Determine the profitability of fixed assets. Calculation and analysis of various profitability indicators for a number of periods
Introduction 1. Overall profitability 2. Profitability current assets 3.Profitability of production assets4.Profitability of enterprise assets5.Profitability financial investments 6. Profitability of production 7. Payback period equity
Introduction
Profitability indicators are designed to assess the overall effectiveness of investing in an enterprise. They are widely used for financial assessment - economic activity enterprises of all industries. These are one of the most important indicators when assessing the activities of an enterprise, which reflect the degree of profitability of the enterprise.
Profitability indicators are formed as follows:
RS&I -profitability of certain economic assets and their sourcesP -profit (net or balance sheet)
Overall profitability
This indicator is the most common in determining the profitability of an enterprise and is calculated as the ratio of profit before tax to revenue from the sale of goods, works and services produced by the enterprise.
The indicator shows what part of the sales revenue is profit before tax, is analyzed over time and compared with the industry average values of this indicator.
 ,Where
,Where
Pdn -profit before tax,Vreal -revenues from sales
Return on current assets
It is defined as the ratio of net profit (profit after tax) to the current assets of the enterprise. This indicator reflects the company's ability to provide a sufficient amount of profit in relation to the company's working capital used. The higher the value of this ratio, the more efficiently working capital is used.
Emergency -net profit,OA -average annual cost current assets
Profitability of production assets
Defined as the ratio of book profit to the average value of the sum of the cost of fixed assets, intangible assets and working capital in commodity and material assets.
The level of profitability of production assets is higher, the higher the profitability of products (the higher the capital productivity of fixed assets and the speed of turnover of working capital, the lower the costs per 1 ruble of products and the unit costs of economic elements (equipments, labor materials)).
P -profit before tax,PF -average annual cost of production assets
Return on enterprise assets
Defined as the ratio of net profit to all assets of the enterprise
Emergency -net profit,VB -balance currency
Return on financial investment
It is defined as the ratio of the amount of income from financial investments to the amount of financial investments.
Pfv -profit of the enterprise from financial investments for the period,FV -amount of financial investments
Production profitability
Production profitability is defined as the ratio of gross profit to production cost.
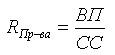 ,Where
,Where
VP -gross profit,SS -production cost
Payback period of equity capital
Payback period of equity capital. It is found by dividing the average annual value of equity capital by the net profit of the analyzed period. It has important for owners and shareholders, since by assessing its size and dynamics, they, as a rule, draw conclusions about the effectiveness of managing their capital.
The payback period of equity capital is calculated using the following formula:
 ,Where
,Where
SK -average cost of equity capital,Emergency -net profit
1) changes profitability of sales,
2) changes in the efficiency of use of fixed assets and intangible assets (through the capital intensity ratio of products),
3) changes in inventory turnover (through the coefficient of inventory consolidation per one ruble of products).
Table 2.6
Initial data for analyzing the profitability of production assets by factors, thousand rubles.
| Indicators | Behind last year | Behind reporting year | Absolute. deviation |
| A | |||
| 1. Profit from sales | +50511 | ||
| 2. Average value of production assets, including: | 204130 | +74526 | |
| 2.1 Average value of fixed assets and production intangible assets | +59985 | ||
| 2.2.Average value of inventories (MPI) | +14541 | ||
| 3. Revenue (net) from sales | +38690 | ||
| 4. Return on sales, % (line 1: line 3x100) | 20,82 | 30,54 | +9,72 |
| 5. Capital intensity of products, rub. (p.2.1:p.3) | 0,6862 | 0,7735 | +0,0873 |
| 6. Coefficient of consolidation of inventories, rub. (p.2.2:p.3) (1/Co) | 0,1668 | 0,1879 | 0,0211 |
| 7. Profitability of production assets, % (line 1: line 2x100) | 24,40 | 31,76 | +7,36 |
| 8. Capital productivity of all production assets (page 3: page 2) | 1,172 | 1,040 | -0,132 |
| 9. Share of inventories in total amount production assets (page 2.2/page 2) | 0,1956 | 0,1955 | -0,0001 |
Let's build factor model:
Rпф = Пп/В x В/(С 1 + С 2) (2.12)
Where Rпф is the profitability of production assets;
Pp – profit from sales;
B – net revenue from sales;
C 1 – average annual cost of fixed assets and production intangible assets;
B/(C 1 + C 2) – capital productivity of all production assets;
C 2 - average value inventories.
