Personal income tax deduction how to calculate. Regulatory basis for calculating the amount of personal income tax to be issued in person
Income tax is a burden imposed on individuals. Tax is withheld from certain types income received by individuals. This could be salary, proceeds from the sale of property, renting it out, gifts, winnings, interest on loans, dividends, etc. In this article we will tell you how to calculate the amount of personal income tax in your hands and answer frequently asked questions.
The main type of income that citizens receive is a salary paid by the employer, who in this case acts as a tax agent. It is in relation to order personal income tax calculations arises from the salaries of individuals greatest number
questions.
What laws should you follow? The procedure for calculating, withholding and paying personal income tax is regulated tax legislation , in particular, it is possible to include in the regulatory framework next articles
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- 210 – the procedure for determining the base for tax withholding is established;
- 217 – a list of non-taxable income in favor of individuals is determined; there is no need to withhold income tax from this income;
- 218-220 – benefits for individuals in the form of social, property and standard deductions, the latter apply only to income in the form of wages; 224 – personal income tax rates, for various types income, as well as for various categories
- for individuals, the rate may vary;
225, 226 – regulation of the calculation procedure. In order to correctly calculate the tax burden on individuals, the employer should first of all become familiar with these paragraphs of the code. The employee also needs to read the indicated points in order to understand his status as a taxpayer and not be deceived by the employer when tax withholdings
, know about your rights and responsibilities.
The procedure for calculating the amount of personal income tax If income is issued in non-monetary form, then personal income tax is withheld at the time of the next issuance of income in the form Money
to this individual. If it is not possible to withhold the amount of tax by the end of the year, this should be reported to the Federal Tax Service by reflecting this information in the annual certificate 2-NDFL (the “attribute” field of this certificate is set to “2”, then the subject to be withheld is indicated, but not withheld tax amount). In general, the calculation procedure income tax
- Find out whether the individual in respect of whom the settlement is being carried out is included in the number of residents of the Russian Federation (the settlement procedure for residents and non-residents is different);
- Calculate the income from which personal income tax must be withheld;
- Install current for given income rate;
- Calculate the base taking into account income and required deductions;
- Calculate personal income tax by multiplying the base by the rate;
- Withhold the calculated tax from the accrued salary amount;
- Pay the employee the earned money minus the withheld and paid income tax
- Pay the withheld personal income tax to the budget.
The calculation procedure is carried out exactly in the order indicated. You need to pay tax to the budget only after actual issue funds to an individual.
Features of calculating personal income tax from the salary of a resident of the Russian Federation
Article 226 requires employers to determine the income of resident employees on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year to which it relates billing month. All wages accrued for a given period are summed up. Subtracted from the resulting value standard deductions, if any. The calculation also takes into account the total amount of deductions provided since the beginning of the year.
For calculus tax burden Residents are charged a rate of 13%. Generally, calculation formula for residents it looks like this:
Personal income tax = (Income from the beginning of the year - deductions from the beginning of the year) * 13% - personal income tax withheld at the time of calculation from the beginning of the year.
Calculation example for a resident
The employee works for the organization and is a resident of the Russian Federation. For the period from January to February, he received a salary of 60,000, the withheld personal income tax is 7,436. The employee is entitled to a deduction for one child in the amount of 1,400. For March, the employee was given an advance in the amount of 15,000 (paid on March 20) and a salary of 15,000 (paid on April 5).
Personal income tax to be withheld:
- From advance payment = 15,000 * 13% = 1,950 (on March 20, the employee receives 15,000-1,950 = 13,050).
- Personal income tax with salary = (90000 - 4200) * 13% - 7436 - 1950 = 3718 (04/05 the employee receives 15000-1950 = 13050.
Features of calculating personal income tax from the salary of a non-resident of the Russian Federation
For this category of working citizens, there is no need to sum up income from the beginning of the year, that is, the cumulative total is not applied. The accrued salary for the billing month is taken and tax is withheld from it at the current rate. The last parameter for non-residents is set as follows:
- 13% - from salary, if the non-resident is a highly qualified specialist or works under a patent, is among the refugees or has temporarily received asylum for Russian territory, this percentage is also established for workers from EAEU countries;
- 30% - on all other accruals, with the exception of dividends, for which the rate is set at 15%.
