Long-term capital in balance. Study and share capital. Passive operations of banks
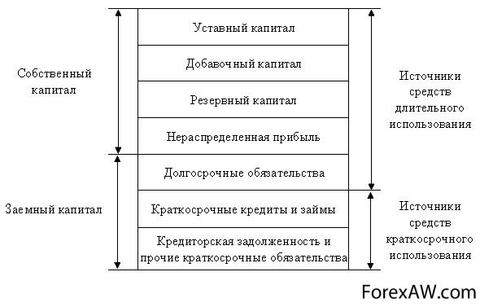
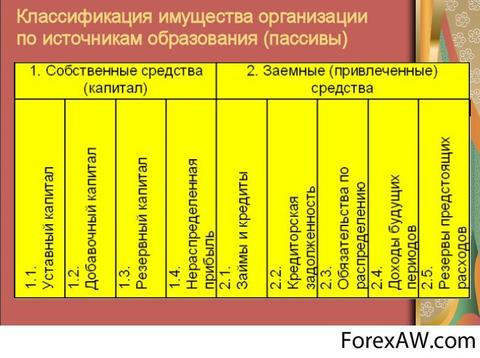
part of the balance sheet (right side), which reflects the obligations and sources of funds of the enterprise, consisting of their own, borrowed and attracted funds grouped by their belonging and appointment, including accounts payable
Definition and interpretation of liability, types of liabilities, theory and practice of liability, liabilities as sources of assets, liabilities of the financial balance, short-term liabilities, current and long-term liabilities, passive management, liabilities of commercial banks and passive operations of the bank, the passive and structure of the enterprise liabilities
Deploy content
Passive is a definition
Passive isthe opposite asset is part accounting balance (right side), which reflects the sources of funds that are at the disposal of the enterprise grouped by their belonging and appointment, as well as the totality of all obligations (sources of formation of funds) of the enterprise, that is, giving revenue and providing liquidity with which it is allocated to who belong to funds and for what purpose they are intended and determined various payouts (interest on bonds, salary, tax payments, etc.).
Passive is material obligations Corporations to which various payments include (interest on bonds, salary, tax payments, etc.).
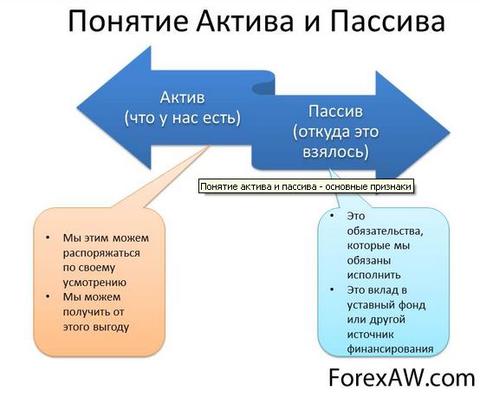
Passive - this ispart of the balance sheet, which reflects the sources of funds that are at the disposal of enterprises grouped by their accessories and appointment. Funds are grouped by articles based on management needs. So, it stands out to whom the funds belong and for what purpose they are intended.

Passive - this is The aggregate of the debts and obligations of the enterprise (as opposed to the asset).

Passive - this is Excess receipts.

Passive - this is The Party of Accounting Balance, which reveals the sources of funding for the funds forming, that is, giving revenue and providing liquidity.
Passive - this isthe opposite asset part of the balance sheet (right side) is a set of all obligations (sources of formation of funds).

Passive -this isthe combination of legal relations underlying the financing of the economic entity and include both borrowed and equity capital.

Passive isobligations (with the exception of subventions, subsidies, own funds and other sources) enterprises consisting of borrowed and attracted funds, including accounts payable.
Passive isthe combination of obligations involving the debt of the organization due to its economic activity, the calculations on which lead to the outflow of funds.
Passive issources of the formation of means of the enterprise, its financing, grouped by their affiliation and appointment (own and borrowed).
Passive iscoverages, constantly used in the economic turnover and therefore equal to their own funds, but not belonging to the enterprise: debt workers and employees wages, reserve of upcoming payments, formed to pay for vacations, etc.
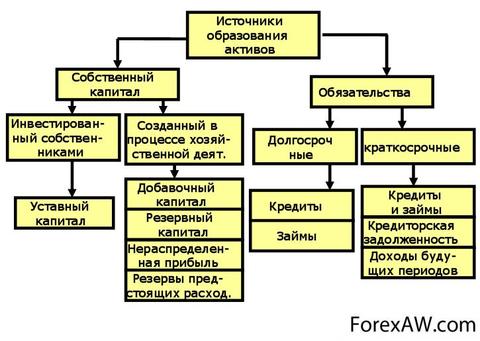
Passive isthe source of origin of assets reflecting whether the assets obtained by own capital Enterprises or due to the emergence of any obligations from the company.

Passive - this isexceeding the country's cash overall costs over its incomes received from abroad.
Passive - this isany obligation to third-party individuals and legal entities is a loan, a commitment to paying tax obligations etc.
Passive is The opposite asset part of the balance sheet (right side) is a set of all obligations (sources of formation of funds).
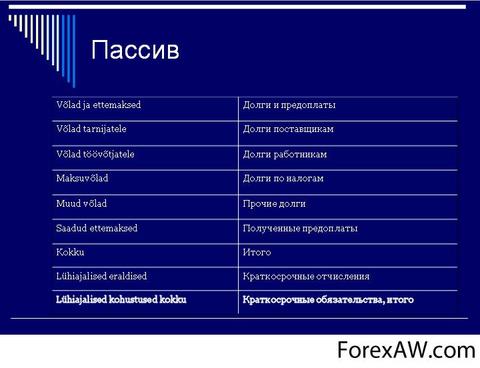
Passive balance - this is Part of the balance sheet (right side), denoting the sources of the formation of means of the enterprise, its financing, grouped according to their composition, belonging and appointment: own reserves, loans of other institutions, etc.
Liaughter and assets
Passive Bank is Reflected in the Balance Report All Exhibited Bank monetary requirementsexcept the requirements of its owners.

Passive enterprises - this sources of financing due to which it became possible to attract required values and funds.

Passive enterprises - this Obligations and sources of funds of the enterprise, consisting of their own, borrowed and attracted funds. Own funds of the enterprise with any form of ownership (except for state) consist of: authorized Fund; shares, share in economic societies and partnerships; Revenues from the sale of primary and additional issues of shares; accumulated unallocated profits (reserves); realized growth of the market value of securities; public fundswhich the company is endowed.
Passive Investment Fund is Short-term obligations of the Fund (payables, debt on deductions to the budget, extrabudgetary funds, etc.) and long term duties Fund (loans, borrowed and other attracted funds).

What is a passive?
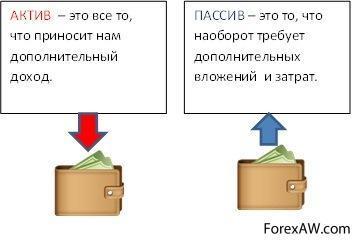
Passives are something that leads to the loss of our resources. Cash liabilities take money from us, that is, create a loss. Temporary liabilities will take time from us, and the power liabilities will take strength and the ability to work. It is very important to take into account the fact that the same things in different time Maybe liabilities and assets. Neparely? Let's deal with the examples!

Cash liabilities
Cash liabilities take money from us, that is, create a loss. For example, the car is definitely a passive. It must be purchased, spending money on gasoline and on maintenance. This is a cash passive. But if you have any goods on this machine, and get wages for this, which will exceed all expenses? It turns out that the car will generate income, which means it will turn into an asset! I think it is understandable. Also, the apartment is a passive: every month you need to pay communal payments etc. But if you rent an apartment for rent, and get rent, then the apartment turns into an asset bringing money income. I think everything is clear with monetary assets and liabilities. We now turn to temporary.

Temporary liabilities
Temporary liabilities take time from us. You came home after work, very tired. You sit down and watch TV. So here is one of the main temporary liabilities. He spends your time. Now let's imagine what you need to write some text. You can write on paper, but now the 21st century is still, so it will be easier to write text on the computer. Of course, it will be even faster on the computer. This means that the computer saves our time, therefore, it is a temporary asset in this situation.

Power liabilities
Power liabilities will take strength and the ability to work. Now consider last species Assets and liabilities, namely power assets. For example, sleep is a power asset. He fills our forces lost throughout the past day. Gym also is a power asset, since it increases our physical strength. But how to imagine power liabilities? Very simple. These are things and people who take physical strength with us, the charge of cheerfulness. It may be a job, and a person who was with you is impolite, and you don't want to do anything after communicating with him. Poor food, because of which you have an indentation of the stomach, is also a power liability!

You can see one feature. If you look at the side of philosophy to the question of assets and liabilities, it can be said that the work is a power liability, but at the same time it is monetary assetSince we get salary for work. And such ambiguous cases can still find a lot.
What is liabilities?
Currently, this approach is generally preserved, but the interpretation of the formula is given in the scene's spirit: assets are equal to the obligations plus capital. Under the influence of Western accountants, we ceased to interpret the capital as the debt of the organization of its owner.
And here there is a general wording: Passive is a list of legal and individualswhich owned assets.

Three important outputs flow from this definition:
Passive is a consequence of an asset, there is no asset - there will be no liability;
Passive can be called the distribution plan by owners of the property specified in the asset;
Grouping passive follows the principle of informability, it is best to start with the fact that it is subject to withdrawal last All.

True, it remains unclear how to interpret such an article as income of future periods?
In theory, and, as a result, in practice there are three interpretations of liability with a purely meaningful side.

Traditional interpretation of liability
This is a traditional understanding of the liability, which considers it as property at the disposal of the owner. This is due, as a rule, two approaches:
Passive is understood as a purely legal category;
As an assets distribution plan, and payables are already normalized by the increasing obligations, and its own means are normalized according to the established and specified limits.

The first option can be considered traditional for domestic accounting. It was divided by all the classics of our accounting department (N.S. Lunsky, A.P. Rudanovsky, N.A. Kiparisov, N.S. Pomazkov, etc.). The second option was developed by accountants, sought by taking into account accounting with Marxist political economy. In both options there are no problems in the interpretation of income of future periods. They are considered as a source of own funds.

New interpretation of liability
It arose relatively recently and serves as a bright proof of the priority of the content ( economic relations) Above the form ( legal relations). The essence of this approach can be expressed like this: Passive is the upcoming outflow of assets.

IN this case It doesn't matter who owns the rights to paid funds: it is only important to know the exact or probable payment schedule. Under this distribution of payments is understood as repayment of payables and the write-off of reserved funds. (Moreover, it is necessary to take into account the possible removal of funds by the owners.) From here, the revolutionary interpretation of accounts payable, under which it should now be understood not only obligations, that is, debts to legal entities and individuals, but also reserves that also suggest outflows in Starned time.
Compared to the options of the first interpretation in this case, we are confronted with a different understanding of the relationship between commitments and own funds, because the reserves are obviously own funds - are already interpreted as the means of incompatible, but the income of future periods is understood as well as at the first interpretation.
Schmalenbah Passion Interpretation
E. Schmalenbach (1873-1955), German accountant, determined the passive as:
Revenues that have not yet become expenses.

In fact, the owners have invested capital, that is, the company received revenue from his owner (at the beginning of the case, and during the work capitalized payables and their income).
The funds obtained must be investigated. This means that they should acquire equipment, materials, goods, etc. In order for these income of the enterprise to turn into its costs.

