How to recognize a relationship as civil law. Establishing labor relations: practice of courts of general jurisdiction
Since the entry into force of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, labor legislation has provided for the following rule: if the court establishes that a civil law agreement is actually regulated labor Relations between an employee and an employer, the provisions of labor legislation.
Plenum Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in paragraph 8 of the resolution of March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by courts Russian Federation Labor Code of the Russian Federation" established a similar rule: if during judicial trial it will be proven that a civil law contract actually regulates the labor relations between the employee and the employer; the provisions of regulations containing norms must be applied to such relations labor law. As practice has shown, these provisions did not make it possible to effectively combat the substitution of civil law employment contracts and did not ensure adequate protection of the rights of workers. In this regard, in the labor legislation from January 1, 2014, clear prohibitions and new order recognition of a concluded civil contract as an employment contract.
Civil contract in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: what has changed
Which article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for a ban on the conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations?
The definition of labor relations is given in Art. 15 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In order to protect the rights of citizens with whom civil law contracts were illegally concluded, Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 No. 421-FZ “On Amendments to Certain legislative acts Russian Federation in connection with the adoption Federal Law"ABOUT special assessment working conditions” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 421-FZ) Art. 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation was supplemented with part two from January 1, 2014: “The conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations between an employee and an employer is not allowed.” Previously, labor legislation did not contain such a clearly formulated prohibition.
Our company enters into many civil contracts for the implementation individual works. For example, we conclude such agreements with illustrators: they receive an order to prepare sketches and draw pictures for a separate publication. We collaborate with some artists on a regular basis and enter into several agreements calendar year, others participated in one single project, and relations with them were no longer renewed. All these employees work from home, interaction takes place via e-mail, V in rare cases they come to the office - when, for example, a face-to-face meeting with a customer is required. Each contract ends with the delivery of work and payment for it. Can we continue this practice after January 1, 2014? Or now employers are in principle prohibited from entering into civil contracts for the performance of certain work?
The norm of part 2 of Art. 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, of course, does not mean that from January 1, 2014, an employer, in principle, cannot enter into civil contracts for the performance of certain works or the provision of services. Moreover, any business relationship must be confirmed by an agreement corresponding to their actual nature.
Judging by the story, the relationship between the customer company and the artists is really civil nature. Of course, there is not enough information, and each time it needs to be checked according to many indicators. But if we are really talking about one-time projects, the company is only interested in getting a certain result by certain period, and the contractor under the contract, although he does not have the rights of an employee under an employment contract, does not bear any obligations, for example, to comply with the rules labor regulations and obey the orders of the employer, then there is no reason to conclude employment contract No. In this case, it will be fictitious - not corresponding real situation things and the nature of the existing relationships.
The grounds for the emergence of labor relations are enshrined in Art. 16 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. By general rule they appear on the basis of an employment contract concluded in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In some cases, this requires the presence of a set legal facts(events or actions during which it is possible to conclude an employment contract). Such cases are called complex legal compositions emergence labor relations. Currently, this list, provided for in Part 2 of Art. 16, supplemented with new legal composition.

As you can see, the list of grounds for the emergence of an employment relationship has been supplemented with a fundamentally new provision.
Before January 1, 2014, in the event of a court recognizing a civil law contract as an employment contract, there was no formal basis for the proper execution of an employment contract, since a court decision on concluding an employment contract is not identical to the decision on recognition civil relations labor In the first case, the court makes a decision on concluding an employment contract when a person was illegally denied its conclusion, that is, when the employer was obliged to accept this person to work, but didn't do it. In the second case, the court recognizes that the employment relationship has actually developed, and therefore the employment contract is considered concluded from the date when the contractor began performing work under the civil contract. What is required here, in fact, is not the conclusion of an employment contract, but only its proper execution in accordance with the rules established by Art. 63–68 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Since previously part 4 of Art. 11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provided that recognition of a concluded civil law contract as an employment contract is possible only in judicial procedure, this norm has also been changed.