The peculiarity of taxation of income of non-residents is also the absence of the right to tax benefits in the form of deductions, they are due only to Russian residents. For these persons, it is necessary to calculate separately the income for billing period
for each basis (separately salary, bonus, etc.), personal income tax is calculated from the resulting value at a rate of 30%.
The calculation formula for non-residents looks like this:
Personal income tax = Income * 30%.
Calculation example for a non-resident An employee who is not a resident of the Russian Federation works in an organization and receives a salary for his work. Moreover, this employee is not a refugee, has not received temporary asylum in Russia, does not have a patent, and his position is not highly qualified. For March 2017 given to the employee
a salary of 24,000 rubles was accrued. and a bonus of 5000 rubles.
- Personal income tax payable for March on non-resident income:
- Personal income tax with salary = 24,000 * 30% = 7,200 rubles.
Personal income tax on bonus = 5000 * 30% = 1500 rubles.
That is, the calculation is carried out separately for each type of accrual, the rate in this case is 30%, no deductions are applied.
How to calculate personal income tax from money to issue
- To do this, you need to use the following calculation formulas:
- Salary to be accrued = Salary in hand / (100%-13%) = Salary in hand / 0.87.
Personal income tax = Salary to be accrued * 13%.
An example of personal income tax calculation from salary to payment
- The head of the sales department, Popov, was promised a salary of 70,000 rubles. (including personal income tax withholding), that is, Popov will receive this amount in his hands every month. The task is to determine from what amount the accountant should calculate personal income tax, and how much tax should be paid to the budget.
- Salary to be accrued = 70000 / 0.87 = 80460
Personal income tax = 80460 * 13% = 10460
FAQ Question No. 1.
When do you need to withhold personal income tax? The tax reduces the income received by an individual, and therefore directly withholds sum of money
Personal income tax is due at the time of payment. If an advance is issued, the employer can determine for himself whether to pay the entire amount of the advance in full, and withhold personal income tax from the advance at the time of salary payment, or withhold tax immediately when issuing the advance funds. The Ministry of Finance confirms that it is possible to withhold the entire amount of tax (from the advance payment and from salary balances) when paying at the end of the month.
However, in practice, it is more convenient to deduct the tax immediately when issuing an advance. An employee may get sick, go on leave without pay, or quit, then the salary for the second part of the month will not be accrued to him, therefore, there will be nothing to withhold tax from. If income is issued in material form
, then the tax must be directly withheld at the time of the next release of income in the form of cash. Question No. 2.
When should personal income tax be transferred to the budget?
- Articles 223 and 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determine the deadlines for paying income tax:
- From an advance – at the time of payment of salary tax for the second half of the month;
- From salary - on the day of direct payment of funds or not the next day; From income to material form - Not later in the day
, following the day of payment of the nearest funds. Question No. 3.
Is it possible to pay personal income tax before the actual payment of wages?
The answer to this question is ambiguous. On the one hand, clause 4 of Article 226 requires payment of tax upon the actual issuance of income, but if personal income tax was paid earlier, then this is not recognized as tax. On the other hand, the transfer took place, so it is impossible to hold the tax agent accountable for non-transfer. There is no corpus delicti, which means there is nothing to punish for. Due to such an ambiguous situation, it is still recommended not to pay income tax earlier in the day
payment of income to an individual in order to avoid claims from the tax authority. If the payment is made before the payment of money, then the Federal Tax Service will most likely transfer the matter to court. The court, most likely, will not hold the organization liable for the absence of a violation of the fact of transfer, however, the tax agent will have to work hard to prove his case in court. The most common tax in all countries of the world is income tax, which is imposed on all persons receiving wages . The Russian Federation is no exception, and the way personal income tax is calculated is one of the most current issues
for any of our compatriots. In today's article we are real examples
We will show you the rules for calculating personal income tax, talk about the rates of this tax and what consequences may arise from evading its payment. Personal income tax, or as it is often called, income tax, payroll tax , is one of the main government fees in Russian Federation
It is worth noting that the concept of “income tax” is not entirely correct to interpret as a tax on income received by individuals. In fact, this category also includes. However, in our country this interpretation is stable.
Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the procedure for calculating, making payments for personal income tax and submitting reports on this fee to the budget. It contains all the aspects necessary for the correct calculation of personal income tax. It is worth noting that, unlike many other countries, Russia has adopted not a progressive, but a flat tax scale. Personal income tax rate does not depend on the level of income, solely on the category of income and the taxpayer himself.
- Taxpayers are individuals - residents and non-residents of our country who received income during the period under review. In addition, personal income tax is paid individual entrepreneurs.
Residents pay income tax on total income, non-residents - only those received on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- Object of taxation serves as income in the form of wages, income from business activities, or other income (for example, dividends, interest on deposits, lottery winnings, sale of property).
Please note that there is an extensive list of income on which personal income tax is not charged, so if in doubt, it is recommended to check current list exceptions.
- The tax base for individuals – all income received. Individual entrepreneurs have the opportunity to calculate personal income tax based on the amount reduced by the amount of confirmed expenses.
For individuals and entrepreneurs, it is also possible to reduce the base and amount of personal income tax through a variety of tax deductions – a separate article is devoted to them on our website.
- Tax rate is established depending on the status of the payer (resident or not) and the nature of the tax received (salary, dividends, winnings, etc.).
The basic personal income tax rate is 13%. Also quite often used are rates of 15% and 30%, at which the income of non-residents is taxed.
Who and how is income tax calculated and paid?
 Above we talked about the basic categories of personal income tax as a tax, what income is subject to it and at what rates. However, taxpayers are much more interested in practical questions– who should carry out the calculation and transfer the tax to the budget, how often reports are submitted, whether advance payments need to be made.
Above we talked about the basic categories of personal income tax as a tax, what income is subject to it and at what rates. However, taxpayers are much more interested in practical questions– who should carry out the calculation and transfer the tax to the budget, how often reports are submitted, whether advance payments need to be made.
The calculation and payment of personal income tax, as well as the submission of reports on this tax to the inspectorate, is the responsibility of the payer’s tax agent, and only in his absence- the individual himself.
As a rule, as a tax agent in the case of receiving wages the organization acting as the employer. It doesn’t matter whether you work according to employment contract or concluded GPC agreement– personal income tax deductions are still maintained by the enterprise’s accounting department. In this case, the employee already receives his salary minus tax contributions.
If we're talking about about income that is not official wages, responsibility for personal income tax payments lies on the physical person itself. This does not apply only to some lotteries and prizes, as well as income from deposits - most often an organization or bank takes on all the hassle of paying contributions to the budget.
When an individual or entrepreneur receives income on OSNO, he automatically acquires the obligation to personal income tax payment. It is the taxpayer who is obliged to control whether the organization that paid him the money is tax agent or not.
So, for example, opening notary office When receiving fees or earning money from the sale of property, an individual is obliged to independently calculate personal income tax and submit a tax return.
The tax agent (or, depending on the situation, the payer himself) is obliged to deadlines submit to the tax office tax reporting and make payments.
Reporting and deadlines for personal income tax payment for tax agents
Depending on the type of income received, both the taxpayer himself and his employer can pay personal income tax to the budget. In each of these cases, tax payments and reporting have their own characteristics that should be taken into account.
If the organization that paid the income to the individual acts as a tax agent:
- Taxable period- 1 year.
- Personal income tax accrual produced on an accrual basis throughout the year.
- Personal income tax is calculated with each payment of income(salaries, dividends) and is immediately retained by the organization. The employee receives the amount minus tax.
Tax is calculated monthly on the entire amount of income received, upon payment personal income tax advances not charged.
- Tax transfer occurs no later than the day following the payment of wages.
- Personal income tax reporting are 2-NDFL declarations, which are prepared separately for each employee. Since 2016 there has also been a new declaration 6-NDFL. This is a reporting form containing generalized personal income tax indicators for the period for the tax agent.
There are two types of 2-personal income tax. Declarations with attribute 1 – for income from which personal income tax was withheld. With sign 2 – for income from which tax could not be withheld. For example, when income was paid not in cash, but in material form.
- Due dates. 6-NDFL is filled out on a cumulative basis and submitted quarterly. Deadline – last number month following the reporting month. The final declaration for the year is submitted no later than April 1 of the coming year. 2-NDFL is submitted once a year: with sign 2 - before March 1, with sign 1 - before April 30.
