How much taxes does the employer pay for the employee? Pension Fund. Social Insurance Fund. Compulsory health insurance fund
The legislation of our country obliges the employer to make payments for each employee in the state. They are regulated by the Tax Code, Labor and other norms. The employer acts as an intermediary between the state and the employee. Everyone knows about the famous 13% personal income tax. But how much does an employee actually cost an honest employer?
Insurance payments
Starting in 2017, employee contributions are transferred to the Federal Tax Service (FSN) and the Social Insurance Fund (FSS). The tariffs that are set every year by the government of the Russian Federation are general. This year it is necessary to list:
Pension insurance - 22%,
For compulsory health insurance - 5.1%,
In the Social Insurance Fund - 2.9% (excluding contributions for work-related injuries).
Employers who have benefits can see them in the tax table.
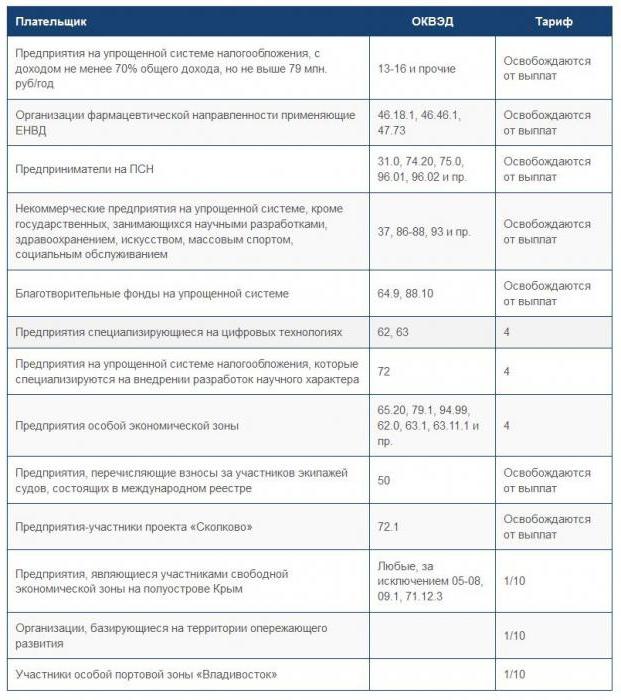
There are also reduced tariffs, they are presented in the table below.
| Taxpayer category | ||||
| Pharmacy organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs (licensed pharmacists) working on UTII | 20 | - | - | 20 |
| NCOs on the simplified tax system dealing with social services, education, science, sports, health care, art and culture | ||||
| Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system (only preferential activities). Provided that the limit of 79 million rubles is not exceeded. | ||||
| Organizations conducting charitable activities (only on the simplified tax system) | ||||
| SP on PSN (does not include property lease, catering and trade) | ||||
| Participants - Sevastopol and Crimea | 6 | 0,1 | 1,5 | 7,6 |
| Individual entrepreneurs and organizations working in the tourist-recreational and technical-innovative area (only SEZ) | 8 | 4 | 2 | 14 |
| IT organizations (two conditions must be met: there must be more than 7 employees and at least 90% at the end of three quarters) | ||||
| Organizations with the status of a member of the Skolkovo project | 14 | - | - | |
| Individual entrepreneurs and organizations making payments to members of ship crews (only for those registered in the Russian International Register of Ships) | - | - | - | 0 |
All issues of social insurance were regulated by Federal Law No. 212. This year it was replaced by Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Articles 419-425 define taxpayers, the accrual base, objects of taxation, tariffs and reporting periods. The chapter also contains the procedure for calculating taxes and other organizational issues.
In general, the object of collection of insurance premiums is considered to be any payments intended for an individual. And the base is the amount of payments taken for a certain time period, separately for each insured person.
Personal income tax
This is one of the direct taxes. Calculated as a percentage of total income less tax-exempt amounts. These include fees, real estate profits, bonuses, gifts, winnings, paid sick leaves, etc.
How much taxes does the employer pay for the employee at the basic rate?
As you know - 13%. In some cases, the tax base can be reduced through tax deductions. They only apply to income subject to a 13% rate. Personal income tax is deducted most often and transfers them to the budget of the tax agent. He is an intermediary between the state budget and an employee (taxpayer) who is charged with the obligation to transfer contributions to the state budget. Usually the employer is recognized as the tax agent. He withholds a certain amount and transfers it to the tax office at the place of registration of the organization (firm, individual entrepreneur) on the day of the transfer of wages to employee cards.
In this case, the financial burden lies with the employee, and the calculation and payment of the tax - with the employer. While, for example, from the sale of real estate, a citizen independently calculates the amount of payment, having previously declared the profit received.