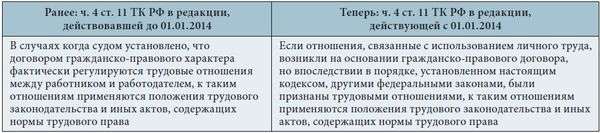
Recognition of a civil contract as an employment contract: expert opinion on innovations
I.A. Kostyan, Doctor of Law. Sciences, Professor of the Department of Labor Law, Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov, talks about the innovations provided for in Art. 19 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The norms provided for in Art. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, regulate the rules (methods, procedure) for protecting the rights of a person who, as a result of concluding a civil contract, has actually become a participant in labor relations.
This is possible in two situations:
- the parties are openly mistaken and admit legal error, concluding an agreement of the wrong type;
- The parties, when concluding a civil contract, deliberately conceal the existence of an employment relationship.
The first situation occurs in practice, although not as often as the second. For example, when agreeing on the conditions for a person to perform certain work (provide services) or carry out labor activities, the parties are in good faith mistaken about legal nature relations and regulate them by civil law agreement.
Previously, the law did not provide for the ability to independently eliminate legal errors accepted by the parties to the agreement. Although it is possible to note isolated cases of transformation of a civil law contract into an employment contract, when the parties additional agreement to the civil law contract, they recognized it as an employment contract and, in order to bring its contents into compliance with labor legislation, made appropriate changes to it, on the basis of which an order was issued to recognize civil law relations as labor relations, and in work book appropriate entries were made. But the consequences similar procedures and their assessment by supervisory authorities and authorities judiciary it was difficult to predict.
Today, conscious attempts to formalize labor relations by illegal imprisonment civil contract. The employer wants to minimize its costs, leave the employee without the guarantees provided for by labor legislation, make it easier to terminate the relationship, etc., and for this purpose avoids concluding an employment contract. Note that most employers succeed in this, and in court general jurisdiction Persons performing work under the terms of a civil contract are rarely able to prove the existence of an actual employment relationship.
Realizing the injustice of this situation, the legislator made an attempt to ensure adequate protection persons carrying out labor activity on the basis of a civil contract, as a result of which an employment relationship actually arises. A new rule for recognizing a civil law contract as an employment contract was formulated.
Firstly, significantly expanded subject composition– the circle of persons entitled to recognize a civil law contract as an employment contract has been increased. Now such a right is assigned not only to the court, but also to the customer using personal labor under the specified contract.
We emphasize that the state labor inspectorate does not have such a right. She has the right to check compliance with labor legislation and, if violations of the rules are detected, including those prohibiting the conclusion of civil contracts that actually regulate labor relations between the employee and the employer (Part 2 of Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), issue an appropriate order.
Secondly, the commented article defines the following grounds for recognizing relations arising as a result of the conclusion of a civil law contract as labor:
- written statement individual who is the executor under the contract;
- order of the state labor inspector to eliminate the violation of the requirements of Part 2 of Art. 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, not appealed to the court in in the prescribed manner;
- solution judicial authority, made on the basis statement of claim a person who is a performer under a civil contract, or based on materials (documents) sent by the state labor inspectorate, other bodies and persons having the necessary powers for this in accordance with federal laws. Such persons may include, for example, supervisory authorities, trade unions represented by authorized bodies.
In the first case, the employer’s decision depends on how he himself assesses the current situation. He has the right to satisfy the application of an individual, agreeing with his demand, or to refuse to recognize the relationship as an employment relationship.
In two other cases, recognition of the relationship as an employment relationship is mandatory, since the employer does not have the right to refuse to fulfill court decision, who joined legal force, as well as requirements supervisory authority, not contested in the prescribed manner.
Thus, a citizen has the right to choose a method that is convenient for him to protect the rights that, in his opinion, have been violated, provided that the relations that arose on the basis of a civil law agreement concluded with him have not been terminated (exist, continue). IN otherwise Only a court can recognize them as workers.