Rpf 0 = P p 0 / B 0 x B 0 / (C 1 + C 2) 0 = 20.82 x 1.172 = 24.40%
Rpf condition1 = P p 1 / B 0 x B 0 / (C 1 + C 2) 0 = 88506/239310 x 1.172 = 43.35%
Rпф conv2 = P p 1 / B 1 x B 1 / (C 1 + C 2) 0 = 30.54 x 1.420 = 43.37%
Rpf 1 = P p 1 / B 1 x B 1 / (C 1 + C 2) 1 = 30.54 x 1.040 = 31.76%
Influence of factors on the profitability of production assets:
A) profit from sales:
43,35 – 24,40 = + 18,95%
b) sales revenue:
43,37 – 43,35 = + 0,02%
c) Average value of production assets:
31,76 – 43,37 = - 11,61%
Balance of factors: 18.95 + 0.02 – 11.61 = + 7.36%
Or: Rпф = Пп/В x В/(С 1 + С 2) = Rп x Фo (2.13)
Фo – capital productivity of all production assets (its inverse value is capital intensity);
Rп – return on sales.
Rpf 0 = Rp 0 x Fo 0 = 20.82 x 1.172 = 24.40%
Rpf condition = Rp 1 x Fo 0 = 31.76 x 1.172 = 37.22%
Rpf 1 = Rp 1 x Fo 1 = 31.76 x 1.040 = 31.76%
Influence of factors:
A) the profitability of production assets increased by 12.82% due to an increase in profitability of sales:
37,22 – 24,40 = + 12,82%
b) and decreased by 5.46% due to a decrease in capital productivity (according to an increase in capital intensity):
31,76 – 37,22% = - 5,46%
Balance of factors: 12.82 – 5.46 = + 7.36%
Rpf = Rp x Ko x D (2.14)
Where Ko is the inventory turnover ratio (Revenue/Average annual inventory);
D – share of oil reserves in total cost production assets.
Rpf 0 = Rp 0 x Ko 0 x D 0 = 20.82 x 5.995 x 0.1956 = 24.40%
Rpf condition1 = Rp 1 x Ko 0 x D 0 = 30.54 x 5.995 x 0.1956 = 36.81%
Rpf condition2 = Rp 1 x Ko 1 x D 0 = 30.54 x 5.321 x 0.1956 = 31.78%
Rpf 1 = Rp 1 x Ko 1 x D 1 = 30.54 x 5.321 x 0.1955 = 31.77%
Influence of factors on production assets:
A) profitability of sales:
36,81 – 24,40 = + 12,41%
b) inventory turnover ratio:
31,78 – 36,81 = -5,03%
c) the share of industrial production in the total cost of production assets:
31,77 – 31,78 = - 0,01%
Balance of factors:
12.41 - 5.03 – 0.01 = 7.1% (deviation from tabular data due to rounding).