Social insurance fund
Payments, in accordance with the norms of the law, are made by the employer. The FSS distributes tax to social funds. These contributions give citizens the right to receive cash benefits in special cases. For example, when:
Loss of a breadwinner
Getting a disability
The birth of a child,
Reaching retirement age.
Obtaining the status of a poor or large family.
How much taxes does the employer pay for the employee to this fund? 2.9% of the employee's accrued wages. They are listed either before the 15th day of each next month, or once a year until December 31st.
The rate of deductions to the Social Insurance Fund depends on the level of hazard at work.
When assessing working conditions at a specific enterprise, the following tariffs are applied:
Dangerous (+ 8%),
Harmful (+ 7.2%),
Acceptable as well as optimal (+ 0%).
Employment injury insurance premiums must be paid every month, along with salary. Moreover, any mistake in the KBK, the name of the bank or company will delay the transfer, and payments in this case will be considered imperfect.
If the last day of payment of contributions is non-working (for any reason), then it can be postponed to the first working day. This rule does not work everywhere. For example, payments for industrial injuries must go ahead, that is, when the last day of payments falls on a weekend / holiday, they must be made a day earlier.
Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are recorded separately for each employee. Late payments to the FSS entail penalties in the form of 5% of the monthly amount charged.

In theory
The employer makes contributions to the Social Insurance Fund from his own funds. These payments are divided into two types: actual and contingent. The first is paid to third-party non-state and state funds. Most often, health and social insurance, as well as the Pension Fund. For example, a social fund will make payments to an employee who is injured during work activities.
Conditional payments remain on the accounts of the organization (firm, individual entrepreneur). They are designed to ensure an adequate standard of living for employees who are dependent, for example after an injury at work. And:
Childcare benefits,
Compensation for moral damage (the amount of payment is determined only by the court),
Payment to employees who quit due to layoffs or in case of liquidation of the enterprise.
Pension fund of the Russian Federation
Pension fund contributions depend on the employment relationship. That is, the contributions will be different for citizens working under an indefinite employment contract, a combination or a fixed-term contract. Payments to this fund are made from the accounts of the organization (company, individual entrepreneur) in the generally accepted amount - 22% of the accrued wages. The date of deductions to the Pension Fund is the 15th day of the next month.

Federal Compulsory Health Insurance Fund
What other taxes does the employer pay for the employee? Contributions to FFOMS. At a rate of 5.1% of the salary of each employee, they are transferred to the needs of free medical care.
This fund was created for financial assistance with problems related to medical care. Thanks to the current regulations and federal legislation, any citizen of our country can receive qualified medical and / or drug assistance.
Contributions to the compulsory health insurance fund are intended for:
The unemployed population, including children,
Provision of medicines to privileged categories of citizens,
Implementation of compulsory insurance measures accepted for implementation.
FFOMS - federal property
The reason for this is a number of tasks assigned to it, directly related to social protection of the population, preservation of its health, well-being and provision of certain services.
The Mandatory Health Insurance Fund oversees the efficiency of spending money received on accounts. Also, reports are drawn up, which are reviewed and approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. All monetary transactions carried out by the fund are controlled and regulated by the Federal Treasury.
Since the beginning of 2017, the social insurance sector has become subordinate to the Federal Tax Service. The changes are not cardinal. They only influenced the reporting procedure.
Preferential income categories
Federal legislation provides for a number of categories of employees' income that are exempt from paying contributions to non-budgetary funds. These include:
Cash compensation, for example, in connection with dismissal;
Benefits assigned by the state - these can be payments in connection with temporary disability, injury during the production process, etc.
Financial assistance provided in connection with the death of a relative, the birth of a child or the loss of property due to force majeure events.
On average, the amount of contributions to all funds is 43% of the assessed - these are assessed taxes on wages, 30% is paid by the employer.
SP
And how much taxes does the employer pay for the employee, if the first is an individual entrepreneur? Entrepreneurs without forming a legal entity pay insurance premiums of a fixed amount. They are calculated from the level The rate is still 26% and 5.1% - in the FFOMS. And the amount of the payment has changed, as the minimum wage has increased. In 2016, it was 6,675 rubles, today - 7,500, and since July 1, approved by the government - 7,800.
Doesn't list.
Upon reaching an individual entrepreneur's profit of 300,000 rubles, payments to the Pension Fund and FFOMS are reduced to 1%.
Features of the simplified taxation regime
The simplified tax system is preferential. Therefore, payments are calculated differently. This refers to the types of activities listed in Article 58 212 of the Federal Law (production of toys or goods for sports, construction, education, etc.).
Legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs making payments in favor of citizens, are exempted from contributions to the FFOMS and the FSS. The percentage transferred to the Pension Fund has been reduced for them to 20%.