An important novelty of the commented article is the establishment by the legislator of a special assessment of evidence during the consideration of individual labor disputes. Irremovable doubts arising during the trial are subject to interpretation in favor of the labor relationship. This means that if none of the parties can prove the existence (or absence) of an employment relationship, if there is no possibility of presenting evidence confirming or refuting the existence of civil legal relations, taking into account their admissibility and relevance, the court, by its decision, must recognize such relations are labor relations, despite the existence of a civil law contract concluded by the parties.
The main characteristics of the two types of contracts, features of requalification of a civil contract, and the risks arising in connection with this for employers.
Many have seen the note on vacancies - “work without an employment contract”, but it is not serious violators of the law who write this way. Often employers are unwilling to enter into employment contracts with employees. The reasons for this vary. Some employers are trying to optimize taxation, while others simply do not need an employee for this position at permanent job. And since a fixed-term employment contract can be concluded only in a few cases, an option is to use a civil law contract (hereinafter referred to as the CPA), which is also mistakenly called an employment contract. However, the so-called labor hire- this is not so safe for employers. The main risk is the reclassification of a civil contract into an employment contract.
The difference between an employment contract and a civil law contract
To find out how you can protect yourself from retraining a civil law contract into an employment contract, you first need to understand what fundamental difference between them:
- legal regulation. Everything related to the conclusion of an employment contract is regulated Labor Code, everything related to the GPA - Civil Code.
- parties to the contract. It is worth paying attention to the fact that in an employment contract the parties are the employee and the employer, and in the GPA - the contractor (performer) and the customer.
- subject of the contract. Employment contract – fulfillment of the conditions stipulated by the employment contract or job description labor function, GPD – a specific task (for example, a series of events).
- purpose of concluding the contract. An employee under an employment contract is included in a long labor process that has no end (except for dismissal), and in the case of a labor contract, the final result is important.
- subordination to local regulations, working conditions. The employee is subject to local regulations (for example, Internal Labor Regulations), and the person working under the GAP is subject to the actual terms of this agreement.
- term of the contract. The GPA has an initial and deadline. An employment contract is usually of unlimited duration. In any case, the law contains exhaustive list grounds for concluding a fixed-term employment contract - it is difficult to “get into” them.
- payment. According to the employment contract - regularly, at least twice a month. According to the GAP - by agreement of the parties. As a rule, payment under the GPD is timed to coincide with the stages of work, or is advanced, or is even made only after the work has been completed.
- guarantees and compensation. According to the employment contract, the employee is provided with annual paid leave and days off, paid for business trips and days of temporary disability, etc. In accordance with the GPA social guarantees are not provided to the contractor.
- document flow. Together with the employment contract, it is necessary to issue an order for employment, an employment contract, personnel records documents and other documents accompanying the employee’s work activity. Information about the work is entered into his work book. The contract is accompanied only by an act or acts of work performed. When concluding a work contract, information about the work is not entered into the work book, but registration personnel documents not required.
Advantages of a civil contract
So, as we see, working without an employment contract, using GPA instead, frees the employer from large quantity responsibilities such as:
- provision of annual paid leave or compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal;
- payment of temporary disability certificates;
- pay wages at least every half month and payment of interest based on the discount rate bank interest for violation of these deadlines;
- payment for downtime due to the fault of the employer or due to circumstances beyond the control of the employee and the employer;
- compliance with labor protection legislation requirements;
- maintaining personnel documentation;
- and much more.
Signs that indicate a civil contract
In addition to the main risks of manipulating labor relations, which will be discussed below, we should also not forget that not all labor functions can be replaced by contracting. For example, for the position “secretary” it is not possible to determine the result of work as a certain number of received telephone calls and fax messages, and answers to questions from visitors.
Organizations should consider that essential conditions work under an employment contract, which determines its difference from the performance of work (provision of services) under the GPA, are:
- assigning to an employee a position, specialty, profession indicating qualifications in accordance with the organization’s staffing table or assigning a specific job function to him;
- payment for the labor process (and not its final result) in accordance with tariff rates, official salaries employee, taking into account additional payments, allowances, incentive payments, compensation and benefits;
- providing the employee with appropriate working conditions;
- providing the employee with types and conditions of social insurance;
- compliance by the employee with the internal labor regulations of the organization. Based on these characteristics, an agreement concluded by an organization with an individual can be qualified as an employment contract, in contrast to a civil law contract, which does not have these characteristics.