2.5. Ways to increase enterprise profits Achieving high performance results of an enterprise involves managing the process of generating, distributing and using profits. Management includes profit analysis, profit planning, and a constant search for opportunities to increase profits. Many enterprises have a division economic services who are constantly analyzing costs and looking for ways to reduce them in order to increase profits. But to a large extent this work is ensured by inflation and rising prices for raw materials and fuel and energy resources. In conditions of sharp rise in prices and lack of own working capital for enterprises, the possibility of increasing profits as a result of lowering costs is excluded. Increasing the volume of product sales in in kind ceteris paribus leads to increased profits. Increasing production volumes that are in demand can be achieved using capital investments, which requires using profits to purchase more productive equipment, mastering new technologies, and expanding production. This path is now difficult or almost impossible for many enterprises due to inflation, rising prices and the unavailability of long-term credit. An enterprise that has the funds and capabilities to make capital investments actually increases its profits if it provides a return on investment above the rate of inflation. Accelerating the turnover of working capital, which also leads to an increase in production volumes and product sales, does not require capital expenditures. However, inflation quickly depreciates working capital, enterprises are directing an increasing part of them to purchase raw materials and fuel and energy resources; non-payments by buyers and required prepayments divert a significant part of funds from buyers’ turnover. In general, Russian enterprises are characterized by a decline in production volumes over the course of recent years. In this situation, it would seem logical to assume a sharp drop in the mass of profits. But statistics indicate the opposite. As production costs increase and production volumes decrease, profits increase due to constantly rising prices. An increase in price in itself is not negative factor. It is quite justified if it is associated with an increase in demand for products, improvement of technical and economic parameters and consumer properties manufactured products. Since profit from product sales occupies the largest share in the structure balance sheet profit, then the analysis of the factors that determine it is important for identifying growth reserves for the entire balance sheet profit. Under stable economic conditions, the main way to increase profits from product sales is to reduce costs. This is especially important for enterprises in the manufacturing industries, where the share of the cost of raw materials in production costs is significantly higher than in similar enterprises developed countries, the weight of waste is significant. In particular, in mechanical engineering, the share of metal waste in the total consumption of ferrous metals has consistently been more than 20% for many years, and the share of chips in general education metal waste - 45%. This also indicates the use of obsolete equipment. In industries focused on the end consumer, the volume of production and sales of products determined by demand and the level of cost are of decisive importance, but without compromising quality consumer goods. The amount of profit from sales of products is influenced by the composition and size of unsold balances at the beginning and end of the period. A significant amount of balances leads to incomplete receipt of revenue and loss of profit. The reserve for increasing balance sheet profit may be the profit received from the sale of fixed assets and other property of the enterprise. Options for increasing profits are shown in Fig. 4.Fig. 4 Options for increasing profits If previously operations related to the disposal of fixed assets did not have a noticeable impact on financial results, then now that enterprises have the right to dispose of their property, it makes sense to get rid of unnecessary things and not installed equipment, having previously weighed what is more profitable - to sell it or rent it out. Other operations, e.g. gratuitous transfer fixed assets of the enterprise are not included in the balance sheet profit, but are reimbursed from net profit intended for accumulation. Profit can be obtained from the sale of intangible assets that are in demand in the market. Their selling price is determined by their ability to generate income. To calculate profits from selling price costs associated with the creation or purchase of intangible assets are excluded, taking into account the costs of bringing them to a state in which they are capable of generating income. In addition to the factors of increasing production volumes and increasing prices for promoting products to unfilled markets, the problem of reducing the costs of production and sales of these products and reducing production costs is inexorably put forward. In the traditional view, the most important ways to reduce costs is to save all types of resources consumed in production: labor and material. Thus, wages play a significant role in the structure of production costs. Therefore, the urgent task is to reduce the labor intensity of manufactured products, increase labor productivity, and reduce the number of administrative and service personnel. Reducing the labor intensity of products and increasing labor productivity can be achieved different ways. The most effective of them are mechanization and automation of production, development and application of progressive, high-performance technologies. However, measures to improve the equipment and technology used will not give the proper return without improving the organization of production and labor. Material resources occupy up to 3/5 in the structure of production costs. Hence the importance of saving these resources and their rational use is clear. The use of resource-saving technologies comes to the fore