Accounting nuances
Tax calculation is carried out separately for each employee. First, the employee himself needs to know how much taxes the employer pays for him to various funds. Secondly, there are certain limits, after which, the percentages of the transferred contributions are reduced. For example, if the total taxable income rises above 796,000 rubles, then payments to the Pension Fund are reduced to 10% (but this does not apply to entrepreneurs working under the simplified taxation system).
The limit for transfers of taxes to the FSS is fixed at 718,000 rubles. After this amount, contributions to the social insurance fund cease.
Since last year, the limit on tax collection in the FFOMS has been canceled. Contributions are calculated at a 5.1% rate with no exemptions. Details can be found in the tax tables on the Internet, in the public domain.
Salary: which shade to choose
Unofficially in our country there are three types of wages: "black", "gray" and "white".
In the media, the term "white" (read "small") salary appeared in 1998. It means the officially registered amount of salary in the employment order and employment contract. "White" salary can consist of:
Bonus payments,
Allowances for degree, length of service, quality mark, etc.,
Vacation,
Regional coefficient (increases wages, compensating for the difficult climatic conditions in which you have to work),
Sick leave.
Employers dislike "white" wages because of the "headache" with taxes. Employees, on the other hand, feel protected with her.
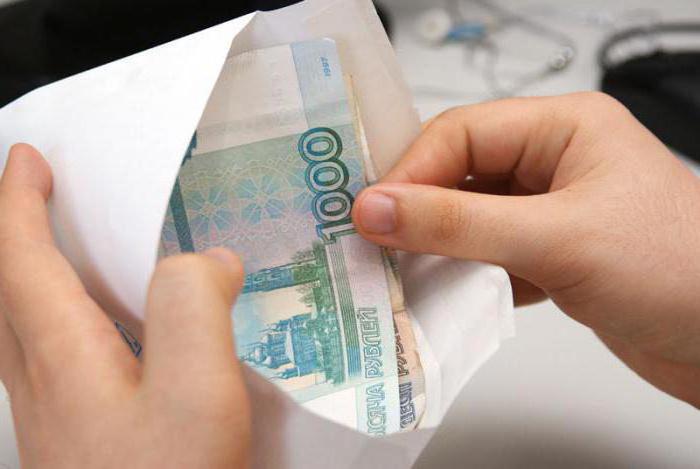

"Gray" (or salary in an envelope) does not reflect part of the money earned. Employees of organizations and firms that practice such payments receive officially small salaries, and the additional payment, which is not reflected in the accounts, is given in envelopes. Naturally, the employer allocates significantly smaller amounts to various funds. In this case, the employee does not have adequate protection. For example, there are cases when money in envelopes is "forgotten" to give out.
The concept of "black" wages appeared in 1996. It both then and now means an unconfirmed documentary salary. What taxes does the employer pay for the employee in this case? It is clear that none. Naturally, there is no talk of paying for maternity or annual leave, sick leave, etc.
- How to get TIN via the Internet - step-by-step instructions
- The title page of the work book: all the nuances and a sample of filling
- SNILS for a newborn: instructions on how to get
- Help 3 personal income tax - what is it?
- How to fill out a cash flow statement: line example
- Registration of an incoming cash order: filling and examples
- What documents are needed to receive snills for a child
- Form AO-1. Advance report
- Rules and procedure for filling out an advance report by an accountant and accountable persons
- Help 2-NDFL sample filling
- How to fill out an application in the form of UTII-2
- Admissions campaign in full swing
- Novosibirsk State Medical University
- Tver State University (TvSU): Faculty of Education
- What documents are needed to receive snills for a child
- Form AO-1. Advance report
- Rules and procedure for filling out an advance report by an accountant and accountable persons
- Help 2-NDFL sample filling
- How to fill out an application in the form of UTII-2
- How to fill out an expense cash order and what it is