Reporting and deadlines for personal income tax payment for individuals and entrepreneurs
If we are talking about an individual or entrepreneur - a taxpayer who calculates personal income tax himself, the situation is different:
- Taxable period- 1 year.
- Calculation and payment Personal income tax occurs once a year, no later than April 1.
In this case, the taxpayer, at the request of the inspectorate, may pay quarterly advance contributions. This usually applies to entrepreneurs and individuals in private practice.
- Reporting form– declaration 3-NDFL, which indicates all income received (except for those for which tax is paid by the employer or other agent).
- 3-NDFL for rent Once a year, no later than April 30.
Procedure and formula for calculating personal income tax
 Paying tax under 3-NDFL is not difficult even for a person who is far from tax-economic subtleties. To ensure that the inspection does not have any claims against you, you must fill out a declaration, indicating all income for the year, and calculate income tax. After this, you just have to pay the contribution to the budget within the established time frame and submit a declaration.
Paying tax under 3-NDFL is not difficult even for a person who is far from tax-economic subtleties. To ensure that the inspection does not have any claims against you, you must fill out a declaration, indicating all income for the year, and calculate income tax. After this, you just have to pay the contribution to the budget within the established time frame and submit a declaration.
The formula for calculating personal income tax is as simple as possible: in order to calculate the amount of tax, you need to multiply the rate by the tax base.
In most cases the base is the entire amount of income, however, it may be reduced due to special deductions, including professional ones.
The procedure for calculating personal income tax in general view as follows:
- All received income is divided into categories(at applicable rates).
Obviously, it is necessary to separate ordinary wages, for which a rate of 13% is applied, from valuable prizes and gifts, where the tax is already 35%.
- Tax deductions are determined, which can be applied to the taxpayer’s income.
- The tax base is decreasing on the amount of deductions.
- Personal income tax is calculated by multiplying the tax rate by the calculated base.
- The total amount is calculated tax by summing the individual components.
The easiest way to do all the calculations is with help - this will protect you from errors in the calculations.
An inexperienced taxpayer may not only underestimate, but also significantly overestimate personal income tax amounts. This happens if you do not apply tax deductions or include in the base income that is not taxed (for example, alimony, compensation). In order not to overpay, you must carefully study the lists of exceptions and deductions specified in Tax Code.
How to calculate personal income tax from salary
As a rule, the employer is responsible for calculating and paying income tax on wages, and the employees themselves receive the amount in their hands minus payments to the budget. However, the question how to calculate personal income tax from salary, appears quite often - after all, individuals want to know in advance the amount of “net” income that they will receive in a particular case.
 What points should an employee pay attention to?
What points should an employee pay attention to?
- Tax amount determined by the formula (Monthly income) * 13%. In this case, all payments are taken into account, including bonuses, vacation pay, advances, and wages.
- If the employee is entitled to benefits(for example, if there is minor children), then the base is reduced monthly by the amount of tax deductions, and personal income tax is calculated on this difference.
Note that this happens until earnings for the year on an accrual basis do not exceed 350 thousand rubles. From this moment on, tax deductions cease to apply.
- The calculated amount is deducted from wages before they are issued to the employee.
Personal income tax “due” on the advance share is collected at the time the main part of the salary is paid.
- The taxpayer may, in some cases, make personal income tax refund (when paying for treatment, training). To receive a refund, he must submit supporting documents to the accounting department or tax office.
The amount of tax deductions is 2800 rubles (for 2 children). The tax base is 65000-2800=62200 rubles. The tax amount for January-May 2017 is 62200*13%*5=40430 rubles. In June 2017, Ivanov’s income exceeded 350 thousand rubles, therefore, the deductions ceased to apply. For June-August the tax amount is 65,000*13%*3=25,350 rubles. Total personal income tax for January-August is 65,780 rubles.
How to calculate personal income tax based on the amount of income of an entrepreneur
In the case when the money is received not in the form of wages, but as business income , personal income tax payment falls on the shoulders of the individual entrepreneur or self-employed citizen. The calculation procedure in this case is complicated by the existence of so-called professional deductions. Speaking in simple language, an entrepreneur can reduce the tax base not only due to social benefits, but also for the amount of expenses incurred.