Re-qualification of a civil law contract into an employment contract
In the meantime, we get to the most basic negative consequence conclusion of the GAP instead of an employment contract: in court, civil legal relations can be reclassified as labor relations.
The very same requalification of GPD The employment contract is regulated, which came into force on January 1, 2014.
Art. 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes several ways to reclassify civil law relations into labor relations:
- By the customer written statement an individual who is the executor under the contract.
- By the customer based on the order state inspection labor (GIT), if this instruction was not in deadlines appealed to the court.
- By the court on the basis of an application from the executor - an individual (the latter has the right to go to court directly, bypassing the appeal to the customer, or upon receiving a refusal to requalify from the latter).
- By the court on the basis of materials received from the State Tax Inspectorate or another authorized body.
During the trial, circumstances of legal significance are established:
- whether the contract specifies the specialty, category (qualification) listed in the organization’s staffing table;
- whether a specific labor function was assigned to the contractor (performer);
- whether there is a specific task from the customer in the contract;
- whether the contractor was required to comply with the organization’s internal labor regulations;
- whether the customer organization kept track of the contractor’s (performer’s) working time;
- whether payment was made for the result of work performed (services rendered) or for time actually worked in accordance with tariff rates, official salaries of the employee, additional payments, allowances, incentive payments;
- whether acts of acceptance and transfer of work performed (services provided) were drawn up and how they were formalized;
- whether the customer fulfilled the obligation to ensure working conditions, etc.
Consequences of requalification of a civil contract
In case of retraining, the customer-employer finds himself in an extremely unpleasant situation. Firstly, part 3 of Art. 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides that the recognition of civil law relations as labor relations entails their establishment as such from the date of commencement of work under a civil law contract. By this time, the employee, who becomes the contractor, may have accumulated several consecutive ungranted vacations, arrears of payment overtime, if any is recorded, there may be additional payments due to harmful or dangerous conditions labor and so on. Secondly, such an employer will automatically be in violation of the provisions of labor legislation, and the employee will have the right to collect interest in the manner of compensation moral damage.
Thirdly, the consequence of the court’s re-qualification of the contract will be the accrual of arrears on the unified social tax and insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, as well as fines and penalties for late payment. In addition, mandatory liability will not be long in coming - violation of labor and labor protection legislation entails the imposition of administrative fine on legal entities- from 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to ninety days.
Please note that when interpreting the terms of the contract, the court, guided by , takes into account the literal meaning of the words and expressions contained in it, and in case of ambiguity, it is established by comparison with other articles and the meaning of the contract as a whole.
Will an employee be able to prove an employment relationship if there is no full-time position for his work?
An employer always takes risks when he enters into a civil law agreement instead of an employment contract. Employees, realizing that a contract or service agreement does not guarantee payment for sick leave and vacation, often go to court. Now the risk of such appeals has increased several times, since the executor, bypassing the court, can appeal directly to the State Tax Inspectorate. The procedure for filing a complaint with this body is much simpler than filing a claim. To prevent a company from being accused of concluding a civil contract instead of an employment contract, a number of conditions must be met. In particular, the performer cannot be accused of being late, since the regime prescribed in the internal labor regulations does not apply to him. In addition, such work needs to be paid only after acceptance of the work, and not according to salary slips. And you certainly shouldn’t report it together with the organization’s employees. Otherwise, suspicions of substituting civil relations for labor relations cannot be avoided.
The staffing table should not contain a position with the same function as the performer
Most job seekers seek to conclude an employment contract with the organization. After all, it is in labor relations that the employee is best protected. But some employers, to reduce financial expenses, deliberately do not include individual positions in the staffing table and invite candidates to sign a civil law agreement. Conflicts cannot be ruled out on this basis.
It is possible that after the study staffing table and other documents, the court may come to the conclusion that the existence of an employment relationship has not been proven.