In this case, the entire passive can be understood as income or past and / or future periods. And by and large, the border between its own and attracted capital, in essence, will disappear.
The features of this interpretation is that its supporters interpret the liabilities as a cause, and asset as a result. For the first time, Russian Accountant L.I. drew attention to it. Gomberg (1866-1935). In fact, an understanding of what can be interpreted as a reason, and what, as a result, is very conditional. For example, the receipt of goods is reflected both by the asset and in the liability. It can be said that suppliers delivered goods (reason) and the enterprise has increased the commodity mass (consequence). But equal success can be argued that an increase carriage (reason) led to an increase in accounts payable (consequence). The theory is "what the clashes that breathe, where they turn, there and came out."

On passive accounts reflect the sources of formation of economic funds. The remains on these accounts show how and where these funds came from. Otherwise, the combination of sources of funding is called the obligations of the enterprise.

According to the definition, the obligation is the existing on certain date The debt of the organization, which arose as a consequence of accomplishment of economic operations, the repayment of which should lead to a decrease in the respective assets. It may be payment money, the transfer of other assets (provision of services), or replacing one type of obligation to others.
Authorized and share capital
Borrowed capital


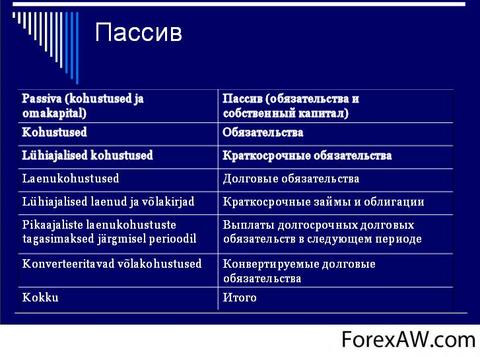
Short-term liabilities
Short-term liabilities (Credit Debt (before employees of the enterprise, landlords, founders, budget), short-term loans and loan obligations (payment for which it comes during the year), reserves of upcoming expenses).
Current liabilities
Current liabilities (current responsibility) Is short-term financial obligationsthat should be repaid during the year from the date of the accounting balance (or the current operating cycle of the enterprise, this time more). This definition It implies that current obligations are repaid by assets classified as current in the same balance sheet. The obligations of enterprises arise due to existing (due to past operations or events) of the enterprise debts, or regarding the transfer of certain assets or services to another enterprise in the future (prepaid).
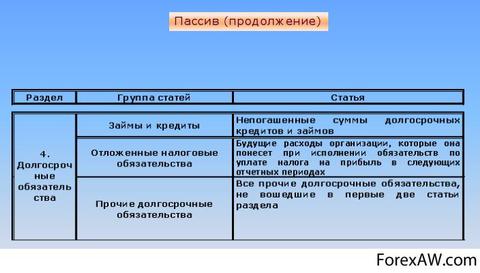
Long-term liabilities
Long-term liabilities (long-term loans and loans, deferred tax liabilities).
Theory and Practice of Liability
What is the theory, such is practicing. In the developed economy, accountants seek to embello on the balance, in undeveloped - accountants are privileged and most of all think how to hide, by different reasons, profit. In this regard, the principle of conservatism (the requirement of diligence) is very indicative, which involves the accuracy of assets and exaggeration of liabilities.

It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the theory of liability and practice of working with it, despite the confusion of terminology and many interpretations, however, quite simple compared to the understanding of the asset. It should be said to the accountant: if you understand well what an asset is (and it is very difficult to understand), then you can easily figure out what a passive is. Think about the asset, and the understanding of the liability will come by itself.
Passives - sources of assets
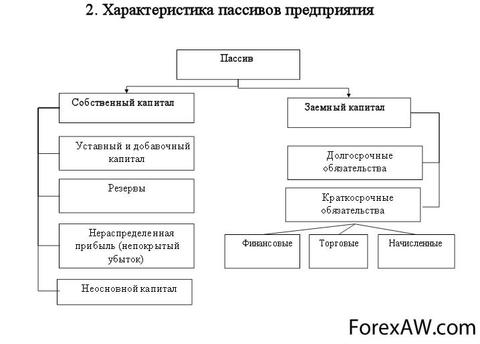
The composition of the liabilities contains its own capital - the authorized and equity, as well as the borrowed capital (loans, loans) grouped according to the composition and maturity. In passive indicated in the sum of the capital and the obligations of the organization.
Passives are sources of assets and consist of the following sections:
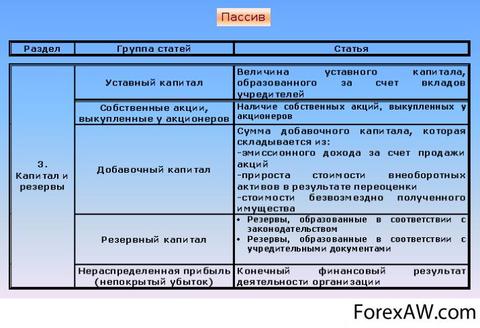
Authorized or equity capital;
Profit.
Authorized or equity
Authorized or equity capital is the so-called initial capital. Basically, this accumulation or relatives helped, here you have bought a furnace, containers, transport, initial flour, yeast. Can buy an office or took it for rent.

Accounts payable
Credit debt, these are your debts to someone. It happens its initial capital, you take a loan in the bank for the purchase of these furnaces, tanks, transport and something else. Also the bakery almost always happens for utilities, for water, e / energy, phone, if only because payments produce in until the 10th next month. Maybe they took flour, and some time did not pay. Those. What time do you use other people's funds.

Profit
Profit. Those. This is the profit you received as a result of your work. Revenues minus all your expenses and a profit remained. And you buy it an extra oven, more flour, i.e. expand their production.

Passive financial balance
In accordance with international standards financial accounting And reporting under liabilities is the sources of the facility of the enterprise. The balance sheet of the balance is reflected in the selection of sources of financing investment solutions of the enterprise, the result of which is the acquired assets.
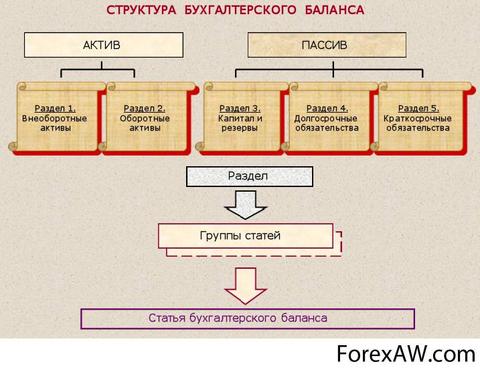
The main sections of the balan-sa liabilities are:
Equity;
Long-term accounts payable (long-term commitments, long-term borrowed capital);
Short-term payables (short-term obligations, short-term borrowed capital).

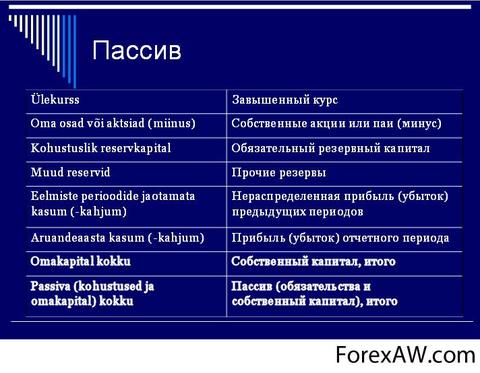
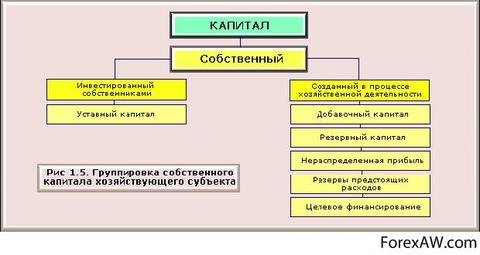
Equity
Section "Own Capital". As already mentioned above, in basic course financial Management The management of the company's funds of the joint stock formation will be considered. At the stage of creation joint-stock company Equipped capital is equal to share capital. Equity existing enterprise Includes many subsections.

Invested capital, including:
Share capital;
Extra capital;
Funds and reserves;

Share capital
Article "Share capital". Usually in balance reflect permanent share capital and the number of actually issued shares at the date of the balance of the balance (issued shares are their own shares in the portfolio). Shares are reflected in the balance sheet in accordance with their type in Articles: "Simple Shares" and "Preferred Shares".

Simple shares give their owners the right to vote at the resources of shareholders. According to ordinary shares, non-inflicted dividends are charged, the size and payment of which depend on the financial results of the enterprise. Privilege-based shares do not give their owners to vote at the meeting of shareholders. For preferred shares, fixed dividends are charged, the payment of which, in general, does not depend on the financial results of the enterprise.

Preferred shares can be cumulative and non-mulatory. Cumulation means the property of preserving dividen-dy. If in some year because of the difficult financial position of the enterprise dividends on simple and even privilege-based shares were not paid, the owners of cumulative shares will be able to receive them in subsequent periods. On the wrong shares, the dividends unpaid in the current period are not preserved in the current period.

The owners of preferred shares possess predominant right to receive dividends and return invested capital in the event of the liquidation of the enterprise. Shares have the nominal value, which is fixed in the balance sheet, and the course (market) cost.
What is the difference between ordinary shares from preferred shares
The article "Extension Capital" is formed by:
Emission income from the sale of a part of the shares at a price above nominal;
The increase in the cost of N. current assets (reassessment reserve);
Positive term difference By deposits foreign currency in authorized capital.

The article "Reserve Capital" includes various funds and reserves that are created in case of unforeseen expenses and are considered as a measure of a reasonable precaution. In the inspence of sources of formation and timing, the use of funds and reserves may be reflected both in the section "Own capital" and in the section "Leaving Capital".

There are two groups of reserves.
First Installation Group:
Reserves prescribed by law;
Voluntary reserves (formed in accordance with accounting documents).

The second group by nature:
Reserves having an additional capital;
Reserves intended to cover current or future losses or expenses;

Reserve dubious debt;
Reimbursement Funds (depreciation funds, etc.).

In the classification by nature, the first group of reserves is a reserve capital, the source of the formation of which is net income. The second group of reserves is an estimated reserve. The source of their form is gross profit. Estimated reserves Created to protect the enterprise from unstable situation and inflationary losses and are reflected in the reporting in the form of a ski-dock subject to deduction from the corresponding articles of the Ba Lans asset.

Undestributed profits
Article " Undestributed profits»Includes as nonprole-divided profits ( uncoated loss) past years and non-distributed profit (uncovered loss) of reporting rest.
The "Retained Profit" article records the accumulated profits, calculated in the accumulated profit report.

As part of the accumulated profit, a profit reserve may be allocated, which is formed by annual deductions from net profit As long as the reserve value does not reach a certain amount (25% of the cost of share-stock-LA). This reserve is not affected by the distribution of dividends, but can be used to maintain them at the proper level at loss years or addressed to share capital by the resolution of the Board of Directors.

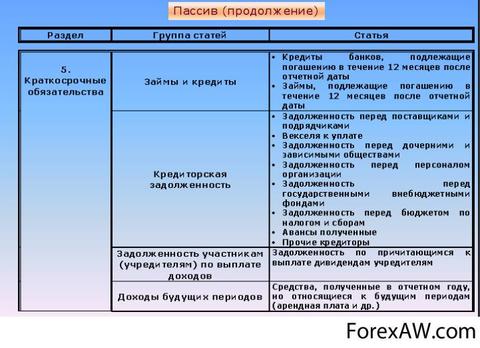
long term duties
The "Long-term liabilities" section includes the obligations that must be repaid during the term exceeding the year, including:
Long-term payables;
Long-term bonds;
Debt in pension payments.

Long-term loans
The Long-Term Credential article includes liabilities of long-term loans received by a pre-prunity. Part of the long-term accounts debt, which comes in the current period, is translated into the "Short-term obligations" section.

