not difficult to notice that financial leverage is an indicator inverse of the coefficient autonomy (1/Autonomy coefficient).
Average interest rate calculated as a ratio total cost borrowed capital in the analyzed period to the amount of borrowed capital.
Where Interest in SB- interest accrued in the analyzed period
on loans included in the cost of production, den. units;
Interest from profit- interest on loans accrued in the analyzed period, attributed to financial results, den. units; Interest allocated to financial results is not cleared at the income tax rate.
Borrowed capital is defined as [Borrowed capital (at the beginning of the period) + Borrowed capital (at the end of the period)]/2
The difference between the return on total capital and the average interest rate is called lever differential. The leverage differential provides information for selecting an appropriate structure of financing sources. IN in this case The choice of an appropriate structure of funding sources means the choice of the “cheapest” sources for the organization.
The product of financial leverage and its differential determines the magnitude of the leverage effect

The sign of the leverage effect (leverage differential) reflects the feasibility of increasing borrowed capital:
· positive leverage effect- An increase in debt capital increases the return on equity.
· negative leverage effect- increasing borrowed capital is inappropriate, it reduces the return on equity.
That is, if the return on total capital is less than the cost borrowed sources financing, it is advisable to increase the share of own funds.
The absolute value of the leverage effect reflects the degree of influence of the structure of financing sources on the return on equity.
The influence of the structure of funding sources on return on equity can be represented as a formula:
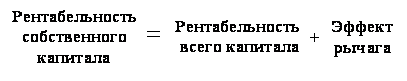
When calculating profitability indicators, it is necessary to use unified approach- carry out calculations based on average values for the period of analysis, or on the basis of values for a specific reporting date. This will ensure comparability of calculation results.
The analysis of factors that influenced the change in return on equity is carried out using the DUPONT formula. The DUPONT formula establishes the relationship between return on equity and three main financial indicators enterprises: sales profitability, turnover of all assets and financial leverage in one of its modifications.
The impact of changes in the listed indicators on return on equity capital is assessed using the technique chain substitutions. According to this technique, the indicator that has the maximum absolute value of the influence coefficient has the greatest influence.
Return on equity and financial stability have inverse relationship. It is enough to pay attention to the formulas for the coefficient of autonomy and return on equity capital.
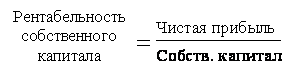
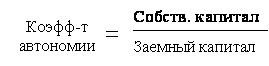
With an increase in equity capital, the financial stability of the organization increases and the return on equity decreases. In this regard, the statement that it is always advisable for an enterprise to increase its own capital is ambiguous. Own funds must be sufficient to ensure financial stability. Task financial management at the enterprise - providing financial stability, contribute to the growth of return on equity.
97. Indicators of business activity of the enterprise.
Business activity commercial organization measured using a system of quantitative and quality indicators. Business activity ratios allow you to analyze how effectively the company uses its funds. Analysis of business activity consists of studying the levels and dynamics of financial turnover ratios.
Qualitative criteria are the breadth of sales markets (domestic and external), business reputation the company, its competitiveness, the presence of regular suppliers and buyers of finished products. These criteria should be compared with similar characteristics competitors operating in the industry. The data is not primarily taken from financial statements, but from marketing research.
Quantitative criteria of business activity are characterized by absolute and relative indicators. In number absolute indicators includes: sales volume of finished products, the amount of assets and capital used, including equity, profit.
It is advisable to compare these quantitative parameters over a number of periods (quarters, years). The optimal ratio between them: Growth rate of net profit > Growth rate of revenue from product sales > Growth rate of asset value > 100%
That is, the enterprise’s profit should increase at a higher rate than other parameters of business activity. This means that assets (property) should be used more efficiently and production costs should decrease. However, in practice, even in stable operating organizations, deviations from the specified ratio of indicators are possible. The reasons for this may be: the development of new types of products and technologies, large capital investments in the modernization and development of fixed assets, reorganization of the management and production structure and other factors.
Relative indicators business activity characterizes the efficiency of using the organization's resources, this financial ratios, turnover indicators. average value indicators are defined as the chronological average for a certain period (based on the amount of available data); in the simplest case, it can be defined as half the sum of indicators at the beginning and end of the reporting period.
All coefficients are expressed in times, and the duration of the turnover is in days. These indicators are very important for the organization. Firstly, the size of the fund depends on the speed of turnover of funds. annual turnover. Secondly, the size of the turnover, and, consequently, the turnover rate is associated with the relative value of production (circulation) costs: the faster the turnover, the less costs there are for each turnover. Thirdly, the acceleration of turnover at one or another stage of the circulation of funds entails an acceleration of turnover at other stages. Financial position organization, its solvency depends on how quickly funds invested in assets turn into real money.
Indicators of asset turnover (assets turnover) and equity turnover (equity turnover) characterize level of business activity of the enterprise and are calculated as the ratio of annual revenue from sales of products (works, services) to average annual cost assets and equity, respectively.
This group of coefficients allows you to analyze how effectively the company uses its funds. It is especially important to compare business activity indicators with industry averages, since their value can fluctuate significantly depending on the industry.
To analyze the business activity of organizations, two groups of indicators are used: general indicators turnover; asset management indicators.
The turnover of funds invested in the organization’s property can be assessed: turnover rate– the number of turnovers made during the analyzed period by the organization’s capital or its components; turnover period– the average period for which they return to economic activity organizations cash, invested in production and commercial operations.
Turnover analysis includes four types of analysis:
- turnover of the company's assets;
- turnover accounts receivable;
- turnover accounts payable;
- inventory turnover.
When analyzing financial and economic activities, various economic indicators, including profitability.
Profitability is the main indicator economic efficiency investments in various financial objects of an economic entity.
- The profitability ratio is understood as the ratio of profit to asset items or sources of their formation.
- Profitability is usually expressed as a percentage.
What is return on equity?
The most indicative economic coefficient of an enterprise’s activity is return on equity (ROC), which shows the size of the return on invested capital.
For business owners, the IC profitability ratio is very useful, since it characterizes the usefulness of the investment of the participants’ funds, and not the attracted capital.
- The SC profitability formula is the ratio of profit to SC.
- To calculate as a percentage, the result is multiplied by one hundred.
- For a more accurate calculation, use the average arithmetic value own funds for the analyzed period.
Based on financial statements, profitability can be determined:
Line 190 (at the beginning of the period): 0.5 (line 490 (at the beginning of the period) + line 490 (at the end of the period).
When determining the profitability of an insurance company, the Dupont formula is also used:
SK profitability = (Net profit: Revenue) x (Revenue: Assets) x (Assets: SK) = Net profit margin x Asset turnover x Financial leverage.
The normal value of this indicator for developed economies ranges from 10-12%
But for Russian economy with the inflation component this figure should be higher.
When analyzing the profitability of an insurance company, the resulting indicator is compared with the value of the alternative return that the owners could receive when investing their funds in another enterprise.
Return on total capital