However, for many courts the lack of staffing will not be of decisive importance. Back in 2009 constitutional Court The Russian Federation expressed its position on the issue of considering disputes regarding the recognition of labor relations (determination dated May 19, 2009 No. 597-О-О). In his opinion, the courts should proceed not only from the presence or absence of formalized acts, in particular the staffing table, but also establish whether there were in fact signs of labor relations and an employment contract.
Therefore, the lack of suitable staffing units- not the best good way justify the refusal to hire in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, such an argument does not always look convincing enough. And since personnel decisions are the prerogative of the employer (paragraph 2 of clause 10 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2), then he has the right at any time to supplement his staff with the required unit and hire a specialist for it.
The main argument in the event of a dispute, what matters to the court will be the fact that the employee is admitted to perform a job function, and not the presence or absence of a position in the staffing table.
What conditions in a civil contract can lead the court to think about labor relations?
An even more successful situation (for the employee) will arise if his duties coincide with the functionality of the position provided for in the staffing table. Thus, in one case, similar circumstances allowed the employee to convince the court to classify the relationship that arose between him and the employer as labor. The employer insisted that the documents evidencing the employment relationship (staffing schedule, timesheets, salary slips) were drawn up formally, but the court found these arguments dubious. He pointed to the norm of Part 3 of Art. 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which irremovable doubts when considering such disputes are interpreted in favor of the existence of labor relations ( appellate ruling Pskovsky regional court dated April 29, 2014 in case No. 33–642/2014).
In another precedent case, admission to work by position in accordance with the staffing table also played a significant role (appeal ruling of the Pskov Regional Court dated May 6, 2014 in case No. 33–672). This circumstance (along with other signs) convinced the court that an employment relationship had arisen.
Documents confirming the employment relationship:
Job description.
Time sheet
Salary statement.
An analysis of practice shows that it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of establishing labor relations by excluding from the staffing table vacant positions for the sake of hiring a contractor civil contract. But the presence of a vacancy suitable for concluding an employment contract will increase the risk of finding fault with the company many times over.
A civil contract cannot include a condition regarding the subordination of the performer to the employer.
In practice, organizations quite often entrust work to specialists on the basis of contract agreements, paid provision services, orders or agency agreement. The nature of civil law relations that arise between a citizen and a company differs significantly from labor relations. Firstly, the parties have equal legal status, and, secondly, according to the law they have much more freedom when determining the terms of the contract.
When choosing such a model of interaction, it is important that both parties are interested in this type of relationship and sign a civil contract on the basis of a free and voluntary expression of will. A similar conclusion was made by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated May 19, 2009 No. 597-О-О.
But in cases where these contracts have a similar subject matter with an employment contract, problems often arise. For example, cleaning work can be entrusted to both an employee under an employment contract and a contractor under a civil contract. In this case, the employee can try through the court to recognize the relationship between him and the company as an employment relationship.
Arbitrage practice:
An agency agreement was concluded with the citizen, according to which his duties included collecting Money from the sale of goods and applications for the supply of products. Subsequently, he went to court and asked to recognize the relationship that arose between him and the employer as labor. The court noted that the functionality assigned to the employee allowed the conclusion of an employment contract, but the same duties could be performed within the framework of an agency agreement. As a result, the court concluded that the relationship was of a civil nature, since the specialist carried out instructions at a convenient time for himself and did not obey internal regulations employer, and payment depended on the result of work (appeal ruling of the Kostroma Regional Court dated 08/07/2013 in case No. 33–1286).
In another case, similar circumstances also did not allow the employee to prove labor character relations (appeal ruling of the Murmansk Regional Court dated April 29, 2014 No. 33–1228). The employer provided evidence that the specialist performed his duties outside the organization’s premises and appeared only to resolve issues that arose under the contract. In addition, internal labor regulations did not apply to him. Payment of labor under a civil law contract was confirmed by the receipt cash order, and not a statement for receiving wages, as happens in labor relations. The result of the case was a win for the employer.