Bonds
The Bond article includes bonds issued in the tasks of attracting additional funds for the financing of the enterprise's activities. Bonds relate to debt securities And they personify the relationship of the loan. When buying a bond between the bonder (creditor) and the issuer's enterprise (borrower), a contract is drawn up, in accordance with which the issuer's enterprise undertakes to a set-up period (repayment period) to return the principal amount of debt and pay accrued interest. Bonds can be sold at par, with a premium (higher than the nominal) or discount (denied denominations). Both the premium and Dis-contacts, as well as the costs associated with the release of bonds (related to deferred expenditures), are gradually debited (amortized) during the term of loan treatment.

The issuer's enterprise on the basis of an agreement with bond-rum shall form a bond repayment fund due to periodic contributions from profits. Fund tools for the period before dogging, bonds can be invested in revenue securities. Control over the admission and consumption of funds of the Fund is carried out by bonds or a designated loan trust. The presence of the bond repayment fund causes greater pre-belief of investors to the issuer's securities.

Rent payments
The article "Rental payments" is recorded in the section of long-term liabilities if the company rents funds on the terms of long-term (capital) lease. Under the rental is understood as urgent and compensated possession and use of property based on the contract between the banner of the property - the landlord and the tenant.

Rent is recognized as long-term if at least one of the following conditions is satisfied:
The lease term covers 75% and more than the usefulness of the use of property;
Upon expiration of the leased, leased assets are transferred to the ownership of the tenant;

The tenant has the ability to resume it after the lease term expires minimum price (much lower middle-nights);
The discounted value of minimal rental plans is equal to or exceeds 90% of the current value of the property.

Funds leased on long-term lease conditions are recorded in the asset of Western balance as their own, which is manifested by one of the principles of incorporating data into report - the predominance of economic content over the legal norm. The balance of the balance sheet records the entire amount of rental payments, which the company must pay during the lease term.
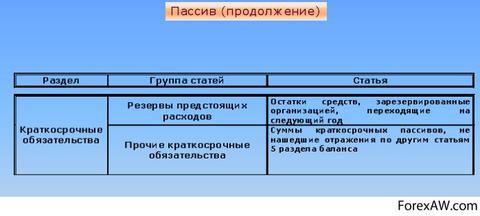
Reserves and Funds
Reserves and funds. As part of the section "Long-term obligations", due to deductions from profit before tax, funds and reserves that have the nature of debts may be created. They are from them: pension funds of enterprises; long-term depot - employees; Reserve for paying bonuses staff and so on. Debt on pension payments arises if the company has a pension fund. Source of form pension Fund Enterprises serve periodic contributions to the employer and employees. Fund funds are sent to pensions payments, disability benefits or in the event of the death of an employee. The presence of a pension fund at first glance is indicative of the stable financial position Enterprises. However, for the completeness of the picture it is necessary to find out how profi-naked pension obligations.

Articles "Long-term liabilities" and "short-term obligations" in the balance of the Western enterprise may arouse-notify entitled " external obligations" In accordance with international standards of financial accounting and reporting under external obligations, future losses in the economic benefits that may arise as a result existing obligations Enterprises transfer funds or provide services to other enterprises as a result of transactions or events incorrect.
Short-term liabilities
The "Short-term liabilities" section includes the obligations that are covered by turnover assets or ride as a result of the formation of new short-term obligations. The term of repayment of short-term liabilities does not exceed the year. Short-term commitments are fixed in the balance sheet or at the current price reflecting the future outflow of funds; Either at a price at the date of repayment of debt. At the same time, these estimates are significantly different from each other due to the short repayment period.
Accounts for payment
The article "Accounts for payment" includes liabilities, coming when buying goods or services under the terms of the commercial loan, i.e. With a delay of payment, as a rule, for a period of 30 to 60 days. At the same time, a commercial loan is made in publishing open account.

Bill of exchange for payment
The article "Waits for payment" includes bills for payment by trading operationswho are written obligatory enterprises to pay in a certain time goods or services purchased on conditions commercial loan.

Short-term debts
The article "Short-term debt testimonies" includes short-term debt evidence due to a pre-office of a cash loan by banks or other credit institutions. The amount of repayment of a short-term loan includes a nominal amount and accrued interest.

The short-term debt testimonies include a part of long-term liabilities, which comes in the period of the following cases:
If an enterprise implies to pay the appropriate debt at the expense of funds reflected in the composition of current assets;
If this debt should not be resumed;
If this debt is not expensive due to the release of new akmy;
If the enterprise has violated the terms of the contract for the provision of borrowed funds, which gives the right to the lender one to claim his money.
Tax debt
The article "Tax Debt" reflects the ownership of an enterprise before the budget.
![]()
Delayed taxes
The term "delayed taxes" includes accrued, but non-paid taxes. Deferred taxes are a kind of loan form, which the state provides enterprises.
Wage debt
The wage arreft article includes on-numerical, but not paid to employees wages.

Received advances
The article "The received advances" includes various advances received by the enterprise. Under advance is meant the amount of de-gentle funds issued to the upcoming payments for pre-delivered goods, work, service.
The article "Part of long-term liabilities" includes a part of the long-term obligations, which comes in the period of payment.

The article "Accumulated obligations" includes the obligations accrued in the reporting year, but not yet paid at the date of the balance sheet.

Unforeseen obligations
The "Unforeseen obligations" article includes the obligation of an enterprise that may arise in the future as a result of operations in the past. The reasons for possible losses must be disclosed in reporting notes. The inclusion in the balance sheet "Unforeseen obligations" is an expression of the principle of caution (diligence, conservatives), according to which, as mentioned above, the enterprise must take a greater potential loss than potential profits.

Passive management
To manage liabilities, it is advisable to use their classification to their own and borrowed capital, which corresponds to the classification of financing for internal and external:
Articles of equity - sources of internal financing;
Cross-capital articles - sources of external financing.

Internal financing (self-financing) is carried out at the expense of own funds of the enterprise in the following areas:
Self-financing to maintain production levels;
Self-financing in order to increase production.

Self-financing in order to maintain production levels is carried out at the expense of the depreciation fund. Self-financing in the proceedings of production is carried out by retained earnings and formed through its part of the funds and reserves.

External financing (external obligations) is carried out by attracting under conditions of urgency, payability, cash rotation of funds belonging to other business entities. Cash attracted in this way are called borrowed funds, or borrowed capital. Borrowed funds are fixed in the balance of the balance and predict the obligations of the enterprise. Building loan tools (obligations) to a certain level contributes to an increase in the profitability of own funds of the enterprise (effect financial lever).

Passive as an asset expression
"For an understanding of accounting," Cher says, it is extremely important to see in this opposition not just an obvious analytical equation, but to understand its deeper meaning; It is it that represents opposition, on the one hand, the exchange values, real, existing in a tactile form differentiated in economic and legal categories component parts all property property ( left-hand side equations) and, on the other hand, flowing from here abstract magnitude, capital owner this economy».

The fact that the passive is an abstract expression of an asset explains the objectivity of the equality A \u003d P. The expression in the monetary assessment is also justified by the fact that the passive represents only a certain expression of the asset. Capital (passive) as an expression of an asset must be evaluated according to the same exchange valueAs an asset at the date of the balance of the balance.

Any change to (algebraic amount) should proceed from change - increase or decrease - composite parts of property (items). Under the "K" here is understood as the amount of capital as an expression of an asset, that is, the magnitude of the balance of accounting balance in modern understanding;

No change to (amount) may not occur if the change in parts of the property consists only in moving values, that is, in a simple exchange transaction;
Any change in the value of the parts of the property, which is not compensated by another change, should cause a corresponding increase or decrease in (amount);
Both sides of the equation should always be in a state of equilibrium, balance.

These rules are essentially being the development of Pachet's postulates, give a completely new semantic load to the balance sheet equality. Balance equality here is objectively not because it leads to this accounting wiring Method double recordingBut because the passive is a certain expression of the capital's capital of the company submitted in the asset, and, therefore, repeat the assessment of the liability only reflects the assessment of the company's asset, its capital demonstrated in the balance sheet.
Assets and liabilities: Balance Balance
Balance equation
Balance equation (Balance Sheet Equation) - formula, in accordance with which the amount of assets of the corporation should exactly equal to the amount of liability (obligations and equity). Word Passive latin origin And literally means "suffering", which gives this word, in contrast to the word asset, some sad shade.

Formula expressing the equality of asset and liability. There are two main forms of recording of this equation:
Assets \u003d Attracted means + Own capital;
Own capital \u003d assets - attracted funds.

The first form is a look of a businessman at the enterprise (that is, assets are funded at the expense of own and attracted funds), the second is the replying of the owner, when the proportion of the owner is defined as an excess of assets over debt.

It is easiest to understand the creditor of the enterprise under the passive. And so accountants were interpreted for many centuries.
TO eND XIX. The century famous Swiss accountant I.F. Cher (1846-1924) expressed this understanding in the famous capital equation formula: that is, if from all the asset (a) deduct payable debt (P), then the value of the capital or the amount of the enterprise's own funds will be determined. So they understood the passive in all countries, and so before the beginning of the 20th century they interpreted it and in our country.

"For accounting, - revealed this approval of Cher, - has paramount importancethat is taken by the starting point - the balance equation (A \u003d P) or the capital equation (A - n \u003d K). Balance equation correspond to exterior form Accounting: Each debtor (Debet article) should resist the creditor (credit article). ... Capital equation (A - P \u003d K) expresses, on the contrary, the most essence of accounting; The algebraic amount of the components of the property (A - P) is equal to pure property (K); Here, thus, the calculated clean property, the concept of capital, is opposed to the decomposition of this abstraction on various articles of real, tangible components of the property. "

But at the very beginning now the last century is a wonderful Russian accountant, mathematician for education, N.S. Lunsky (1876-1956) introduced a completely different understanding of the liability. In the works of N.S. The term "sources" is found for the first time, while the majority of specialists under the balance sheet of balance understood only payables, and their own capital was determined by the settlement. N.S. Lunsky spread the concept of liability and equal capital. Such an understanding led to a new study of the debit and credit of accounts. The theory of Lunsky received wide use. He modified the Shar formula:

As a result, the balance equation was obtained, in the left part of which the property was presented, and its sources were provided. He called the whole right of the passive, because according to today current rule About the property isolation of the organization from its owners, what is called capital, there is nothing more than the payables of the organization of its owners. Consequently, the whole right of the balance equation is the essence of the essence of the liability in the broad sense of the word.

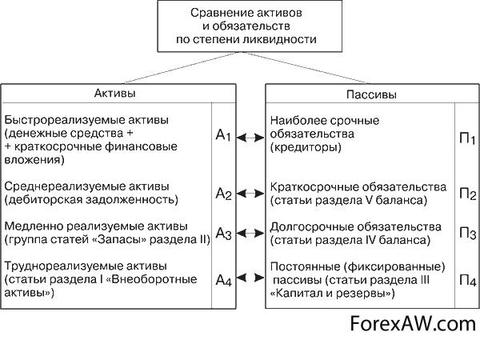
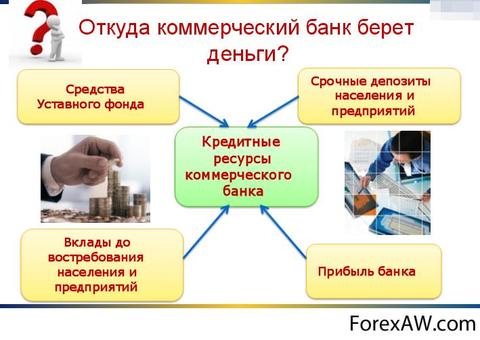
The liabilities of commercial banks are the direct opposite of assets - this is the obligations of the Bank to third parties. But do not be them, there would be no assets. Thus, it turns out that liabilities are sources, resources of own funds credit institution. They are also accepted to divide on species.