here. technological processes. It is also important to increase the demands and widespread use of input control for the quality of raw materials, components and semi-finished products received from suppliers. Reducing depreciation costs of fixed assets can be achieved by best use these funds, their maximum load. At foreign enterprises, such factors for reducing production costs as determining and complying with optimal size batches of purchased materials, the optimal size of the batch of products purchased for production, deciding the question of whether to produce ourselves or purchase from other manufacturers individual components or components of products. It is known that the larger the batch of purchased raw materials, the greater the average annual stock and the greater the costs associated with storing these raw materials. However, purchasing raw materials in large quantities has its advantages. Costs associated with placing an order for purchased goods, accepting these goods, monitoring the passage of invoices, etc. are reduced. Thus, the task arises of determining the optimal amount of purchased raw materials and supplies in order to avoid unnecessary costs and increase profits. The same rules apply when determining the optimal size of a series of launched products. When producing products in a significant number of small batches, storage costs finished products will be minimal, due to which profits will increase. In combination with traditional ways of reducing production costs, newly emerging factors will make it possible to collectively bring the value of production costs to optimal level, therefore increasing profits. Profits may increase as a result of increased production, increased specific gravity products with more high profitability, reduction in production costs, growth wholesale prices, while improving the quality of products. The range of products produced has a direct impact on profits. When the assortment structure changes in the direction of increasing the share of products with higher profitability, an additional increase in profit is ensured. Among the factors influencing profit growth, the leading role belongs to the reduction in product costs. The choice of ways to reduce current production costs is based on an analysis of the cost structure. For material industries industry, the most typical way is saving material resources, for labor-intensive - improving the use of fixed capital, for energy-intensive - saving fuel and electricity. When producing products of higher quality, operating costs most often increase. However, as a result of selling these products at higher prices, profits also increase. Profit planning is also the way to increase it. The most important issue Managing the profit planning process is planning profit and other financial results. The main goal when planning is to maximize income, which makes it possible to provide financing for a larger volume of the enterprise’s needs in its development. In this case, it is important to proceed from the amount of net profit. The task of maximizing the net profit of an enterprise is closely related to optimizing the amount of taxes paid within the framework of current legislation, preventing unproductive payments. The object of planning is the planned elements of balance sheet profit, mainly profit from the sale of products, performance of work, provision of services. The basis for the calculation is the volume production program, which is based on consumer orders and economic contracts. Profit planning – component financial planning And important area financial and economic work at the enterprise. Profit planning is carried out separately for all types of activities of the enterprise. This not only makes planning easier, but also has implications for the expected amount of income tax, since some types of activities are not subject to income tax, while others are subject to higher rates. Exist tax benefits, among which it should be noted the exclusion from taxation of the costs of repaying bank loans received and used for these purposes, as well as the amount of contributions for charitable purposes. In the process of developing profit plans, it is important not only to take into account all the factors influencing the amount of profit, but also, after considering the options for the production program, to choose the one that ensures maximum profit.
Nitetsky V.V., Gavrilov A.A. Financial analysis in auditing. – M.: Delo, 2001. P.91.
Data taken from additional data in the manual.
Dontsova L.V., Nikiforova N.A. Analysis financial statements: Textbook, 4th ed. – M.: DiS, 2006. P.190-195.
Column 2, paragraph 2 of additional data from the manual.
From the profit and loss report (according to the assignment of the 9th option) for period 010 for the reporting period.
Page 4, group 2 of the manual (additional data)
From the income statement, line 010 for similar period previous year.
See table. 2.2.
See gr. 7, p.2 table. 2.2
According to the note on page 9 “ Guidelines“The student has the right to choose other forms of tables that seem more preferable to him,” we took advantage of this right.
Line 14 + page 15, group 1 of additional data from the manual
Gruzinov V.P., Gribov V.D. Enterprise Economics - M.: UNITI, 2001. P.257
Profitability- This relative indicator characterizing the financial results of the enterprise.
Profitability is also called an indicator of the efficiency of an enterprise.
There are various profitability indicators, which are divided into 3 groups:
- indicators characterizing the efficiency of use of property
- indicators characterizing the use of sources of property formation
- indicators characterizing the efficiency of the enterprise
Profitability is often identified with the indicator “profitability”, “return”.
Each profitability indicator gives an idea of how many rubles of profit can be obtained from each ruble of property, sources of property, costs, etc.
Most often, net profit indicators are used, but the enterprise, at its own discretion, also profits from sales, profit before tax (accounting).