 How to calculate personal income tax in this case?
How to calculate personal income tax in this case?
- Although taxable period is 1 year, in most cases required advance quarterly payments.
- Tax rate for business income (or other income related to professional activity) is 13%.
- Tax base is the amount of income reduced by the amount of deductions.
In case of professional deduction It is worth remembering that expenses must be included in the list of accepted expenses and have documentary evidence. Unconfirmed expenses are accepted for deduction not in in full, and in the form established by law percent of income (from 20% to 40%).
- There is no need to calculate and pay personal income tax after each operation.
Example How personal income tax is calculated in practice: the income of entrepreneur Petrov for the 1st quarter of 2017 amounted to 150 thousand rubles, confirmed expenses for the same period - 32 thousand rubles. In addition, Petrov rented out own apartment for 15 thousand rubles per month. We will calculate the amount of personal income tax for 3 months to make an advance payment.
The tax base for business income was 150-32 = 118 thousand rubles. Personal income tax amount 13%*118=15.34 thousand rubles. Income from renting out an apartment is 15*3=45 thousand rubles, the amount of personal income tax is 13%*45=5.85 thousand rubles. The final tax amount is 15.34+5.85=21.19 thousand rubles.
How to calculate personal income tax if you have other income
One of the most difficult moments when calculating personal income tax is accounting of all income arising during the tax period. In addition to salary and income from labor activity, other income is also subject to tax, including those not expressed in explicit monetary form.
If you were given something very valuable, you will have to pay personal income tax on the cost. The same is the case with financial assistance in the amount of more than 4 thousand rubles.
To avoid trouble with tax office and significant fines for underestimation or non-payment of tax should be attentive to maintaining a personal or business budget. Accounting for all transactions performed and profits received will allow you to calculate the amount of tax as accurately as possible.
Let's list the most common sources additional income, which are often not taken into account by taxpayers when filling out a declaration:
- Renting out real estate.
- Rendering professional services without registration legal entity(freelance, various part-time jobs).
- Receiving winnings.
- Receiving gifts of valuables, shares, cash.
- Interest income.
- Profit from trading.
WITH full list possible income can be found in the Tax Code. For each such income tax is calculated individually, and rates may vary significantly depending on the nature of the transaction.
It is worth recognizing that now typical behavior for Russia is evasion of personal income tax, which until now the state has turned a blind eye to. However, in last years tax authorities especially intensified due to the widespread underestimation of income by both payers themselves and their employers. Counteraction to “gray” payroll schemes threatens in the near future unpleasant consequences, so it’s worth thinking about changing your attitude towards paying personal income tax.
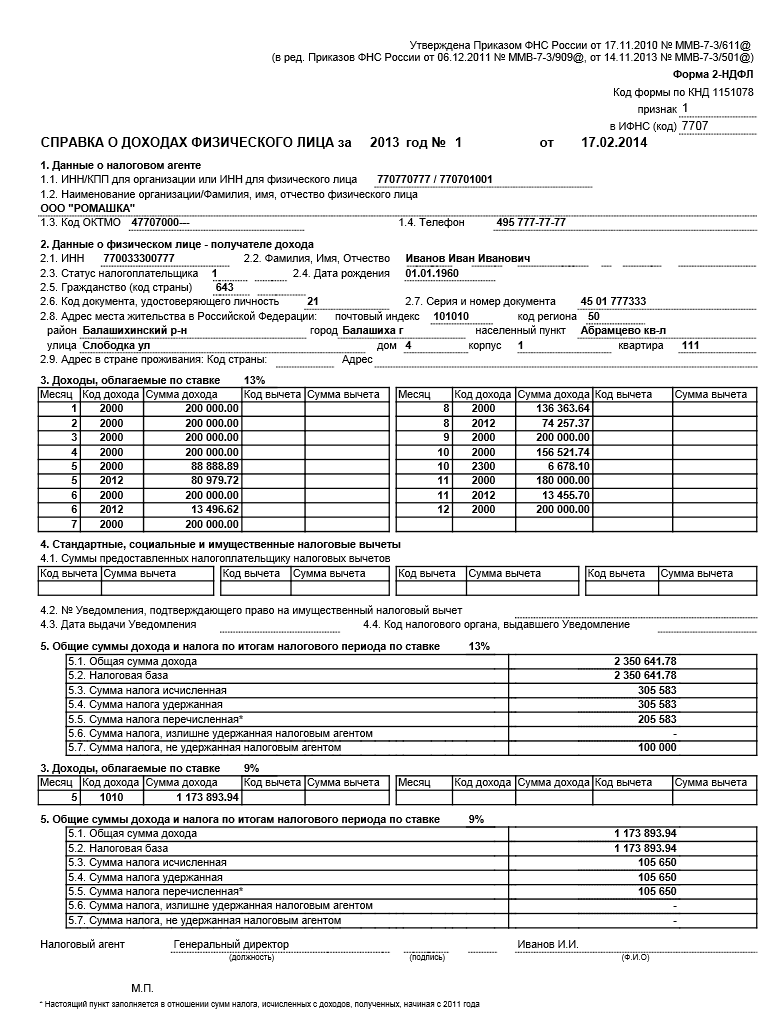
Personal income tax example
Conclusion
Income tax is one of the main sources of budget replenishment in the country. All individuals (including leading entrepreneurial activity) who receive income.