Types of bank liabilities
Liaughter of Russian commercial banks
Emissions of securities. Most often, large banks are joint-stock companies that produce their own shares. Thus, selling its securities on the stock market, the bank attracts additional working capital. He has an obligation to shareholders for the payment of shares, if the investor wants to sell its shares, but on the other hand he gets additional meanswhich can be used in turnover and achieve a certain profitability.

Deposit operations
Deposit operations. Everyone knows that commercial banks Through advertising and other funds, free cash of the population and legal entities are attracted. In this case, the funds attracted are also sent to the replenishment of assets to extract income.

Profit direction
The direction of profits received from the Bank's activities on the formation of reserves for impairment of securities or to cover possible losses. This value positively characterizes the activities of the bank. The greater the reserve fund, the more his year in the year, the more stable and more reliable than the bank. And this in turn affects investor solutions about the contribution of money in this bank.

Loans
Loans obtained from other commercial and state Structures. A huge part of these obligations is sent to the Bank's credit activities. After all, as a rule, this is the most profitable activity. And, as you know, money should work and generate income, as well as justify interest and other payments that are charged at a busy money bank.
Passive operations of banks
The definition of the bank as an institution that accumulates free cash and places them on the return OS-Nov, allows for passive and active operations in its activities.

Passive operations. With their help, the bank form their resources. Their essence is in attracting different species Intections, receiving loans from other banks, emissions of own securities, as well as other operations, resulting in bank resources.

Historically, passive operations played the primary and definition role in relation to active, as it is for the design of active operations prerequisite is the sufficiency of resources. Special form Bank resources are provided by the Bank's own funds (capital).

In the practice of Russian commercial banks to passive operations include:
Receiving deposits (deposits);
Discovery and maintenance of customer accounts, including corresponding banks;
Release of own securities (shares, bonds), financial instruments (bills, deposit and savings certificates);
Obtaining interbank loans, including centered credit resources.
Own capital, having a clearly pronounced legal OS-Novu and functional certainty, is financial Base Development of the Bank. It allows compensation to payments to depositors and creditors in the event of losses and bankruptcy bankruptcy, maintain the volume and types of operations in accordance with the tasks of the bank. As part of own funds of the Bank, there are: authorized, reserve and other special funds, as well as non-rapid profits during the year.
Statutory fund
The main element of the bank's own capital is the authorized capital. It is formed depending on the form of the Bank's organization. If the bank is created as a joint-stock company, its authorized capital is formed at the expense of shareholders' funds, which have written from the implementation of shares. Bank that is a society with limited liability, Forms the authorized fund due to the participants' contributions.
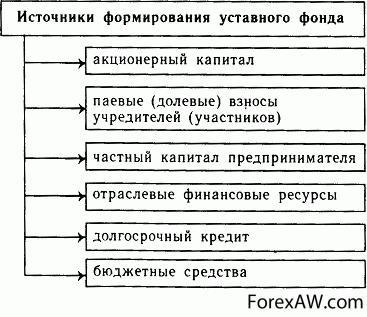
Regardless of the organizational and legal form of the Bank, its authorized capital is fully formed by the contributions of the participants (legal entities and individuals) and serves as ensuring their obligations.

The size of the authorized capital, the order of its formation and measurement is determined by the Bank's Charter. The amount of authorized capital is not legally limited, but to ensure the resilience of the bank Central Bank The Russian Federation establishes mini-large amount of authorized capital. An increase in the authorized capital can be carried out both at the expense of shareholders (shareholders) of the bank and its own funds (reserve and special funds, shareholders dividend shareholders, profits).

Reserve Fund
The reserve fund is designed to cover the possible loss of bank on the operations produced by them. The magnitude of it is set to attracts as a percentage of the statutory fund. The source of the formation of the reserve fund is deductions from profits. It is formed by the annual deductions in the amount of at least 5% of net profit until it is 25% of the validity of the authorized capital.

Special funds
Banks form other special funds: "wear of Os-new tools", "wear of low-value and spending items", formed by depreciation charges; Funds economic stimulationcreated from the profile. TO special Funds Bank also includes funds seized by him from the revaluation of fixed assets conducted by the re-evidence of the Russian government; Funds from the sale by the Bank of Akmy them to their first owners in excessive cost, etc.

Own capital as part of the Bank's resources is a small amount, as a rule, not more than 10%. At the same time, in banks of countries with developed market relations, the share of its own funds as part of the resources is higher and is determined by 15-20%, which makes it possible to ensure sufficient stability of the function-leveling of banks and their sustainability.
The main part of the resources of banks is formed by attracted funds that cover up to 90% of the entire need for monitoring agents for the implementation of active banking operations.
Commercial Bank It has the ability to attract funds of enterprises, organizations, institutions, publics and other banks in the form of deposits (deposits) and the opening of them of the corresponding accounts.
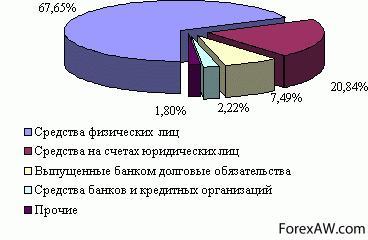
The passive operation of commercial banks is the half of the centralized credit resources. Credits of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation are provided to banks in re-financing and on competitive basis.

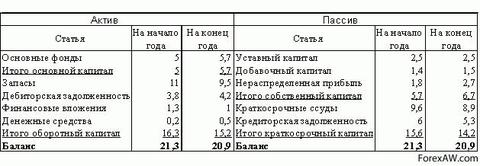
The information that is listed in the balance sheet allows you to determine which changes have occurred in the structure of own and borrowed capital, as attracted to the turnover of the enterprise of long-term and short-term funds, i.e., the passive shows where the funds aimed at the formation of the enterprise property came from.

The financial condition of the enterprise largely depends on what funds it has at their disposal and where they are invested. According to the degree of affiliation, the capital used is divided into its own and borrowed. Duration of use distinguish capital long-term (permanent) and short-term. The need for equity (liability) is due to the requirements of self-financing enterprises. Private capital is the basis of the independence and independence of the enterprise. However, it is necessary to take into account that the financing of the enterprise's activities only at the expense of own funds is not always beneficial for him. It should be borne in mind that if prices are financial resources low, and the enterprise can provide more high level Rotate for invested capital than paying credit resources, then attracting borrowed funds, it can increase the profitability of equity.

At the same time, if the funds of the enterprise are mainly created at the expense of short-term liabilities, its financial position will be unstable, since with the capital of short-term use is necessary operational workaimed at monitoring their timely return and on attraction to turnover dear time other capital.
Therefore, on how optimally the ratio of its own and borrowed capital, the financial position of the enterprise largely depends. The development of the right financial strategy is one of the main conditions for the effective activities of the enterprise.
In the analysis of sources of the formation of the enterprise, absolute and relative changes in their own and borrowed funds of the enterprise should be considered. In our case, the main source of the formation of the property of the enterprise is its own capital. At the beginning of the year, his share in the structure of liabilities was 98.39%. At the end of the reporting period, the share of equity in the structure of liabilities has slightly decreased (by 7.07%) and amounted to 91.32%. Such a structure of sources of property formation is a sign of high financial stability of the enterprise.
At the same time, it should be noted that the assessment of the changes occurring in the capital structure may be different from the standpoint of the investor and the enterprise. For banks and other investors more reliably, if the share of own capital from the client is higher. This eliminates the financial risk. Enterprises are usually interested in attracting borrowed funds. Having received borrowed funds under little percentagethan the economic profitability of the enterprise, it is possible to expand the production and increase the profitability of the company's own capital.

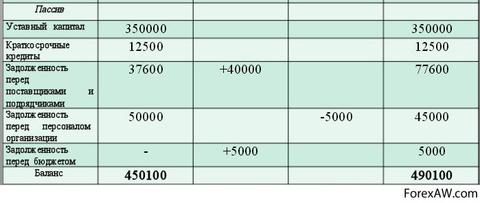
Building enterprise liabilities
We will analyze in more detail the structure of liabilities. The obligations of the enterprise, the term of the execution of which comes in the near future and those whose execution period will come in a year or later are unequal. For the enterprise is of fundamental importance, whether creditors will require debt credits now or this will happen, for example, in a year. Usually, large loans Enterprises take on long term. This can happen, for example, when buying expensive equipment. Then for the user financial statements It is fundamentally important to know whether these several million are current debt Or is it necessary to calculate it gradually?
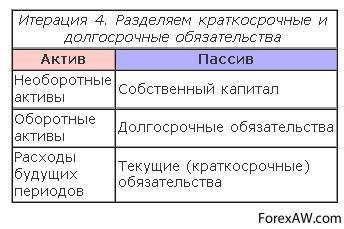
Thus, liabilities should be divided into "long-term liabilities" and "short-term obligations". Now the structure of our balance is much better reflecting the features financial state Enterprises. But still the structure of assets and liabilities is not fully complete.
![]()
It often happens that the company is at the same time the costs that, in fact, are not quite related to the current period. For example, vacation staff. The company carries the cost of paying the employee's leave once a year, but it would be more correct to say that every month an enterprise employee in general Gets the right for two days of paid vacation. This means that it is better to "postpone" in advance - reserve a certain amount and attribute it to the costs of the current period. We can say the same if the company is customary to pay the awards at the end of the year. Another one similar case There may be bank loans, bond loans and similar payments, if they, for example, are paid once a quarter or half a year.
If you keep records "for all the rules", then every month the company should reflect in account of a certain amount that shows that in the near future the deadline for the execution of the enterprise's obligations will come. And it is quite fair. For example, if you return for example with the same holidays, it is rightfully notice that the cause of expenses for vacation payments are just those months to which the employee is conscientious. Therefore, it would be logical to be included in the cost of the current period of payment of two days of the future vacation, at the same time reflecting this amount in obligations, because it will be paid when the employee takes a vacation. This is called the creation of obligations and payments.

Thus, in our balance sheet, another section should appear - "Providing future expenses and payments". Well, if we have "expenditures of future periods", there must be income of future periods. Therefore, the final balance structure should look like this:
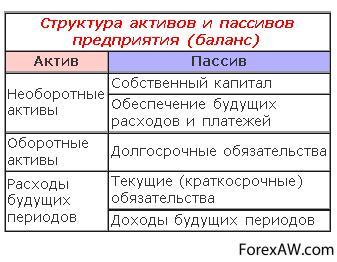
Thus, the structure of assets and liabilities of the enterprise contain three groups of assets and five groups of liabilities. The balance of the balance is a group of articles in the assets or liabilities of the balance grouped according to the principles of destination, urgency and turnover. Their grouping is subordinated to the tasks of controlling and analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise.