Another important indicator of civil law relations is the lack of subordination to the employer. In other words, the company cannot require a specialist hired under a contract or service agreement to carry out the orders and instructions of the manager. The inclusion of such a condition in the contract will call into question its civil nature (decision of the Sverdlovsk Regional Court dated July 30, 2013 in case No. 33–9056/2013).
This will not happen unless there is evidence that the specialist, when providing services, had to carry out the orders and instructions of the manager (appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) dated June 16, 2014 in case No. 33–1844/14). In other words, the optimal situation is in which the specialist himself organizes his work and decides when and how to perform the task assigned to him. In turn, on the part of the employer, the level of control should be reduced to a minimum.
Payment for the contractor’s services must be made only based on the results of acceptance of the work.
Work under a civil law contract, as well as under an employment contract, is subject to payment. But so that there are no complaints against the employer from the inspectors and the employees themselves do not doubt the nature of the relationship with the company, the issuance of money for each of the said agreements must be carried out according to different rules.
A civil contract specialist does not need to pay sick leave
Workers under employment contracts have the right to receive temporary disability benefits, but those who work under a civil contract do not.
The amount of the benefit directly depends on insurance period citizen; the larger it is, the higher the payments due to the employee (Part 1, Article 7 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006; hereinafter referred to as Law No. 255-FZ).
In addition, the employer must pay insurance premiums in the FSS of Russia. This duty is assigned to him in clause 2, part 2, art. 4.1 of Law No. 255-FZ. And if an employee works in a company on the basis of an employment contract, he is entitled to temporary disability benefits (clause 1, part 1, article 2, part 1, article 13 of Law No. 255-FZ).
But a civil law agreement, for example, a contract or the provision of services, does not give such a right. Payments made under these agreements are not subject to contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of Russia (Clause 2, Part 3, Article 9 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009). This means that the company is not obliged to pay the specialist temporary disability benefits.
The employer should not regulate the process of performing work under a civil contract. This sign indicates the existence of an employment relationship (appeal ruling of the Omsk Regional Court dated March 19, 2014 in case No. 33–1611/14).
When is it better for the employer to recognize the contract as an employment contract without waiting for a visit from the State Tax Inspectorate?
Such a request can be granted if the employer doubts the correctness of the civil law contract. But you can refuse if the specialist’s work does not have characteristic features labor relations.
Relationships formalized by a civil contract can be recognized as labor relations. This happens voluntarily or forcibly(Part 1 of Article 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What should an employer do if an employee demands that a contract be recognized as an employment contract?
In the first case, it is enough for the employee to submit an application for recognition of the relationship as an employment relationship, and for the employer to draw up an employment contract, an order for employment and a work book. All documents are drawn up current date, but the employee will be considered working under an employment contract from the moment of actual admission to work.
The compulsory procedure involves the employee going to court or the State Tax Inspectorate. If the claim or complaint is satisfied, the employer will still have to comply with the relevant decision or order, but this time involuntarily.
Employees under employment contracts must receive money on a regular basis, at least twice a month (Part 6 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To calculate the amount to be issued, you will need a time sheet in which information about each employee is entered. In addition, their earnings cannot be lower than the minimum wage (Part 1 of Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Today it is 5554 rubles, but regional minimum wage, as a rule, higher. If the employee receives money in cash, then he signs the statement. And regardless of the method of issuing salaries, each employee is given payslip(Part 1 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In another way, you need to pay for the services of the contractor under a civil contract. There is no need to create a time sheet for him, since this means that his work time is taken into account according to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which means that there are signs of an employment relationship. It is not the work of the performer that is subject to payment, but the result of his work. The transfer of money occurs after drawing up a certificate of completion of work. It is possible to pay an advance on the terms determined by agreement, but it shouldn't remind regular payment salaries in a pre-agreed amount.
Employers who do not comply specified conditions, risk facing claims from the State Tax Inspectorate. In fact, the company itself will present to the state labor inspector grounds for suspecting it of substituting civil relations for labor relations. Moreover, the powers of the State Tax Inspectorate in this area have expanded significantly.
Now the employee does not have to go to court; he can file a complaint with the State Labor Inspectorate and demand that his contract be recognized as an employment contract.