Calculation and payment of personal income tax is carried out either by the employing organization or by the taxpayer himself. Special attention When calculating, you should pay attention to correct definition tax base – the amount of contributions can be significantly reduced through the use of various deductions.
The calculation and withholding of personal income tax is accompanied by the implementation of the corresponding entries in accounting. The article provides a table with entries for calculating tax payable, as well as examples of calculating personal income tax on dividends, interest on a loan and employee wages. After considering this topic, we will deal with personal income tax reporting.
Personal income tax = 50,000 * 9% / 100% = 4,500 rubles.
Postings for withholding personal income tax from dividends
An example of calculating personal income tax on interest received on a loan
Personal income tax = 10,000 * 13 / 100 = 1,300 rubles.
Postings for withholding personal income tax from loan interest
|
Sum |
Debit |
Credit |
Operation name |
|
Received short term loan from Ivanov |
|||
|
Interest accrued for using the loan |
|||
|
Personal income tax accrued on interest |
|||
|
Returned borrowed funds including interest |
|||
|
Tax payable is transferred to the budget |
An example of calculating personal income tax from wages
Ivanov received a salary including a bonus of 30,000 rubles. Ivanov has the right to a deduction of 500 rubles, and he also has one child. We will calculate the personal income tax on this salary and produce necessary postings on its retention:
Salary minus deductions is subject to a tax rate of 13%.
Personal income tax = (30,000 - 500 - 1400) * 13 / 100 = 3653 rubles.
Ivanov will receive a salary in hand = 30,000 - 3653 = 26,347 rubles.
Postings for calculating personal income tax from salary
You can also see an example at personal income tax calculation from wages in the article "".
Posting by personal income tax withholding from wages is made on the last day of the month for which wages are accrued.
Personal income tax on other income is calculated on the day the employee receives this income.
This concludes our discussion of personal income tax. We've dealt with the concept of personal income tax, features of calculation, tax base and tax rates, you can also look at and and . Next, let's get acquainted with another tax - income tax.
- Pike cutlets "Original"
- What color were the insects you saw?
- Delicious snacks with a spicy touch: preparing salads with Korean carrots
- What is binge drinking: symptoms Alcoholic during binge drinking
- Psychosomatic factors of thyroid diseases Psychological causes of thyroiditis
- Tower coastal batteries of Sevastopol 30th coastal battery
- Liberation of Belarus - Operation Bagration
- Lucy Stein's new moment of fame
- Sample plan for writing a speech therapist report
- Letter M, m. Consonant sound i. Letter M, m Corrective and developmental
- Articulation exercises
- Why does a woman dream about a baby kangaroo?
- Runic inscription to attract customers for your business
- What do the numbers mean in fortune telling on coffee grounds?
- Fortune telling on paper with a ronglis pen
- Orange peels: uses, features and best recipes
- Homemade caramel syrup
- What is a spelling chart for schoolchildren
- How to soak meat in vinegar
- How to bake a meat pie - step-by-step recipes for preparing dough and filling with photos