Balance article - a balance sheet, reflecting a specific date of the enterprise (in the asset) or types of sources of their formation (in passive), which contain residues (balance) of one or at the same time several accounting registers presented in as a synthetic value. Each indicator listed in the balance (Balance article) has a name that determines the object of accounting, a monetary assessment of the article (in a single monetary measurement actual cost).
For permanent systematic monitoring of the movement of each type of business and sources of their education, the account system uses. The billing value at the end of each reporting period is the source to fill the balance sheet items.
In the balance sheet for analyzing the financial condition and control of the economic activity of the enterprise (vertical) two rows of data are given: at the beginning of the reporting calendar year (in international financial statements at the beginning fiscal year) And at the end of the last reporting period. Balance currency is the amount of the balance sheets, and the amount of the asset's articles is equal to the sum of the liabilities.
![]()
Sources and links
Sources of texts, pictures and video
ru.wikipedia.org - resource with articles on many topics, free Wikipedia Exclopedia
aBC.INFORMBUREAU.COM - economic Dictionary Terms, events, facts and phenomena in modern Russia
youTube.com - YouTube, the largest video hosting in the world
slovarus.ru - Dictionaries Online Search Values \u200b\u200bin the most popular dictionaries
bE5.BIZ - Portal literature for students
bank24.ru - Vocabulary site economic terms
dictionary-EConomics.ru - informational portal All about economics
termin.bposd.ru - Site Free Dictionary of Terms, Concepts and Definitions for Economics
dic.academic.ru - site of dictionaries and encyclopedias at academician
profmeter.com.ua - information site all about the economy
al-Bout-investments.ru - information portal is all the most interesting in the world of finance and economy
finance-Place.ru - Information portal FININASY ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT
bUH.RU - Internet resource for accountants
buHarick.Ru - Industrial accounting dictionary of accounting dictionary
liga.net - information portal about everything LigabiSnesIneform
banki-delo.ru - Website banking about banks, credits, interest, about money and finance
time.Zp.ua - Information Site Asset Management
yourLib.net - Site Student Electronic online library
malb.ru - Economic portal Small business step by step
economix.in.ua - information portal economy and more
ref.rushkolnik.ru - Training portal of abstracts and practical tasks
ubizNes.ru - information and economic portal All about finance
fingramm.ru - Information portal Financial gramatic
bIBLIOTEKAR.RU - Electronic Library website
proect62.narod.ru - information and training portal for students
my-koshel.ru - My wallet information portal
avenue.siberia.net - Electronic Library Information Portal
studentu-vuza.ru - Educational and information portal by vessels of the university
works.doklad.ru - Information portal educational materials
muratOrdom.com.ua - Information Portal Best Homepage
azBukaucheta.com - Information Portal Alphabet Accounting
fINRUSSIA.RU - Information portal about financial services
aUP.RU - Administrative and management portal about the economy
studsell.com - Information Portal for Students
bibliofond.ru - digital library Bibliofond
knowledge.allbest.ru - information portal knowledge base ALLBEST
web-konspekt.ru - Information website Economy to help
scholar.su - all for literacy
50.Economicus.ru - Economic School Information Site
vocable.ru - National site economic Encyclopedia
myshared.ru - information site of various presentations
Links to Internet services
google.Ru is the largest search system in the world
video.Google.com - Video Search On the Internet through Google
translate.google.ru - translator from the search engine Google
yandex.ru - the largest search engine in Russia
wordStat.yandex.ru - Service from Yandex allows you to analyze search queries
video.yandex.ru - Search video online via Yandex
images.yandex.ru - Search for pictures through Yandex service
video.mail.Ru - Search video on the Internet via Mail.Ru
Links to Applied Programs
windows.microsoft.com - Microsoft Corporation site that created Windows WINTOVS
office.microsoft.com - Corporation Corporation Website Creating Microsoft Office
chrome.google.ru - frequently used browser to work with sites
hyperionics.com - Hypersnap Screen Snapshot Creators Website
getPaint.net - free software to work with images
Creator article
vk.com/id252261374 - VKontakte Profile
odnoklassniki.ru/profile/578898728470 - Profile in classmates
facebook.com/profile.php?id\u003d100008266479981 - Profile in Facebook
twitter.com/Beliann777 - Twitter Profile
plus.google.com/u/1/100804961242958260319/posts - profile for Google +
beliann777.ya.ru - profile on mi yandex ru
beliann777.livejournal.com - Live magazine blog
my.mail.ru/mail/Beliann777 - Blog on my world @ mail ru
liveinternet.ru/users/beliann777 - Blog on Laywinternet
beliann777.blogspot.com - blog on blogberg
linkedin.com/profile/view?id\u003d339656975&trk\u003dnav_responsive_tab_profile_pic - Profile in Linkdin
Introduction
Passive accounting balance
Methods of alternative and conjunctural estimates
Conclusion
Introduction
Information about economic operationsProduced economic subject per certain period Time is generalized in the relevant accounting registers and from them is transferred in a grouped form to accounting (financial) reporting. In system regulatory regulation Accounting Accounting is considered as a system of indicators reflecting the property and financial position of the Organization at the reporting date, as well as financial results Its activities during the reporting period. In turn, the reporting period is the period for which the organization should amount to accounting reporting.
Such a procedure for generalizing the accounting information is needed primarily to the enterprise itself and is associated with the need to clarify, and in some cases the correction of the further course of its financial and economic activities. Therefore, accounting reporting should identify any facts that the content of which can affect the assessment of user state information financial situation, profit and loss. Users of such information are managers, founders, participants and owners of the property of the enterprise. The content of the reporting on the activities of the enterprise, property And the degree of financial sustainability is of interest to potential investors interested in capital investment.
The value of reporting is in its authenticity, integrity, timeliness, simplicity, checkers, comparativeness, efficiency, compliance with strictly established procedures Registration and publicity.
this work Consists of two sections. The first is devoted to the balance of accounting balance. Its essence, sections for timing and regulation of liabilities.
In the second section, the methods of alternative and conjunctural estimates are considered, as well as the definitions of consolidated and consolidated reporting and the need for their use.
Course work was written on the basis of regulatory acts, publications in such magazines as " Chief Accountant"," Practical accounting<#"justify">1. Passive accounting balance
In modern financial and accounting literature and publications are given a large number of liabilities of the accounting balance. Let us dwell on some of them.
Pyats M.L. The article "The content of the accounting balance and the possibility of its analysis" characterizes the liabilities of the accounting balance in accordance with the principle of property isolation as "the Company's payables in front of its counterparties. Own sources of funds are the potential debt of the company in front of their shareholders (owners). Credit Debt is real debts Firms to their counterparties. "
Kondrakov N.P. It gives such a definition: "Passive is a system of indicators reflecting the composition of equity capital, enterprise commitments, as well as their special purpose».
We will focus on the following: "The balance of accounting balance is part of the accounting balance, reflecting the sources of education of the enterprise or institution and their appointment (own reserves, loans of other institutions)."
Since the 1930s, in Russian accounting is the expansion interpretation of the concept of "passive", according to which:
Passives \u003d Capital + payables. (1.1)
And as a consequence:
Assets \u003d liabilities.
Extended passion interpretation, including both borrowed and own sources of funds, Dana russian accountant N. S. Loonsky still at the beginning of the XX century. In his opinion, liabilities characterize the responsibility of the enterprise to primary investors (owners) and creditors, between which no principled difference. Both payables and equity capital has its own price of use. In the first case, it is interest on loans provided and loans, and in the second case - paid dividends to the owners of the enterprise.
In the British-American accounting, under liabilities, only a totality of debts and the obligations of the enterprise is understood, etc. Creditor debt. Thus, the capital of owners (capital) is not included in the liabilities of the enterprise.
And as a consequence:
Assets \u003d Capital + liabilities. (1.2)
Today theory and practice russian accounting oriented on the formula of the balance equation of the truth in the most reporting form No. 1 "Accounting Balance" The expansion name of the right side of "Passive" is maintained.
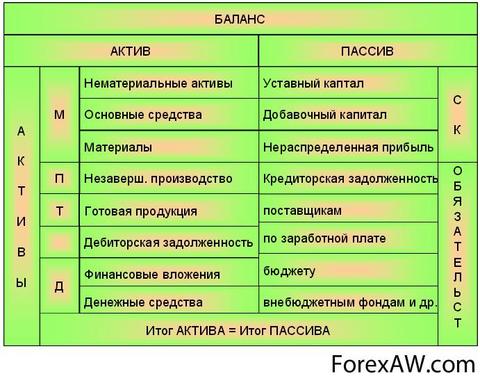
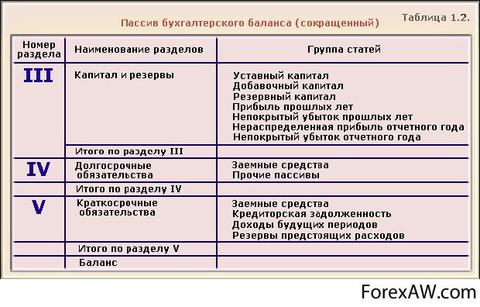
The balance of the balance (intermediate and annual) consists of three sections: III section "Capital and reserves", IV section "Long-term obligations", V section "Short-term obligations" (Table 1.1.)
Section III accounting Balance of "Capital and Reserves" forms information about the amount of equity equity
On line 410 of the balance sheet indicates the credit balance of account 80 "Authorized capital". It must comply with the size of the authorized capital recorded in the constituent documents of the organization.
Table 1.1 The main sections of the accounting balance liability
You can change the magnitude of the authorized capital (increase or decrease) only after making the appropriate amendments to the constituent documents of the organization. The authorized capital of the established joint-stock company (CJSC or JSC) is the sum of the nominal value of the shares of this society, distributed among its shareholders. Minimum size The authorized capital of the newly established CJSC should be at least 10,000 rubles at the date of registration. (100 Mrots), JSC at least 100,000 rubles. (1000 minimum wage).
The authorized capital of the Limited Liability Company (LLC) is the sum of the nominal value of the shares distributed among the participants of the Company. The minimum size of the authorized capital of the newly established LLC must be at least 10,000 rubles at the date of registration.
When creating a joint stock company, all shares must be posted among its founders.
The authorized capital of Ltd., specified in the constituent documents, by the time of registration of the Company should be paid for at least 50%, the authorized capital of JSC and CJSC in the amount of 50% within three months from the date of registration. The remaining part of the authorized capital is made during the year from the date of registration of the Company.
An additional line 411 "Own shares redeemed from shareholders was introduced into the balance sheet. It is filled, if the organization has reflected in the accounting of the organization on account 81 "Own stocks (shares)". The debit of this account reflects the redemption of shares (shares) from shareholders (participants) of society, and on the loan - their disposal (transfer, sale, cancellation). The balance sheet is reflected in the debit balance of the account 81. This is an active account, and when reflected in the balance sheet balance, it acquires the debit negative meaning. Therefore, in the balance sheet "Own shares, redeemed from shareholders" of the brackets, and when calculating the result of section III The amount on line 411 is deducted.
The line 420 reflects the value of the additional capital formed by: - \u200b\u200bthe emission income of the joint stock company, which is a positive difference between the sales and nominal value of shares, except for the cost of selling them; - Amount amounts non-current assets. The value of the extra capital of the organization is shown on the loan of account 83 "Extension Capital".
Row 430 reflects the amount of the reserve capital of the organization. In accordance with the Federal Law "On Joint-Stock Companies", they are obliged to create a reserve fund in the amount of 15% of the authorized capital, and produce annual deductions to it in the amount of 5 \\% of net profit. Such deductions are terminated when the reserve fund reaches the size provided for by the Charter. Other organizations also have the right to create reserve funds At the initiative of the owners of the organization, provided that the procedure for the formation of a reserve fund and its size is enshrined in the constituent documents of the organization. The amount of reserve capital is given on the loan of account 82 "Reserve Capital". Deciphering information on the organization's formed reserve capital is reflected in strings 431 and 432. On line 431 indicates the amount of mandatory reserve capital, formed by joint-stock companies - credit of account 82 subaccount "Reserve Fund formed in accordance with the law".
On line 432 reflected the amount of reserve capital formed in accordance with constituent documents Organizations - account credit 82 subaccount "Reserves formed in accordance with the constituent documents".
Row 450 "target financing and receipts" is intended to reflect information by non-profit and budget organizations Oh unused targets. entrance, membership, voluntary contributions etc. in non-Profit Organizations This information is submitted in the form of a loan balance of 86 "target financing".