From January 2014, by virtue of paragraph. 2 hours 1 tbsp. 19.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation state inspector Labor has the right to issue an order to eliminate violations of Part 2 of Art. 15 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This norm prohibits replacing labor relations with civil ones. And on the basis of such instructions, the employer will have to recognize the relationship as an employment relationship and draw up the documents provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (employment contract, order, work book).
Previously, workers also contacted the State Tax Inspectorate with similar complaints. But, as a rule, they were left without a concrete decision, and the employees were sent to court, since the inspectors at that time did not have the appropriate powers. True, there were isolated cases of issuing orders, and companies were not always able to challenge them (appeal ruling of the Yamalo-Nenets Court Autonomous Okrug dated February 24, 2014 No. 33–347/2014).
Now Art. 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has removed this uncertainty, and the powers of the State Tax Inspectorate in this matter are clearly defined. However, inspectors still have the right to issue orders only in case of an obvious violation of labor laws. Controversial issues must be decided directly in court (determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 10, 2014 No. 5-KG13-146).
In addition, for violation of labor legislation (Part 2 of Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the director and the organization may be fined in accordance with Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The manager will pay from 1 thousand to 5 thousand rubles, and the company - from 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles.
This provision also provides for the suspension of activities, but this is unlikely. This type of punishment is provided for in Part 1 of Art. 3.12 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for very serious violations that pose a threat to human life and health, and others similar consequences. And concluding a civil law agreement certainly does not meet these criteria.
From 2015, the fine will increase: for a director up to 20 thousand rubles, and the organization, in turn, will lose up to 100 thousand rubles.
Having received the order, the employer must carry out a number of activities.
First of all, you need to conclude an employment contract with the employee, including in it the information and conditions provided for in Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. After this, an order for employment is issued (Part 1 of Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The date of acceptance will correspond to the actual start of work under the terms of a civil contract. In addition, it is necessary to obtain a work book from the employee and fill it out in accordance with the Instructions (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated October 10, 2003 No. 69). Now it will be stored in the organization.
It is also important to resolve the money issue with the employee. Claims to recognize the relationship as an employment relationship are usually accompanied by a claim for payment of wages and moral damages. Some employees also try to charge the company for overtime and work on weekends and holidays. If the court satisfies these demands, then the money will have to be paid. It is possible that the court will oblige the company to pay taxes and contributions to the employee for the past time.
When else can a performer under a civil contract be recognized as an employee?
The specialist works in the office from 09.00 to 18.00.
The specialist receives payment for the result of his work.
According to the terms of the contract, the contractor must perform the work personally. A specialist who works in an office according to a certain schedule, and even more so complies with the company’s internal labor regulations, may demand that the contract concluded with him be recognized as an employment contract. Subordination internal rules employer is one of the signs of labor relations.
- What did a kisser do in Rus'?
- Tselovalnik Tselovalniks are officials of Muscovite Rus', elected by the zemshchina in districts and towns to carry out judicial,...
- New
- Tselovalnik - a mysterious profession of ancient Rus'
- The creator of geminoid robots, Hiroshi Ishiguro, will give lectures at Skoltech
- Hiroshi Ishiguro - Japanese engineer, creator of humanoid robots
- Measurement of gamma background in places of residence of the population of rural and urban settlements in the southwestern regions of the Bryansk region
- The latest photos from the Hubble telescope
- Blood of Saint Januarius When the blood of Saint Januarius boils in Naples
- Why do you have nightmares: interpretation of disturbing dreams Causes of disturbing dreams
- Career zodiac sign Pisces How Pisces can achieve success
- Tower coastal batteries of Sevastopol 30th coastal battery
- Liberation of Belarus - Operation Bagration
- Lucy Stein's new moment of fame
- Sample plan for writing a speech therapist report
- Letter M, m. Consonant sound i. Letter M, m Corrective and developmental
- Articulation exercises
- How are these sounds similar?
- What does it mean to go to the panel?
- Pythagoras - Olympic champion What kind of sport did Pythagoras engage in?