Most popular in financial analysis enterprises are the following indicators:
1. Return on assets (Ra) determined by the formula:
R a = PE/A = line 190 F 2 / line 300 F 1
where PE is net profit;
A – assets.
And they are calculated as the average value for the year.
And wed. =(A(n.g.)+A(k.g.))/2;
2. Return on current assets (Rob.a.) determined by the formula:
Rob.a.=PE/A vol. = line 190 Ф 2 / line 290 Ф 1
where Aob are current assets.
Aob - calculated on average per year.
3. Profitability of production assets (RPF) calculated by the formula:
(Rpf) = PE / (OS + M o A) = line 190F 2 / line 290F 1
where: OS – fixed assets;
MoA – raw materials, materials.
OS and MoA are calculated on average per year.
4. Return on equity (Rsk) determined by the formula:
Rsk=ChP/SK=line 190F 2 / line 490F 1
where SK is equity capital.
SC is calculated on average per year.
5. Return on Investment (Rin) calculated by the formula:
Rin = PE / (SK + DO) = line 190F 2 / (line 490F 1 + line 590F 1)
where DO – long-term liabilities
6. Return on sales (RP) calculated by the formula:
Рп=PP/В=str.050Ф 2 /010Ф 2
where PP is profit from sales.
B - revenue
7. Profitability of core activities (Kind) calculated by the formula:
Rod=PP/Z=str.050Ф 2 /(str.020Ф 2 +str.030Ф 2 +str.040Ф 2)
where Z – costs, consisting of: cost of goods sold, commercial and administrative expenses.
8. Profitability of product sales
R r =CHP/V=str.190Ф 2 /str.010Ф 2
This indicator speaks about the efficiency not only of the enterprise’s economic activities, but also of its pricing processes. It is advisable to calculate it based on the total volume products sold(Form No. 2), and for its individual types (information from internal reporting available to the financial manager).
Financial analysts are external users of information and can calculate other profitability indicators depending on the purpose and the availability of information from external reporting. Often these indicators are calculated not as coefficients, but as percentages.
The analysis is carried out by comparing the calculated profitability indicators for a number of periods. For this purpose, a table is compiled:
The calculated indicators in this table make it possible, using the method of horizontal analysis, to identify trends in the use of indicators for a number of periods.
In all cases, a decrease in profitability (deviation with “-”) indicates negative trend decrease in profitability of the enterprise. This worries everyone external users information, incl. potential investors, banks, and also leads to a decrease in the investment attractiveness of the enterprise. Therefore, many Western enterprises strive in the external system financial statements show high values profits, demonstrate an increase in profitability, but on the other hand, this may indicate an unsuccessful depreciation policy, leading to physical and moral aging of equipment, and, consequently, to the deterioration of strategic, forecast indicators, incl. and profitability.
A win-win option for increasing profitability is to search for reserves for reducing the costs of intensive use of equipment, its fuller utilization through economical use and increased turnover of current assets, and increased productivity of workers.
- Homemade caramel syrup
- What is a spelling chart for schoolchildren
- How to soak meat in vinegar
- How to bake a meat pie - step-by-step recipes for preparing dough and filling with photos
- Pike cutlets "Original"
- What color were the insects you saw?
- Delicious snacks with a spicy touch: preparing salads with Korean carrots
- What is binge drinking: symptoms Alcoholic during binge drinking
- Psychosomatic factors of thyroid diseases Psychological causes of thyroiditis
- Tower coastal batteries of Sevastopol 30th coastal battery
- Liberation of Belarus - Operation Bagration
- Lunar calendar for December dream book
- Marshmallow recipe with sweetener: what to add to homemade dessert
- Puff pastries with cottage cheese, from ready-made puff pastry
- Sterlet recipes
- Why does a woman dream about a baby kangaroo?
- Runic inscription to attract customers for your business
- What do the numbers mean in fortune telling on coffee grounds?
- Fortune telling on paper with a ronglis pen
- Orange peels: uses, features and best recipes