The line 460 provides the amount of retained earnings of past years. This profit is a part of a net profit that was not distributed among shareholders (participants in the organization) and remained at the disposal of the enterprise. This line is filled with regard to consideration of the organization's activities for the reporting year, decisions taken On covering losses, payment of dividends. The retained earnings of past years is the loan balance of 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" subaccount "Retained earnings (uncovered loss) of past years." The line 465 reflects the amount of uncovered loss, which the organization received in the past years and has not yet extinguished. The amount for this line is shown taking into account the consideration of the activities of the organization for the reporting year and making a decision on covering losses. The amount of uncovered loss of past years is indicated in round brackets on the debit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss) subaccount" Retained earnings (uncovered loss) of past years. "
Row 470 is designed to reflect the unallocated profits of the reporting year, which is a loan balance in account 99 "Profit and losses".
Line 470 shows the amount of retained earnings or uncovered loss of the organization. Here reflects the entire amount of retained earnings (uncovered loss) of the organization, reflected in the form of balance on accounts 84 (in annual balance) or 99 (in intermediate balance). If the organization wants to separately show the amount of profit (loss), related to past periods and to the current year, it is entitled to introduce additional decoding lines to the balance sheet. The amount of the loss (debit balance in account 84) is reflected in line 470 in parentheses.
The indicator of retained earnings is formed after the Reformation of the balance for the reporting year, that is, an accountant at the end of the reporting year reveals the amount of retained earnings (uncovered loss) on account 99 and writes it to the account 84. At the same time, the amount of retained earnings of the reporting year is added to the amount of the account balance 84, reflecting the retained earnings of past years. Retained earnings of past years reflects both really not used profits and served financial support for investment activity Organizations. The return direction for investment goals is reflected in the internal records on account 84. At the same time, analytical accounting on this account should be organized in such a way that the used and unused part of the net profit can be tracked.
On line 475, the information of the organization with the results of work in the reporting period is submitted, which is shown in parentheses and is a debit balance on account 99 "Profit and losses". Line 490 is reflected total amount Own capital of the Organization, which is the amount of strings of 410 "authorized capital", 420 "Additional capital", 430 "Reserve capital", 450 "Targeted financing and receipts", 460 "Retained earnings of past years", 470 "Retained reporting year earnings" Defining amounts on strings 465 "uncovered loss of past years" and 475 "uncovered loss of the reporting period."
In order to determine the outcome of the "Capital and Reserves" section, from the amount of indicators of all lines it is necessary to subtract the cost of own shares bought from shareholders (line 411), and uncovered loss of the reporting year (line 470).
Section IV. "Long term duties"
Long-term liabilities include loans and loans received by the Organization for a period exceeding 12 months. In accordance with the Regulations on accounting and accounting reporting In the Russian Federation, the amounts of interest due at the end of the reporting period are included in the amount of loans and loans reflected in the "Long-term obligations" section.
The line 510 shows borrowed funds, the debt on which the organization should pay more than 12 months, starting from the first day of the month following the month of receiving a loan or loan.
On line 511 and 512, there is a decoding of enterprise borrowed funds.
On line 511 reflects information on long-term loans to the organization bank or other credit institution in monetary form Based on concluded in writing. The amount of the Bank's long-term loan is shown by the organization on credit account 67 "Calculations on long-term loans and loans" subaccount "Calculations on long-term loans".
The line 512 provides information on long-term loans of the organization, which can be expressed both in cash and in real form. The loan agreement is determined by the agreement between the lender and the borrower and comes into force from the moment of transferring money or things. Parties to a loan agreement can be any faces. The amount of long-term loan is given by the Credit Credit Credit 67 "Calculations on Long-Term Loans and Loans" subaccount "Calculations on long-term loans".
Row 520 "Other long-term liabilities" is designed to reflect the amount of attracted long-term liabilities Organizations that were not reflected in line 510.
On line 590, the total amount of the long-term commitments of the organization, which consists of the amount of strings 510 "loans and loans" and 520 "Other long-term liabilities" are reflected.
Section V. "Short-term obligations" in the section "Short-term obligations" The organization shows outstanding loans and loans that were taken for a period of less than 12 months. In addition, in this section, the debt that was considered long-term in previous reporting periods can be reflected, i.e. That debt, which is translated into short-term and is repayable in the reporting year.
Row 610 are given general About short-term loans and loans that are decoded in strings 611 and 612.
On line 611 indicates the sum of short-term loans of banks obtained by the organization, taking into account accrued and unpaid interest, which is reflected in the balance sheet as a loan balance of 66 "Calculations on short-term loans and loans "subaccount" Calculations for short-term loans. "
Line 612 reflects the sums of short-term loans issued by the organization, taking into account accrued and unpaid interest on these loans. These data are credit balance on account 66 "Calculations on short-term loans and loans" subaccount "Calculations for short-term loans».
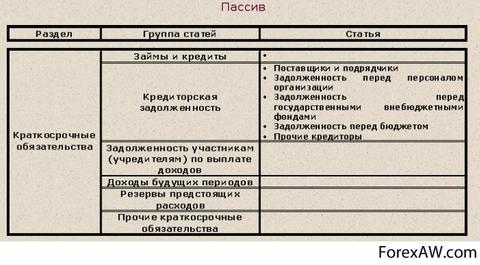
On line 620 "Accounts' debt" shows the total amount of the accounts of the organization, which is specified by strings 621-628.
Line 621 shows the debt of the organization before suppliers and contractors for the values \u200b\u200breceived, the work provided, the services rendered. The amount of debt of the organization to suppliers and contractors is the amount of loan balance on accounts 60 "Calculations with suppliers and contractors" subaccount "Debt to suppliers" and accounts 76 "Calculations with different debtors and creditors "subaccount" Calculations with suppliers and contractors ".
The line 622 reflects the sum of the entire accounts debt of the organization, decorated with simple and translation promissory notes. The amount of debt is defined as the amount of credit balance on accounts 60 "Calculations with suppliers and contractors" subaccount "bill issued" and accounts 76 "Calculations with different debtors and creditors" subaccount "bill of payment".
Row 623 reflects the amount of debt to the subsidiaries and dependent societieswhich is a credit balance on account 76 "Calculations with different debtors and creditors" subaccount "Calculations with subsidiaries and dependent societies".
The line 624 reflects the amount of accrued, but not paid wages to employees of the organization, which is a credit balance of account 70 "Calculations with staff for paying for labor."
On line 625 reflects the amount of the debt of the organization for a single social tax, mandatory pension insurance and insurance against accidents at work and professional diseaseswhich is a loan balance in account 69 "Calculations for social Insurance and provision. "
The line 626 reflects the amount of the debt of the organization before the budget for taxes and fees, i.e. Credit balance on account 68 "Calculations for taxes and fees" per minus amounts on subaccounts "" Debt tax authorities, the repayment of which is expected after 12 months "and" the debt of tax authorities whose repayment is expected within 12 months. "
According to the line 627, information is given on the amount of advances received by the organization for the forthcoming supplies of products (performed works rendered), which is a credit balance of account 62 "Calculations with suppliers and contractors" subaccount "Advances received".
The 628 line reflects information on the accounts of the organization's accounts for those calculations that were not considered in lines 621-627. In particular, information on debt to reporting persons, deposited wages, on property and personal insurance of workers, etc. The amount of payables reflected in the "Other creditors" line will be the amount of credit balance on accounts 71 "settlements with accountable persons" , 76 "Calculations with different debtors and creditors" subaccount: "Calculations for depositated amounts", "Calculations on property and personal insurance", "Calculations for claims", etc.
Row of 630 "Debt participants (founders) for income payments" reflects the debt of the organization to the founders on dividends and interest, which are accrued, but are not paid. Debt is shown on credit account 75 "Calculations with the founders" subaccount "Calculations for income payment".
On line 640 "Revenues of future periods" is given the amount of the income of the organization, which were obtained in the reporting period, but relate to the future. These income includes, for example, the receipt of rent for several months ahead, targeted budget arrivals Commercial organizations, etc., the amount specified on line 640 is a loan balance on account 98 "Incomes of future periods".
The line 650 "reserves of the upcoming expenses" reflects the amounts reserved by the organization to cover their future costs, which are a loan balance of 96 "reserves of upcoming expenses".
The line 660 provides information on the sum of short-term liabilities, which cannot be attributed to other articles section "Short-term obligations".
The line 690 provides the final amount of short-term liabilities, which is the amount of strings 610 "Loans and Credits", 620 "Credit Debt", 630 "Debt participants (founders) for the payment of income" 640 "Incomes of future periods" 650 "Reserves of upcoming expenses" and 660 "Other short-term commitments."
On line 700 "Balance" reflects the sum of the strings 490 "Total according to section III", 590 "Total according to section IV" and 690 "Total according to section V", i.e. The balance of the liabilities of the balance is formed. In accordance with Methodical instructions On the procedure for the formation of indicators of the accounting reporting of the organization, information on the availability of values \u200b\u200btaken into account on the off-balance accounts, i.e. On values \u200b\u200bthat do not belong to this organization.
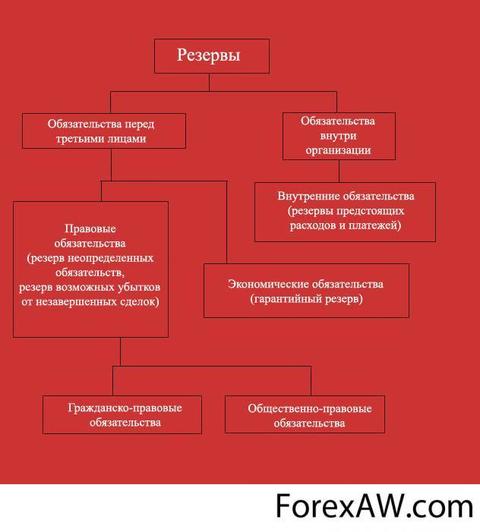
Regulation of accounting liabilities is made by forming various types of reserves. The category "Reserve" arose as a consequence of diligence in assessing assets and liabilities. According to IFRS 37 "Reserves, conditional obligations and conditional assets", the reserve is a commitment to an indefinite amount and with indefinitely repayment. This definition applies only to those reserves that are obligations. At the same time exist the following conditions Reserve recognition:
· the company has a current legal or actual obligation to transfer economic benefits that arose in connection with the past events;
· it is likely that the repayment of obligations will lead to an outflow of resources entering into economic benefit;
· the amount of obligation can be reliably appreciated.
There is no Russian accounting separate position, regulating the concept and conditions for recognizing reserves. Position on accounting and accounting reporting in Russian Federation Determines the types of use of funds and the order of reflection in the balance sheet of the organization's reserves.
The reserve fund is designed to cover the losses of the organization, as well as the repayment of bonds and redemption of their own shares. In addition, in joint-stock companies, the creation of reserve funds avoids the payment of unnecessary, according to the administration, dividends to third-party shareholders. Organizations can create reserves of dubious debts and reserves for the upcoming payment of various types of expenses of the organization in order to uniformly incorporate future costs in the costs of production and circulation. Creating a system of organization reserves allows:
· form your own sources of financing for expanded reproduction;
· maintain the capital of shareholders and owners;
· guarantee social defense employees In the organisation;
· provide financial sustainability organizations;
· to adjust the balance sheet articles based on the principle of caution in the assessment;
· it is evenly included in the cost of production, works, services.
balance conjunctural assessment
2. Methods of alternative and conjunctural estimates
To consider the methodology for alternative and conjunctural assessments of investments, it is necessary to first consider the basic concepts of investments and reflections in the reporting.
In accordance with IFRS No. 27 "Consolidated financial statements and accounting of investments in subsidiaries" Consolidated financial reports These are financial reports of the group (head company and all its subsidiaries), presented as the reporting of one company.
Russian definition A subsidiary is similar to the definition of IFRS. Questions of compilation consolidated reporting In the Russian Federation, the Law of the Russian Federation "On Financial and Industrial Groups" of November 20, 1995 No. 190-FZ, in which financial and industrial groups (FIGs) are defined as a set of legal entities acting as the main and subsidiaries, or partially united their material and intangible assets (participation system) on the basis of the contract for the creation of the FPG.
Among the participants of the FIGs, it is necessary to have organizations operating in the field of production of goods and services, banks or other credit organizations. Investment institutions, non-state retirement and other funds can be included in the FPG participants. insurance organizationswhose participation is due to their role in ensuring the investment process in FIG. Central Company FIG is a legal entity approved by all participants in the Treaty on the establishment of FIGs or the main, in relation to the Participants of the Treaty, the Company authorized (by law or the Agreement) for the maintenance of FIG. Central Company in accordance with the Law and Treaty on the Creation of FIGs:
he speaks of the name of the FPG participants in relations related to the creation and activities of the FPG;
conducts consolidated (consolidated) accounting, reporting and balance of FPG;
prepares an annual report on the activities of the FIG.