Another feature that determines economic stability and constitutes the enterprise profitability index is the return on total capital.
Total capital is the sum of current and non-current assets.
The return on total capital formula is characterized by the ratio of profit to the average annual value of invested capital ( total amount company assets).
According to the financial statements, this indicator can be calculated as the ratio of the value of line 2300 of the profit and loss statement to line 1700 of the balance sheet.
Return on debt capital
To analyze the economics of an enterprise, the return on debt capital ratio is used.
Borrowed capital (LC) is borrowed funds in the form of financial assistance, credits and loans.
ZK profitability determines the ratio of profit to the average amount of borrowed capital for the period
According to the information in the reporting, the profitability of the ZK is determined as follows:
Line 2400 of the Profit and Loss Statement: (Line 1410 + Line 1510 of the balance sheet).
Return on working capital
When determining the economic efficiency of a company's activities, profitability is also used working capital(or current assets).
Working capital is funds allocated for present activities to ensure the production cycle.
Working capital can be divided into constant or variable:
- Constant working capital is the funds that provide the minimum acceptable economic results activities.
- Variable capital is the attraction additional funds to expand production tasks.
Return on working capital is calculated as the ratio of profit to the average annual (or average for the period under review) value of current assets.
You can calculate profitability using accounting data as follows:
Line 2400 of the income statement: Line 1200 of the balance sheet.
Return on invested and permanent capital

Return on invested capital (ROI) characterizes the profitability of funds invested in commercial activities.
- The invested capital is own funds companies and long-term liabilities.
- The profitability of IC is the ratio of profit to the size of IC.
- This indicator is often calculated to assess the feasibility of raising borrowed funds.
When analyzing activities, the concept of return on permanent capital (PC) is also used.
It characterizes the level of efficiency of attracting own and borrowed funds into the company’s activities for a long time.
Profitability (PC) is calculated as profit divided by average cost own capital and long-term loans.
According to the financial statements, the indicator is calculated as follows:
Line 2400 of the income statement: (line 1300 + line 1400 of the balance sheet).
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
- Hiroshi Ishiguro - Japanese engineer, creator of humanoid robots
- 石黒浩 Career In 1991 he defended his dissertation. Since 2003, professor at Osaka University. Heads a laboratory in which...
- New
- Measurement of gamma background in places of residence of the population of rural and urban settlements in the southwestern regions of the Bryansk region
- The latest photos from the Hubble telescope
- Blood of Saint Januarius When the blood of Saint Januarius boils in Naples
- National Emblems in Great Britain
- The meaning of the word cambium in the encyclopedia biology
- Morphological analysis of the verb
- About Great Britain in English
- Is Cyprus still an offshore zone?
- Sample plan for writing a speech therapist report
- Letter M, m. Consonant sound i. Letter M, m Corrective and developmental
- Articulation exercises
- How are these sounds similar?
- What does it mean to go to the panel?
- Pythagoras - Olympic champion What kind of sport did Pythagoras engage in?
- What did a kisser do in Rus'?
- Tselovalnik - a mysterious profession of ancient Rus'
- The creator of geminoid robots, Hiroshi Ishiguro, will give lectures at Skoltech