The procedure for conducting consolidated (consolidated) accounting, reporting and balance sheet of the FPG was regulated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 9, 1997 No. 24.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation issued an order "about methodical recommendations On the preparation and presentation of consolidated accounting reporting "from 30.12.96 No. 112 (as amended from 12.05.99 No. 36N).
The parent company is a company having one or more of subsidiaries.
A subsidiary is an enterprise under the control of the parent company.
Group - Mother's company and subsidiaries.
In accordance with Civil Code RF (GK) is a subsidiary, if the main economical society due to the prevailing participation in authorized capitalor in accordance with the contract concluded between them, or otherwise it has the ability to determine decisions taken by such a society.
A subsidiary is not responsible for the debts of the main society (partnership).
The main society, which has the right to give subsidiary to the Society for him, is responsible to agree with the subsidiary of transactions concluded by them in fulfillment of such instructions (summary reporting - if more than 50% of the voting shares (CC) of JSC or 000).
In accordance with the GC, the economic company is addicted, which is recognized as such, if another (the prevailing, participating) society has more than 20% of the voting shares of JSC or 20% of the authorized capital 000.
A group of persons is a combination of legal or legal entities and individuals, in relation to which one or more conditions are performed: - A person or several persons together as a result of the agreement have the right to directly or indirectly dispose of more than 50% total Votes occurring on shares constituting authorized capital legal entity.
Under indirect order it is understood as the possibility of actual disposal through third parties, in relation to which the first person has the above right or authority;
between two or more persons, a contract was concluded by the right to determine the terms of reference business activities one or more participants in the contract or other persons or to implement them executive organ;
the person has the right to appoint more than 50% of the executive body and the Board of Directors of the legal entity;
the same individuals represent more than 50% of the executive body or the board of directors of two or more legal entities.
Direct control is interpreted as an opportunity for a legal or an individual to determine decisions taken by a legal entity through one or more action. Indirect control is considered as an opportunity for a legal or an individual to determine decisions taken by a legal entity through third parties, in relation to which the first possesses one or more rights or powers.
Consolidated and consolidated statements differ in purpose, the technique of drawing up, the circle of users.
Consolidated reports Compiled:
When forming a summary reporting federal ministries and others federal bodies In accordance with the procedure for drawing up and submitting a consolidated annual accounting reporting by federal ministries and other federal authorities of the Russian Executive Authority. Consolidated annual accounting reporting is represented by the Ministry of Finance of Russia, the Ministry of Economy of Russia and the State Statistics Committee of Russia.
In the preparation of reporting within one legal entity on the basis of the reporting data of its divisions and branches allocated for a separate balance, but not independent legal entities.
If you have the organization of dependent subsidiaries. In all other cases, the group of interrelated enterprises includes consolidated reporting.
The purpose of the consolidated accounting reporting is to show investors and others. stakeholders The results of the financial and economic activities of the group of interrelated enterprises, legally independent, but in fact that are a single economic organism.
The main feature of the compilation of consolidated reports is elimination (exception) individual indicators enterprises included in the group in order to exclude a re-invoice in the final (consolidated) report of the Group. That is, consolidated reporting is compiled by several owners (legal entities) on jointly controlled property.
The consolidated statement is drawn up within one owner or for static generalization.
Consolidated accounting reporting has next composition:
Accounting Balance - Form No. 1;
Profit and Loss Statement - Form No. 2;
Report on Capital Changes - Form No. 3;
Report on cash flow - Form No. 4.
Consolidated statements in accordance with the 4th and 7th directives European Union Includes consolidated balance sheet, profit and loss statement, report on cash flow, notes to them, conclusion of the auditor.
The need for consolidated reporting occurs whenever a corporate family (group) is formed, i.e. There is a fusion of capital. The reasons for the merger can be different, in particular, they can be determined by the needs or desire to expand the area of \u200b\u200bthe application of capital, access new technologies, reduce the timing of the search for new product sales markets, attract experienced management workers to the company. The merger of firms is the usual phenomenon in any type of economy.
Preparation of consolidated financial statements causes the practical interest of accountants and financial professionals in large quantities cases in the presence of conducting business Several companies, and sometimes several formations at the level of individuals. Existing norms Accounting and financial statements often do not suggest broad deviations from the principle of consolidation of "exclusively legal entities". Thus, accounting standards Actually rely on legal content Relations, that is, for the presence of a legally allocated enterprise, a company, in general, a legal entity, on the economic content - business at the level of both legal and individuals.
International Standards The financial statements that are currently harmonized both by the US GAAP and Russian accounting provisions (PBUs), contain a system of recognized requirements and recommendations for the preparation of consolidated financial statements.
By purchasing a part of the share capital of any company, the investor at the same time receives the right to influence its degree or economic policies. The degree of this influence, depending on a number of factors, determines the methods of accounting and reflection in the reporting of the investment made. In most economically developed countries, the following gradation was adopted by the degree of influence of the investor company (MD to another (company E) when investing in share capital:
but) M does not affect economic and financial
policy D., the formal criterion of this - the share of M in the share capital d does not exceed 20%; b) M has a significant impact on the economic and
financial policy D, formal criterion of this - share M
share capital D ranges from 20 to 50%; in) M fully controls the activity of D., formal
the criterion of this - M owns more than 50% of the shares of D. IN last case Both companies form a corporate group, while the company M is called the maternal, and D - subsidiary. In each of these cases, the value of the investment is determined at the date of the transaction in the amount of total expenses ID Acquisition shares. However, further investment in equity and income from them are recorded in the accounting and reporting of the company M in different ways: (a) Investments are constantly reflected in the reporting minimizing the costs or current assessment on the date of the balance sheet; Profit from investments in the amount of dividend received is provided in the income statement (alternative assessment methodology);
b) initially, investments are recorded in the amount of costs, but in the future their value is periodically adjusted to the relevant share of profit (loss) declared by the company D minus the dividends received; owned by the investor share announced by the company d profits (loss) in full (obtained dividends plus reinvested in the company l profits) is reflected in the report on financial results (conjunctural assessment method);
in) consolidated reporting is drawn up.
Differences between the first two methods of accounting for investment in share capital Consider on the example (Table 2.1)
Table 2.1 Comparison of alternative and conjunctural assessments
The method of alternative estimates of the conjunctural assessment company M acquired on January 11, 2007 34 of the stocks of the nominal ($ 10 per share). What is 20% of the total share capital of the company D. Accounting records will be viewed: D-TSC. "Long-term financial investments In the company d »340000 K-TLC. "Cashier" 340 000D-TSC. "Long-term financial investments in the company d" 340000 K-TLC. CASSA 340 000 November 2007 Company D Company announced a profit in the amount of "$ 150,000 (the share of the company M will be I50 LLC * 20% \u003d 30 dollars LLC). The following accounting records will be made: not composed by TSH .." Long-term 30OOO Financial investments in the company D "Ktr." Investment revenues 30 00015 January 2008. The company D announced and paid devuses in the amount of 70 dollars LLC (the company's share was $ 14,000, respectively). Accounting records will be -The. "Cashier" 14,000 kt sch. "Investment revenues" 14000D-TLC. "CASSA" 14 000 K-T SC "Long-term financial investments in the company D" 14000ZA 2003. The company D announced a loss of $ 40,000 . (The share of the company M was $ 8,000, respectively.). Building will be viewed: not composed by TSH. "Losses from investment activities" 8000 K-TLC. "Long-term financial investments in the company D" 8000
Thus, according to the second methodology, the company's profit and loss statement reflects the entire proportion of net profit, the value of investments in the balance sheet increases only on some of this profits, namely, the value of reinvested profits.
The difference between the two methods is very sensible. Thus, the use of the second method can lead to an increase in taxable profits on a very impressive amount.
Conclusion
In conditions market economy The importance of accounting (financial) reporting is increasing, as one of the main sources of information about the property and financial position of the Organization, as well as the results of its activities. To ensure completeness of information on the financial situation of business entities, there is a need to study the principles of building financial statements, its species, models of building and evaluating articles of accounting balance, as well as accounting for many other aspects that determine the content of financial statements.
In this term paper Two questions were considered from the course of "Accounting Financial Reporting".
The first section gives the definition of a liability of the accounting balance.
The balance of accounting balance is part of the accounting balance, reflecting the sources of education of the enterprise or institution and their appointment (own reserves, loans of other institutions).
The balance of the balance (intermediate and annual) consists of three sections: III section "Capital and reserves", IV section "Long-term liabilities", V section "Short-term obligations".
The second examines the methods of alternative and conjunctural estimates.
The value of the investment is determined at the date of the transaction in the amount of general expenses of the acquisition of shares. However, in the future investment in share capital and revenues from them are recorded in the accounting and reporting of the company in different ways:
(a) Investments are constantly reflected in the reporting minimizing the costs or current assessment on the date of the balance sheet; Profit from investments in the amount of dividend received is provided in the income statement (alternative assessment methodology);
b) Initially, investments are recorded in the amount of costs, but in the future their value is periodically adjusted to the relevant share of profit (loss) declared by the company for the disadvantaged dividends received; The share owned by the Investor announced by the profit (loss) in full (dividends received plus reinvested in profit) is reflected in the report on financial results (conjunctural assessment methodology).
List of sources used
1.Civil Code of the Russian Federation, from 30.11.1994 N 51-FZ.
2.RF Law No. 190-FZ "On Financial and Industrial Groups" of November 20, 1995. "
.Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 9, 1997 No. 24. On the procedure for maintaining consolidated (consolidated) accounting, reporting and balance of the financial and industrial group.
.Akoteva MD, Malshakova I.L. Accounting theory: Tutorial. M.: IPK MGUP, 2002.
.Antill N., Lee K. Rating companies. Analysis and forecasting using IFRS reporting. from English M.: Alpina Business Buks, 2007.
.Bakhrushina MA International Financial Reporting Standards: Proc. For universities. M.: Omega-L, 2007.
.Galkina E. V. Economic content Methods of consolidation of financial statements in accordance with IFRS No. 11, 2010.
9.Zabbarova
Kovalev V.V. Potras V.V., Bykov V.A. how to read the balance. 5th ed., Pererab. and add. - M.: Finance and Statistics, 2006
Kondrakov N.P. Accounting. - M.: Infra-M, 2007
Leschinskaya N.V. Accounting (Financial) Reporting M.: Publisher "Perspective". 2003.
Moders S. Modern views On the consolidation of financial statements // Practical accounting
Tumasyan R.Z. Accounting.3-E publication. M.: LLC "Nitar Alliance". 2009
Yastrebkova E. Consolidation of reporting when used in the production of assets purchased within the group. // IFRS: Practice of application. №7, 2008.
Order work
Our experts will help to write work with mandatory verification On uniqueness in the Antiplagiat system
Send a request With the requirements right now, to find out the cost and possibility of writing.
Liaughter organizations are sources of formation of its assets. These include capital, reserves, as well as payables arising from the organization in the process of conducting economic activities.
The balance sheet consists of three sections:
section. III "Capital and reserves";
section. IV "long-term commitments";
section. V "Short-term obligations."
Consider in detail what indicators are reflected in each of these sections.
\u003e Section III "Capital and Reserves"
In this section of the balance, the magnitude of the equity of the organization is reflected. This is authorized, additional and reserve capital, retained earnings and other capitalized reserves.
Row 410 "Authorized capital"
This line reflects the account balance 80 "authorized capital". For joint stock companies and limited liability companies, this is the magnitude of the authorized capital for unitary enterprises - the value of the authorized capital, for full partnerships and partnerships on faith - the magnitude of the share capital, for production cooperatives - unit trust.
The amount in the balance line 410 should correspond to the size of the authorized capital, recorded in the constituent documents.
The size of the authorized capital of the joint stock company may change in the following cases:
With additional issuance of shares;
With increasing the nominal value of shares;
With a decrease in the number of shares;
With a decrease in the nominal shares;
If at the end of the second and each subsequent fiscal year the cost pure assets Societies are less than the authorized capital.
The size of the authorized capital of a limited liability company may change if:
The participants of the Company decided to increase or decrease the authorized capital;
Appeared new participant and made an additional contribution;
One of the participants decided to leaving society. But in case its share, the remaining participants or a third party will buy, the size of the authorized capital does not change;
If within two or more years, the cost of net assets of the Company for the results of the fiscal year is less than authorized capital.
An increase or decrease in the authorized capital is reflected in accounting only after registering relevant changes in constituent documents.
Row 411 "Own shares redeemed from shareholders"
This line reflects the debit balance of account 81 "Own shares (shares)" - the balance of shares (shares) of the organization that it bought from shareholders (participants) for subsequent resale or cancellation.
Before the entry into force of PBU 19/02 (until 2003), the cost of such shares (fractions) was reflected in the balance sheet 250 "short-term financial investments". But p. 3 PBU 19/02 It was found that these assets do not belong to financial investments.
The account 81 is active, but the balance form recommended by the Ministry of Finance of Russia prescribes to reflect the balance on it in the balance sheet. Therefore, the value reflected in line 411 is negative and indicated in parentheses. Thus, this indicator leads to a decrease in the magnitude of the equity of the organization.
Row 420 "Extension Capital"
This line reflects the credit balance of the account 83 "Extension Capital". The account 83 takes into account:
Exchange differences that arise in case contributions to the authorized capital are paid in foreign currency;
Em session income occurs if sales value posted shares exceeded their nominal value (minus sell-related costs);
Amount of completion of fixed assets and other non-current assets.
The amounts of additional capital, accountable on account 83, are usually not written off, with the exception of cases:
When redeeming the amounts of grades of fixed assets due to the amounts of their completion, previously taken into account on account 83;
When sending additional capital amounts to increasing the authorized capital;
When sending additional capital amounts to cover losses of the organization;
When distributing additional capital between the founders.
Rows 430, 431 and 432 "Reserve Capital"
This line reflects the loan balance of 82 "Reserve Capital". This account forms a reserve fund and other similar funds, which are created by distributing part of the profit. They are intended to cover losses, repayment of the bonds of the organization, redemption of their own shares (shares), etc. To decrypt the line 430, strings 431 "reserves formed in accordance with the legislation" and 432 "reserves formed in accordance with the constituent documents".
To form a reserve fund is obliged only joint Stock Company (paragraph 1 of Art. 35 Federal Law dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ "On Joint-Stock Companies"). Therefore, they must fill in the string 431.
Other organizations have the right to create a reserve fund, if it is provided for by the constituent documents, but are not required to do this. Such right is provided, for example, limited liability companies (Article 30 of the Federal Law of 08.02.1998 No. 14-FZ "On Limited Liability Societies"). If LLC creates a reserve capital, its sum is reflected in line 432 and under the generalizing line 430.
Please note: accounts on accounts 14 "reserves for cost reduction material values", 59" reserves for impairment of financial investments "and 63" reserves for doubtful debts"In the liabilities of the balance sheet not reflected. The amounts of these reserves are accepted into a decrease in the accounting asset indicators:
Account balance reduces raw materials, materials and other similar values \u200b\u200bfor rows 211 "and 214" Finished products and the goods for resale ";
Account balance 59 reduces strings of 140 "Long-term Financial Investments" and 250 "Short-term Financial Investments";
Account balance 63 reduces accounts receivableReflected on strings 230 and 240 balances.
Not reflected in line 430 also amounts of reserves, accountable on account 96 "reserves of upcoming expenses". For them, the string is 650 sect. V balance.
Row 470 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)"
This line reflects the account balance 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)":
Credit - if the organization has retained earnings;
Debit - if the company does not cover losses. In this case, the string 470 is driven in brackets. When calculating the value of the string 490 "Total according to section III", the amount of the loss is deducted.
The line 470 reflects the sums of retained earnings (uncovered loss) and the reporting period, and past years. However, if the organization considers it necessary to allocate financial results for the reporting year and past periods, it can introduce additional decoding lines: "Retained earnings (uncovered loss) of the reporting year" and "retained earnings (uncovered loss) of previous years."
Row 490 "Total in section III"
Row 490 - final for section. III "Capital and reserves". It reflects the sum of all own sources Organizations are authorized capital, additional and reserve capital, retained earnings.
The indicator on line 490 is formed as the amount of rows:
410 "Authorized capital";
420 "Extension Capital";
430 "Reserve capital";
470 "Retained profit (uncovered loss)."
At the same time, the indicator shown in line 411 "own shares redeemed from shareholders" is deducted. If the amount in line 470 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" enclosed in round brackets (that is, a loss is formed), it is also deducted, and not added.
Third section of the balance liability "Capital and reserves" Consists of the following articles.
The table below reflects the scheme of the third partition of the balance liability with account indication, the remains of which are reflected in the corresponding line of balance.
"Authorized capital" (line 410).This article shows the magnitude of the authority capital (account balance 80 "authorized capital") in accordance with the provisions of constituent documents. An increase or decrease in the authorized capital is made only after entering into installed manner Changes to the constituent documents (charter) of the organization (organization).
On the line " Own shares repurchased from shareholders " It shows the balance of the value of the organization's own shares, which are redeemed from shareholders, taken into account on the account 81 "Own shares (shares)".
"Extension Capital" (line 420).Under this line, the amount of the increase in the value of the property of the organization, reflected in the balance sheet, detected by the results of their revaluation, as well as the amount of emission income of joint-stock companies (i.e. the amounts obtained in excess of the nominal value of the Company's placed shares are ) and the means of targeted funding received by WVID investment funds. Since the authorized capital is recorded in the constituent documents, then the need to take into account the growth of own capital of the economic entity. For these purposes, the account 83 "Extension Capital" is intended.
"Reserve Capital" (line 430).This article forms sources in the form of reserve funds, the creation of which is provided for by law (by existing legislation Reserve Funds B. obligatory Creates a limited number commercial organizations) or constituent documents of the organization. In mandatory, it should only have joint stock companies. For these purposes, the account 82 "Reserve Capital" is intended.
"Retained profit (uncovered loss)" (line 470).IN this section The amounts of retained profits are given, that is, the profits remaining at the disposal of the organization after the reflection of obligations to the budget. Retained earnings (uncovered loss) past years and profit (loss) reporting year Show one amount. If there is a loss in this section, it shows its size in parentheses.
Fourth section of the balance liability Wears title "Long term duties",it consists of the following articles.
The table presented above reflects the scheme of the fourth section of the balance liability with account indication, the remains of which are reflected in the corresponding line of balance.
"Loans and Loans" (line 510)Here the content of long-term loans of banks and long-term loans is revealed. Long-term loans and loans are taken into account in the account 67 "Calculations on long-term loans and loans". The balance of this account is recorded in the balance sheet 510 "loans and loans", it is not necessary to decipher this amount.
"Deferred tax liabilities" (line 515).For this line, the part of the income tax is reflected, which should lead to an increase in the income tax payable to the budget in the following reporting or subsequent reporting periods. This string is transferred to the balance of the loan of the same name 77.
Deferred tax liabilities appear if the costs of accounting Affairs later than in tax, and incomes - before. This magnitude is calculated by the formula
"Other long-term liabilities" (line 520).This line reflects other names of obligations with a maturity of more than 12 months after reporting date (rental obligations of the tenant long-term lease etc.).
"Short-term liabilities" are the fifth section of the balance liabilitywhich consists of the following articles.
The table presented above reflects the scheme of the fifth section of the balance liability with accounts to indicate, the remains of which are given in the appropriate line of the balance.
Loans and loans (strings 610).This subsection reflects borrowed funds Organizations in the form of loans of banks and loans to be repurchased within 12 months after the reporting date. The string 610 records the balance on the account 66 "Calculations on short-term loans and loans". And decipher how the organization occupied from the bank, other firms or citizens, no need.
Credit debt (string 620).This line reflects the short-term obligations of the organization:
Before suppliers and contractors;
Before the staff of the organization;
Before state-owned extrabudgetary funds;
On taxes and fees (before budget);
Before other creditors.
It is important to pay attention to the amounts of the Unified social tax In part federal budget They are recorded in the line "Debt on taxes and fees".
Debt to participants (founders) on income payment (line 630).The debt of the organization on the accrued, but non-paid dividends should be specified in line 630 "Debt to participants (founders) on the payment of revenues" of the balance. In accounting, there is no separate account for reflection of calculations with shareholders for dividends, so these calculations take into account 75 "calculations with the founders" accounts. The debt of the founders on deposits into share capital is also taken into account, therefore, the account 75 is shown in the assets and liabilities of the balance, and on the article "Calculations on dividends" shows not only the amount of debt on accrued dividends, but also by interest on their own valuable securities (shares and bonds, etc.).
Income of future periods (line 640).This line reflects the balance of the income of future periods, taken into account in the account of the same name 98. These are the so-called revenues obtained in reporting periodbut relating to the future reporting periods, for example, the resulting rent It is transferred to a string of 640 "Incomes of future periods" of the balance. It is important to note that receiving money as a pre-payment or advance payment of future periods is not.
Reserves of upcoming expenses (line 650).For uniform distribution Expenditures An organization can create reserves (for payment of vacations to employees, the cost of repairing fixed assets, on the payment of remuneration on the results of work for the year, etc.). This decision must be enshrined in accounting policies.
The accrual and use of the reserve is reflected in the score 96 "reserves of upcoming expenses". The loan residue on it is postponed to the line 650 "reserves of upcoming expenses".
Under article Other short-term liabilities (line 660) The organization's obligations are reflected by the maturity of less than 12 months that have not included in the previous subsections of the fifth section of the liability of the balance sheet.
- Dismissal of servicemen to reserve and retirement: subtlety procedure
- Dismissal upon the expiration of the employment contract Dismissal of the employee at the end of the labor contract
- The law on the reduction of working pensioners of pensioners is reduced primarily
- How and why get up on the labor exchange after dismissal
- Recovery of material damage from the employee: Procedure
- Reimbursement of material damage: procedure for determining and recovery
- How is the harm for military injury to employees of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and FSIN?
- The procedure for the dismissal of the serviceman in connection with non-compliance with the terms of the contract
- Executive loan production, how to share% retention from zp two executive sheets in the debtor
- Dismissal after child care leave
- Which country is it easier to get a Schengen visa?
- Criteria for the quality of medical care
- Criteria for assessing the quality of medical care
- List of medical activities subject to licensing
- Legislative base of the Russian Federation Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development 328
- Practical recommendations
- Clinical tests of medical devices
- Replacing registration certificates
- Legislative base of the Russian Federation
- How to check license for medical activities Check license for pharmaceutical activities









